Edge computing devices, devices located in proximity to the source of data instead of in large data centers, could perform computations locally. This could reduce latency, particularly in real-time applications, as it would minimize the need to transfer data from the cloud.
The theory of special relativity is rife with counterintuitive and surprising effects, the most famous of which are length contraction and time dilation. If an object travels at a relative speed, which is a non-negligible fraction of the speed of light, with respect to an observer, the length of the object in the travel direction will appear shorter to the observer than it actually is in the object’s rest frame.
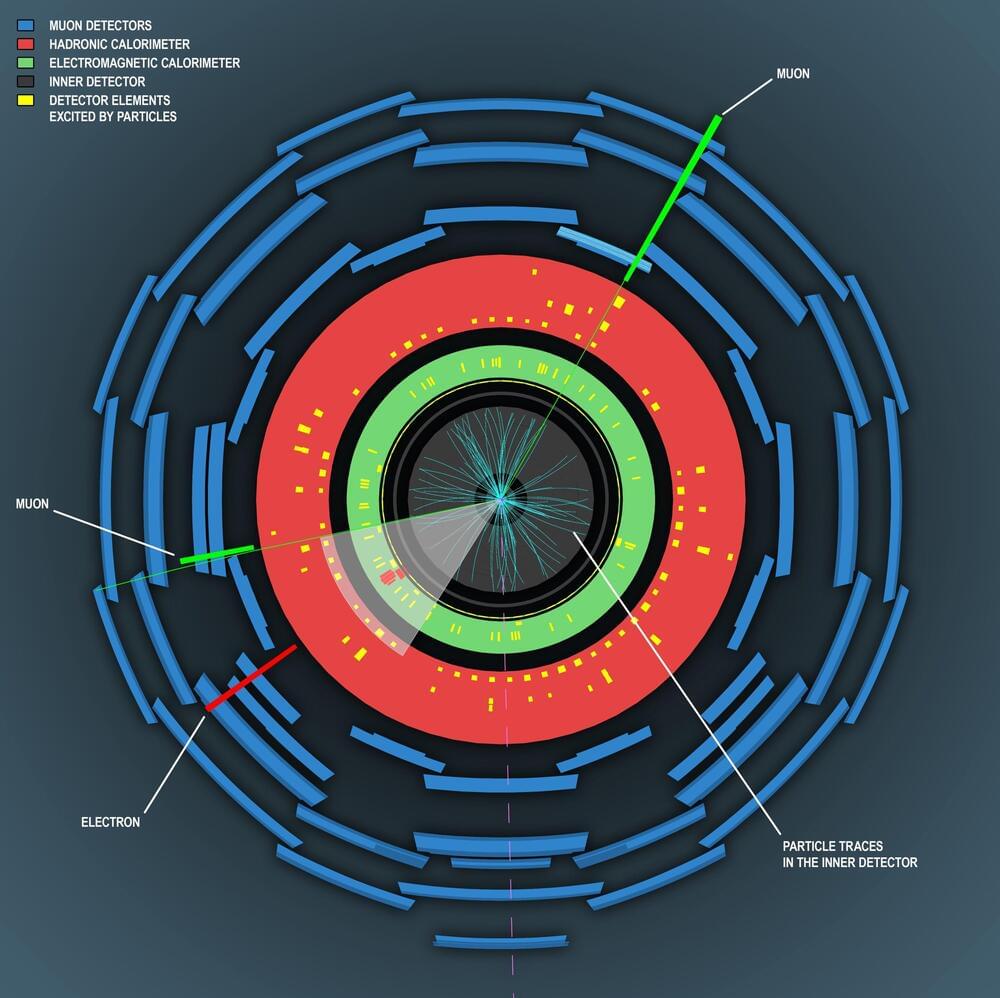
Since the launch of the Large Hadron Collider, there has been ongoing research there into Higgs bosons and a search for traces of physics beyond the existing model of elementary particles. Scientists working at the ATLAS detector have combined both goals: with the latest analysis it has been possible to expand our knowledge of the interactions of Higgs bosons with each other, and stronger constraints on the phenomena of “new physics” have been found.
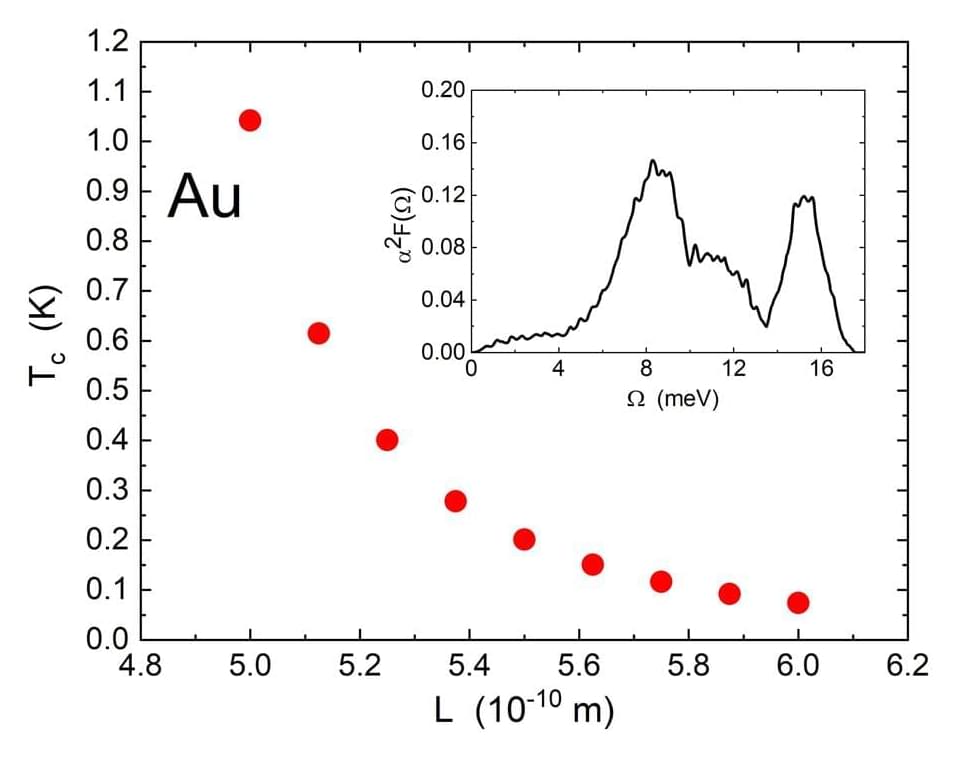
Superconductivity is the phenomenon by which, at sufficiently low temperatures, electric current can flow in a metal with no resistance. While certain metals are excellent superconductors, other metals cannot superconduct at all.
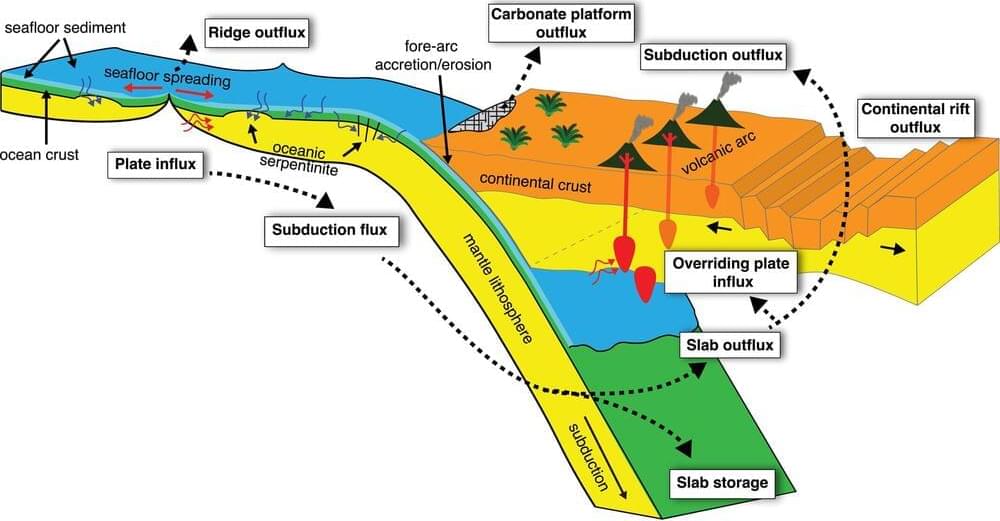
From time to time, when Earth’s tectonic plates shift, the planet emits a long, slow belch of carbon dioxide. In a new modeling study published in Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, R. Dietmar Müller and colleagues show how this gas released from deep Earth may have affected the climate over the past billion years.
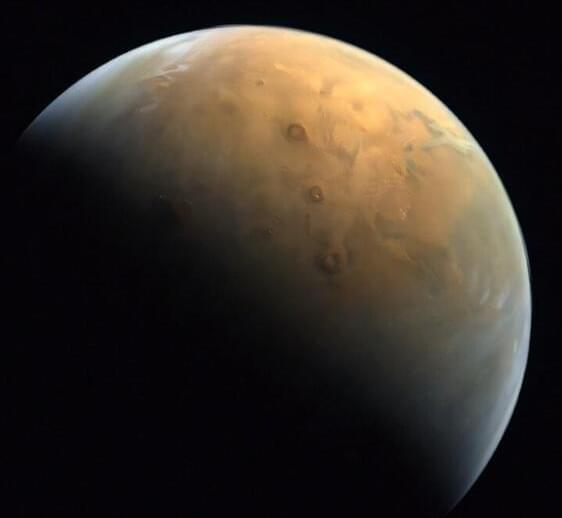
A Chinese rover has found new evidence to support the theory that Mars was once home to a vast ocean, including tracing some ancient coastline where water may once have lapped, a study said Thursday.
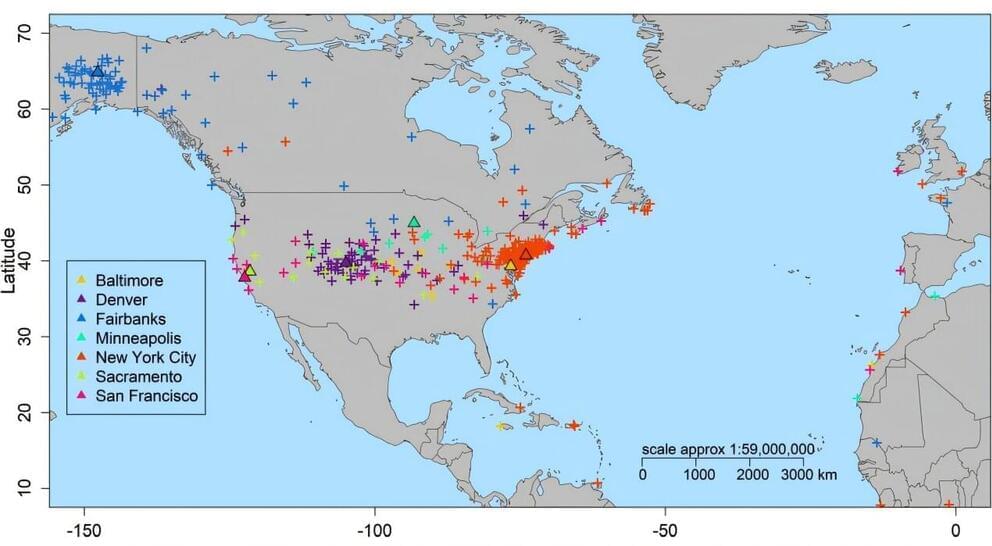
A research team led by Lund University in Sweden has developed an AI tool that traces back the most recent places you have been to. The tool acts like a satellite navigation system, but instead of guiding you to your hotel, it identifies the geographical source of microorganisms.
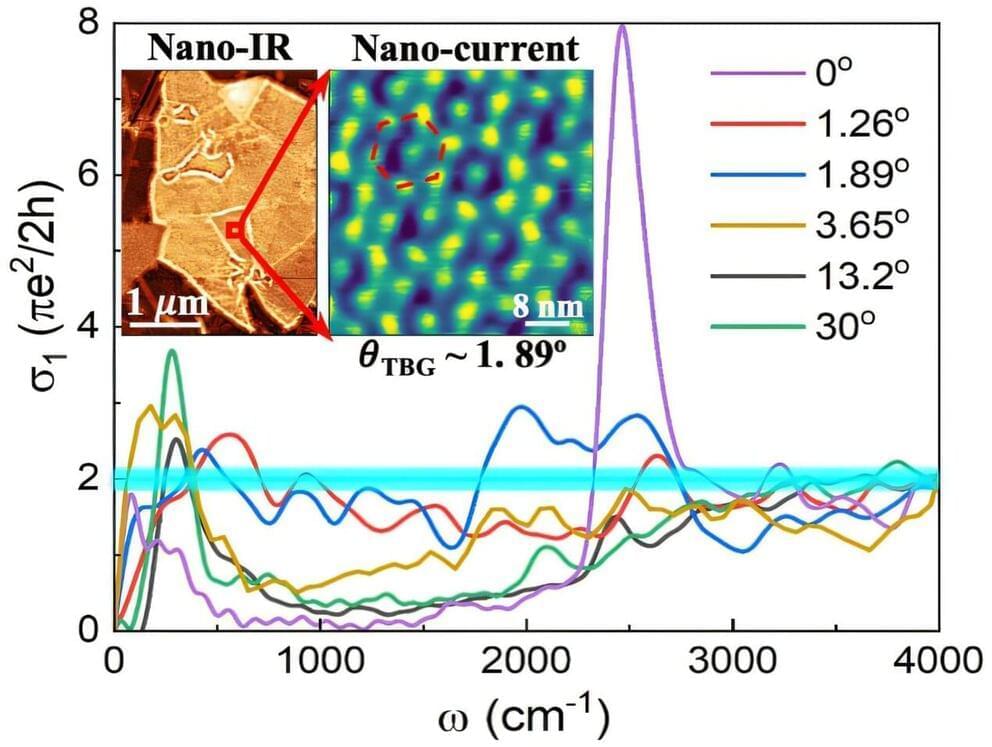
When it comes to electrically conductive nanomaterials, graphene—stronger and lighter than steel and more conductive than copper—has been shown to be an excellent choice for a wide range of technologies.
Mirroring the mechanisms that make human faces and bodies—and those of many multicellular organisms—symmetrical, bee colonies build symmetrical nests when they are placed on either side of a double-sided comb. The finding, published in Current Biology, extends examples of symmetry in biology to the behavior of communities and the architectural structures that they build.
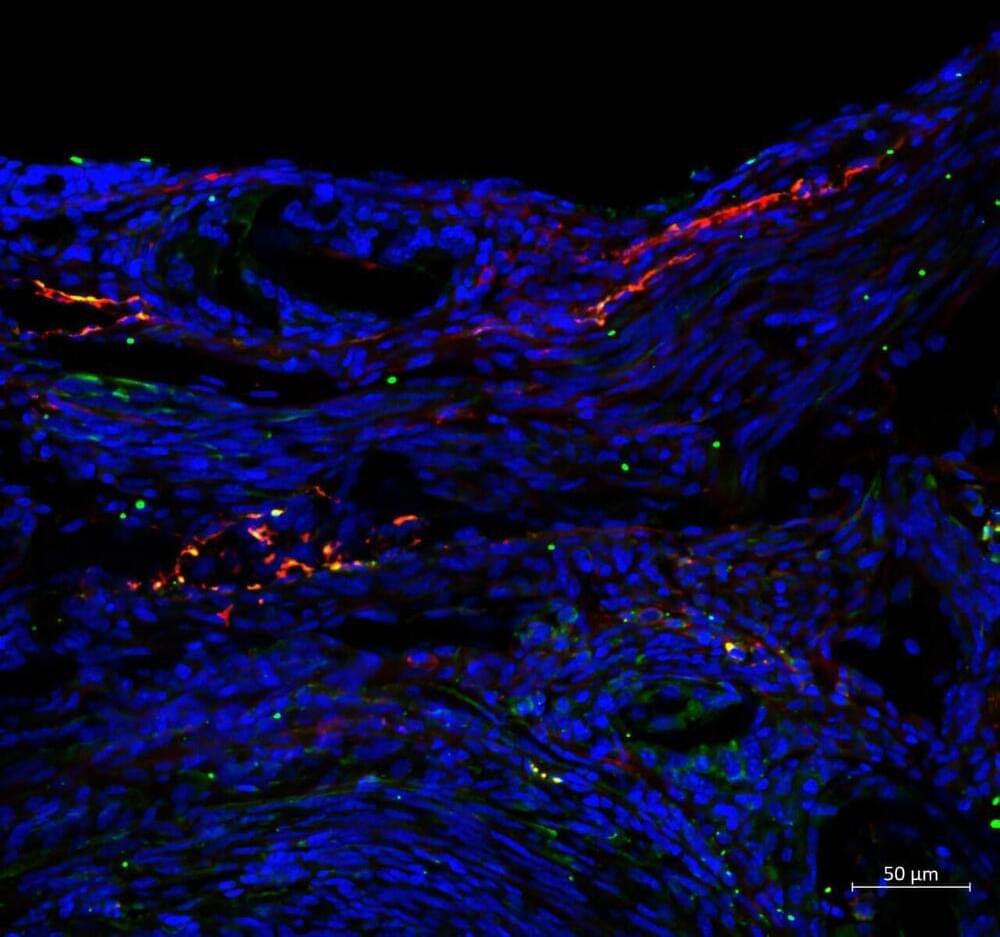
Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School researchers have discovered a neuroimmune communication pathway that may drive endometriosis-associated pain and lesion growth.
Endometriosis is a debilitating inflammatory disease affecting up to 15% of women and is characterized by the growth of endometrial-like tissue outside the uterus. Treatments can currently only target symptoms, with over-the-counter pain medicines and hormonal birth control, or in some cases, surgery.
Endometriosis occurs when cell tissues normally found within the uterus lining take root in areas outside the uterus. This tissue is hormonally sensitive and can become inflamed, especially during menstrual cycles, and can cause severe cramping, pain, and other symptoms depending on the area affected.