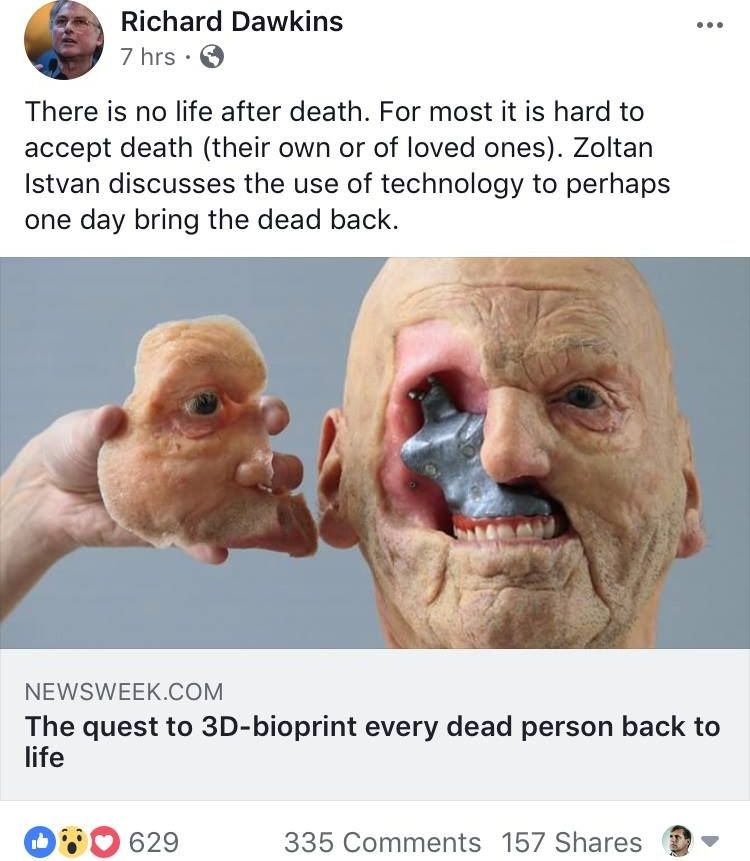
This piece originally appeared at the Institute for Emerging and Evolutionary Technologies website. It is dedicated to Leon Festinger.
Transhumanism is more often regarded as a faith by its detractors than its supporters. For my own part, I have long argued that the signature themes of transhumanism – especially the preoccupation with intellectual immortality and physical resurrection – bear the marks of Abrahamic theology. Indeed, without that theological backdrop, transhumanism’s zeal for mind uploading and cryonics looks simply bizarre. However, in this context, transhumanists can reasonably argue that they are scientifically delivering on those original theological promissory notes. Nevertheless, there remains the potentially pejorative sense of ‘faith’ lurking in what might be called transhumanism’s sense of eschatology – that is, its account of when, how and to whom those promissory notes will be delivered.
History shows that any humanly conceived idea is eventually realized in some form. Most of these ideas are realized fairly shortly after conception and in more or less the manner intended by their conceiver. However, many of the most important ideas – the ones that profoundly alter humanity’s self-understanding — are only realized much later and typically in a context quite alien to those who originally conceived them. Norbert Wiener famously observed that the possibility of an artificial intelligence was first raised in Talmudic discussions of the Biblical Golem. One of the goals of medieval alchemy was the creation of life from non-living materials. As for space travel and the search for extraterrestrial intelligence, they became staples of speculative thought starting with the European Renaissance’s unprecedented confidence in the power of human ingenuity. But in all these cases, the ideas have taken 500‑2000 years to be realized – and many have yet to fully satisfy the ambitions of their conceivers.
The disconnect between the conditions of intellectual conception and realization is quite familiar to writers of history and fiction. Hegel called it the ‘cunning of reason’ and it informs many a plot twist. These authors operate at a ‘meta-level’ to those who conceive and realize the ideas in question. In that respect, they move in the direction of God’s point of view. This enables them to survey with confidence a much broader bandwidth of the space-time continuum than either the conceivers or the realizers of the ideas themselves. However, what stops these second-order observers from achieving complete Olympian detachment is that they can still feel emotion about the consequences. Thus, they – and their readers — are the ones who laugh, cry or are simply amazed at the fate of ideas as they make their way from their conceivers to their realizers. Moreover, those emotions may be quite different from the ones experienced by the people depicted in the works, who by definition operate from more limited horizons and hence are ignorant of the larger narrative context.
We live in a time when many knowledgeable people are projecting radical changes to the human condition in the historical near-term, say, in the next generation or two. These include indefinite human longevity in the bodies of our birth and the prospect of artificially enhancing our minds and bodies, including the ability to upload our minds into machines capable of extending our mental powers indefinitely. Some would go further in the manner of Elon Musk to claim that space travel and colonisation might become so ordinary as to become one channel for solving humanity’s persistent earth-bound problems.
Few doubt that the time it takes to conceive and to realize the most radical ideas has shrunk over the course of history. Much of our intuitive sense of ‘acceleration’ comes from this basic awareness. It was already present in the Italian Futurist movement at the start of the twentieth century, which appealed to the accelerated pace of change – largely in the realms of transportation and communication — more than a half-century before it was operationalised in terms of computational efficiency as Moore’s Law. Moreover, humanity has become increasingly open to multiple realizations of a given idea, such that only professional historians nowadays worry about the loss of the conceiver’s original context as his or her idea comes to be realized in various ways. Indeed, the original Italian Futurists made a point of wanting to destroy all traces of the past as a precondition to freedom and progress, which they equated with the frictionless realization of the products of the human mind. Although transhumanists rarely say anything quite so nihilistic, their privileging of the ‘virtual’ over the ‘natural’ sends largely the same message.
However, transhumanists also seem to believe that the sense of space-time compression implied by an ‘accelerationist’ world-view especially favours the current generation of transhumanists. They typically locate what theologians would call the eschaton, which some transhumanists think of as the ‘singularity’, as occurring within their normal biological lifetime – certainly in less than fifty years and quite possibly within a generation. Not surprisingly, then, transhumanists tend to be middle-aged white males with a reasonable amount of disposable income. These people also tend not to have children, even if they are married. In other words, they are already prepared to enter a world in which, say, price is not a barrier to acquiring enhanced powers or extended longevity, and intergenerational succession is not something one needs to worry about, either at the personal or the public policy level.
But what happens if the eschaton does not occur within such a convenient time-frame? To be sure, I am generally optimistic that science and technology’s direction of travel points to where transhumanists want to go. Nevertheless, for various reasons, the relevant developments may not happen as soon as the likes of Ray Kurzweil or Aubrey de Grey have predicted – or hoped. In other words, the people who might end up benefitting from the transhumanist paradise that awaits Homo sapiens are the descendants of people who lived non-transhumanist lives in our times. Of course, some transhumanists believe that cryonics gets around this problem, but its prospects remain largely as speculative now as they were fifty years ago – at least with regard to human resurrection.
So, do you still believe in transhumanism even if it is unlikely that you will personally benefit from it?