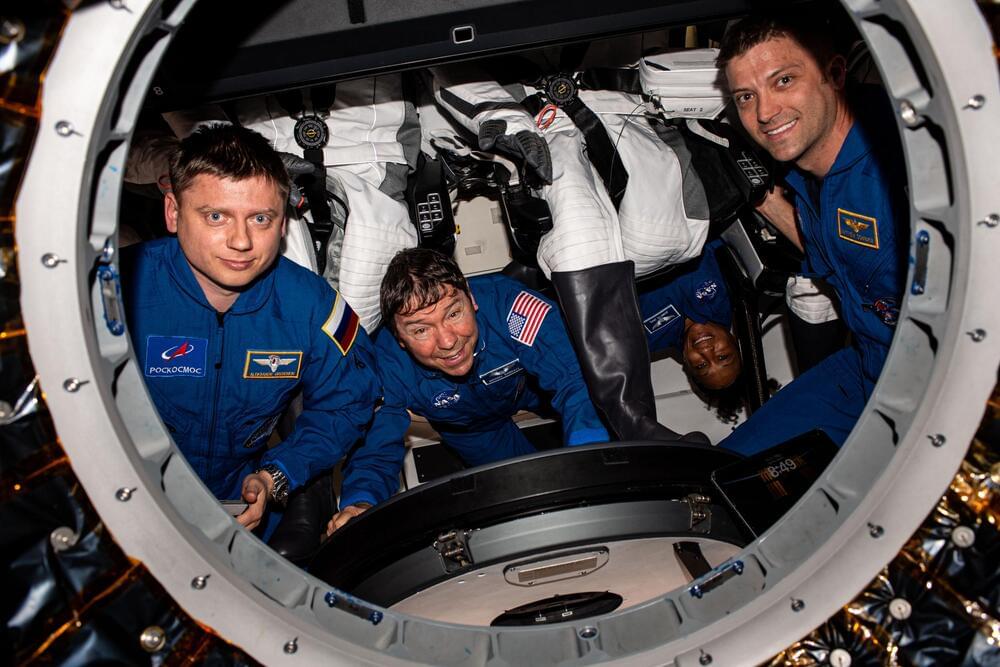
After weeks of hurricane delays, the crew successfully undocked on Wednesday and are on their way back to Earth.
Researchers have identified a key mechanism in the development of Alzheimer’s disease involving the growth and pause of amyloid β fibrils.
A newly discovered antibody can lock these fibrils in their paused state, offering a potential new approach for treatment that targets these critical growth points.
Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Research.
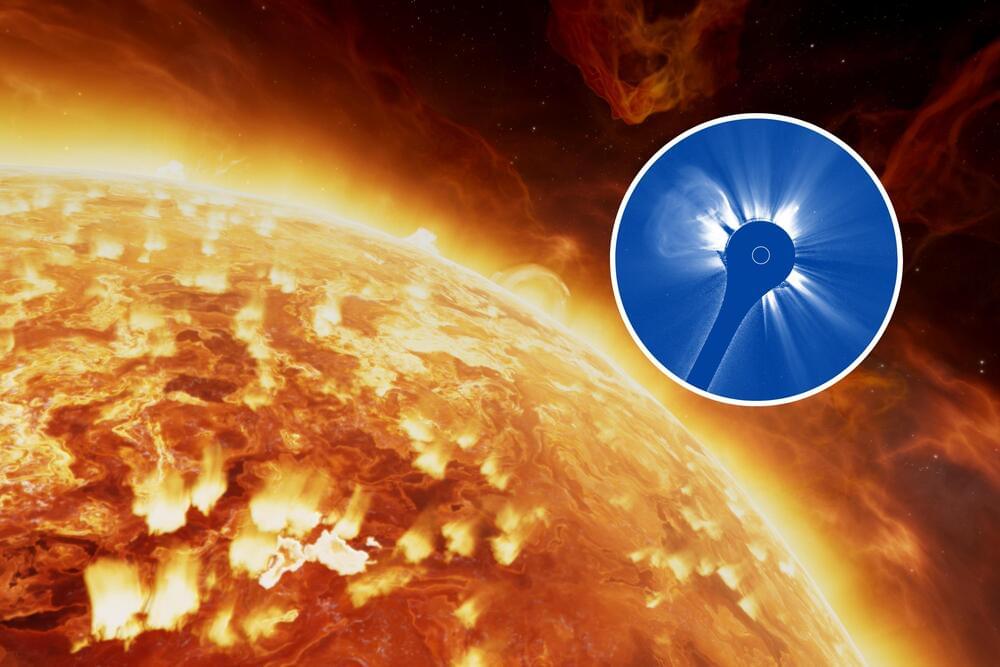
Revolutionary space-based coronagraph provides unprecedented views of solar storms that could impact Earth.
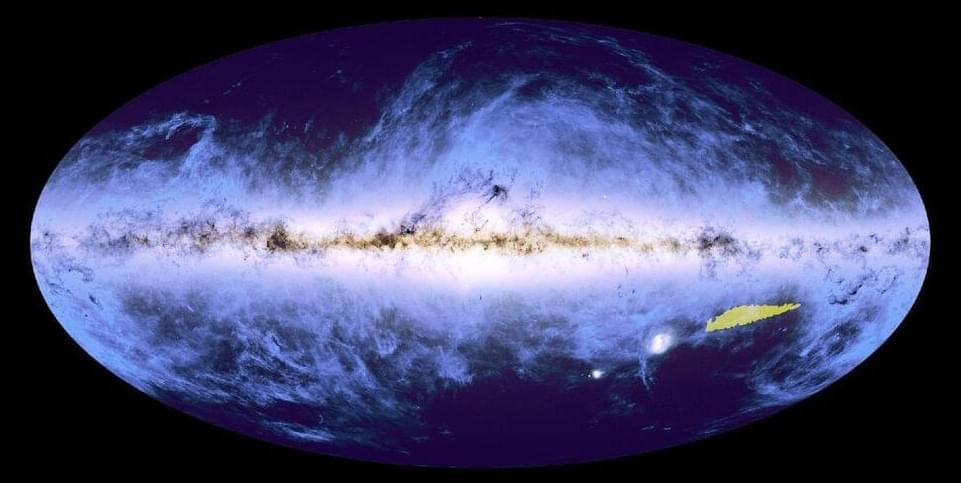
The first piece of the Euclid space telescope’s map of the universe is crammed with 14 million galaxies and 100 million sources of light. The mapping project is now 1% done.
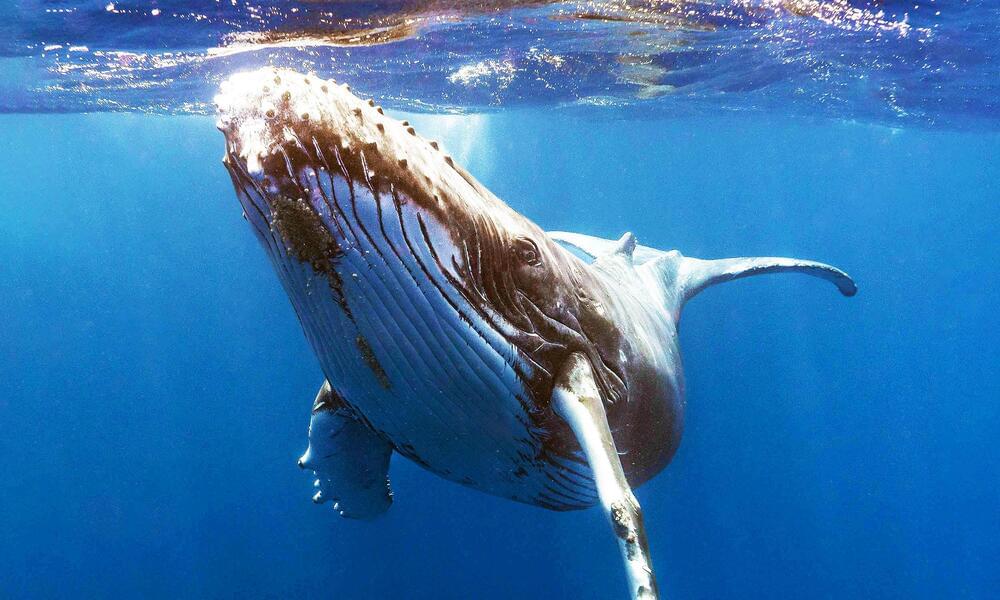
In a remarkable encounter off the coast of Alaska, human scientists had what they describe as a “conversation” with a humpback whale named Twain. Dr. Brenda McCowan from the University of California Davis was at the heart of this unexpected exchange.
Dr. McCowan and her team, known as Whale-SETI, have been studying how humpback whales communicate. They’re aiming to understand whale communication systems to help in the search for life beyond Earth.
Using an underwater speaker, the team played a recorded humpback “contact” call into the ocean. To their astonishment, Twain approached their boat and began responding.
Nuclear fission—when the nucleus of an atom splits in two, releasing energy—may seem like a process that is fully understood. First discovered in 1939 and thoroughly studied ever since, fission is a constant factor in modern life, used in everything from nuclear medicine to power-generating nuclear reactors. However, it is a force of nature that still contains mysteries yet to be solved.
Researchers from the University of Washington, Seattle, or UW, and Los Alamos National Laboratory have used the Summit supercomputer at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory to answer one of fission’s biggest questions: What exactly happens during the nucleus’s “neck rupture” as it splits in two?
The resulting paper is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Researchers Takuma Nakamura, Kazuki Hashimoto, and Takuro Ideguchi of the Institute for Photon Science and Technology at the University of Tokyo have increased by 100-fold the measurement rate of Raman spectroscopy, a common technique for measuring the “vibrational fingerprint” of molecules in order to identify them.
As the measurement rate has been a major limiting factor, this improvement contributes to advancements in many fields that rely on identifying molecules and cells, such as biomedical diagnostics and material analytics. The findings were published in the journal Ultrafast Science.
Identifying various types of molecules and cells is a crucial step in both basic and applied science. Raman spectroscopy is a widely used measurement technique for this purpose. When a laser beam is projected onto molecules, the light interacts with the vibrations and rotations of molecular bonds, shifting the frequency of the scattering light. The scattering spectra thus measured is a molecule’s unique “vibrational fingerprint.”
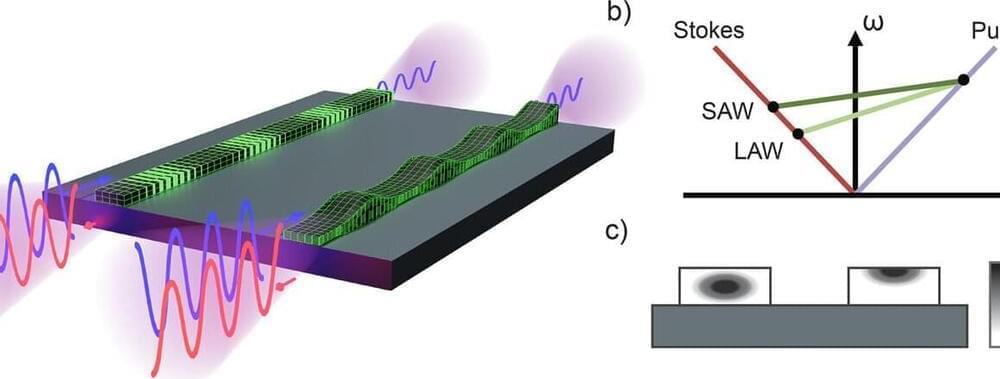
A team of researchers has for the first time successfully used lasers to generate guided sound waves on the surface of a microchip. These acoustic waves, akin to the surface waves produced during an earthquake, travel across the chip at frequencies nearly a billion times higher than those found in earth tremors.
By containing the sound wave on the surface of a chip, it can more easily interact with the environment, making it a perfect candidate for advanced sensing technologies.
The findings are published in APL Photonics.
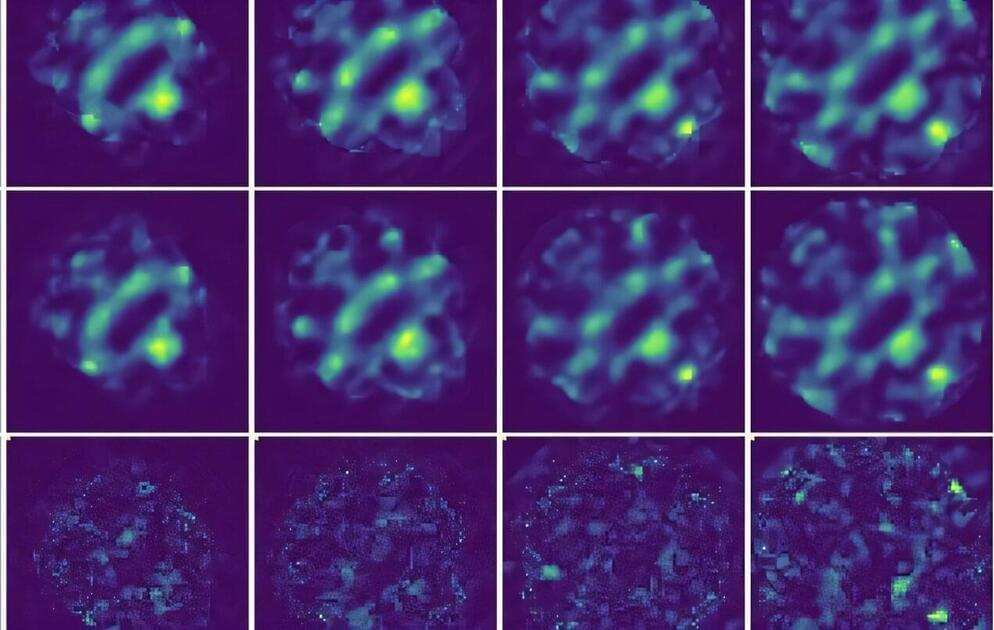
Researchers at Monash University have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) model that significantly improves the accuracy of four-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy (4D STEM) images.
Called unsupervised deep denoising, this model could be a game-changer for studying materials that are easily damaged during imaging, like those used in batteries and solar cells.
The research from Monash University’s School of Physics and Astronomy, and the Monash Center of Electron Microscopy, presents a novel machine learning method for denoising large electron microscopy datasets. The study was published in npj Computational Materials.
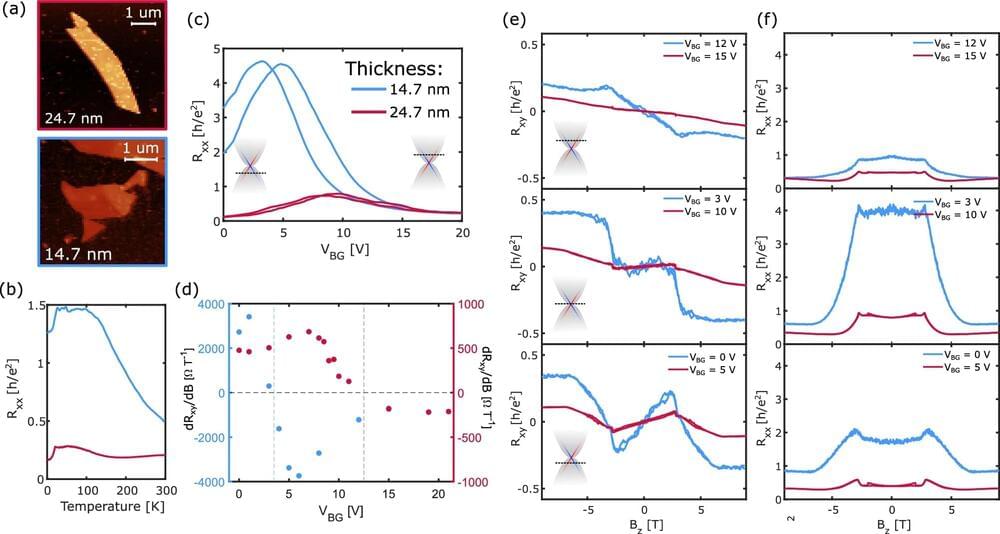
For the first time since the discovery of the material MnBi2Te4 (MBT), researchers at the University of Twente have successfully made it behave like a superconductor. This marks an important step in understanding MBT and is significant for future technologies, such as new methods of information processing and quantum computing.
MBT is a recently discovered material attracting attention due to its unique magnetic and topological properties. In their research, the scientists examined how electricity behaves in the material. The findings are published in the journal Communications Materials.
MBT’s topological properties cause electrons to move only along the edges of the material, and in theory, they should only move in a clockwise direction. However, the experiments at Twente demonstrated that under certain conditions, the electrons can rotate both clockwise and counterclockwise.