Money might not buy love, but it can buy better health. And, to live as long as possible, the world’s wealthy are willing to pay up.
The wealthy are willing to pay for a longer life. The successor to income inequality is longevity inequality.


Scientists pride themselves on being keen observers, but many seem to have trouble spotting the problems right under their noses. Those who run labs have a much rosier picture of the dynamics in their research groups than do many staff members working in the trenches, according to a Nature survey of more than 3,200 scientists. The results suggest that a lack of training in lab and personnel management is one of the strongest contributors to an unhealthy lab culture.
A Nature survey of 3,200 scientists reveals the tensions bubbling in research groups around the world.
VR companies around the world are planning to offer live views of the Earth from space within the next few years.
Dr Stuart Clark writes Across the Universe for the Guardian, and is the author of The Search for Earth’s Twin (Quercus).
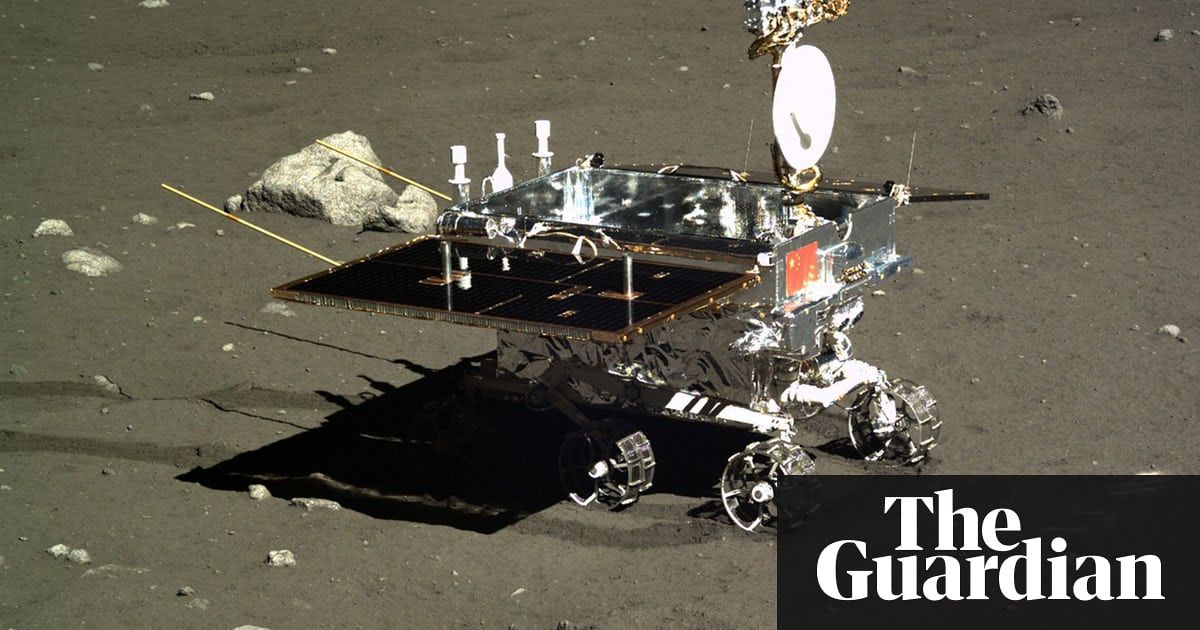

Magpie Bridge relay satellite will communicate with lunar lander to be deployed later in the year.

Government officials, business leaders and academics attending China’s second World Intelligence Congress, abbreviated WIC 2018, envisioned people’s liberation from labor with the help of artificial intelligence.
With the theme “The Age of Intelligence: New Progress, New Trends, New Efforts,” the three-day event began in north China’s Tianjin municipality on Wednesday.
Lin Nianxiu, deputy director of China’s National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), said at the opening of the congress that the aspirations to make machines more intelligent and liberate human beings from as much labor as possible have been major impetuses driving worldwide technological advances and industrial innovation.
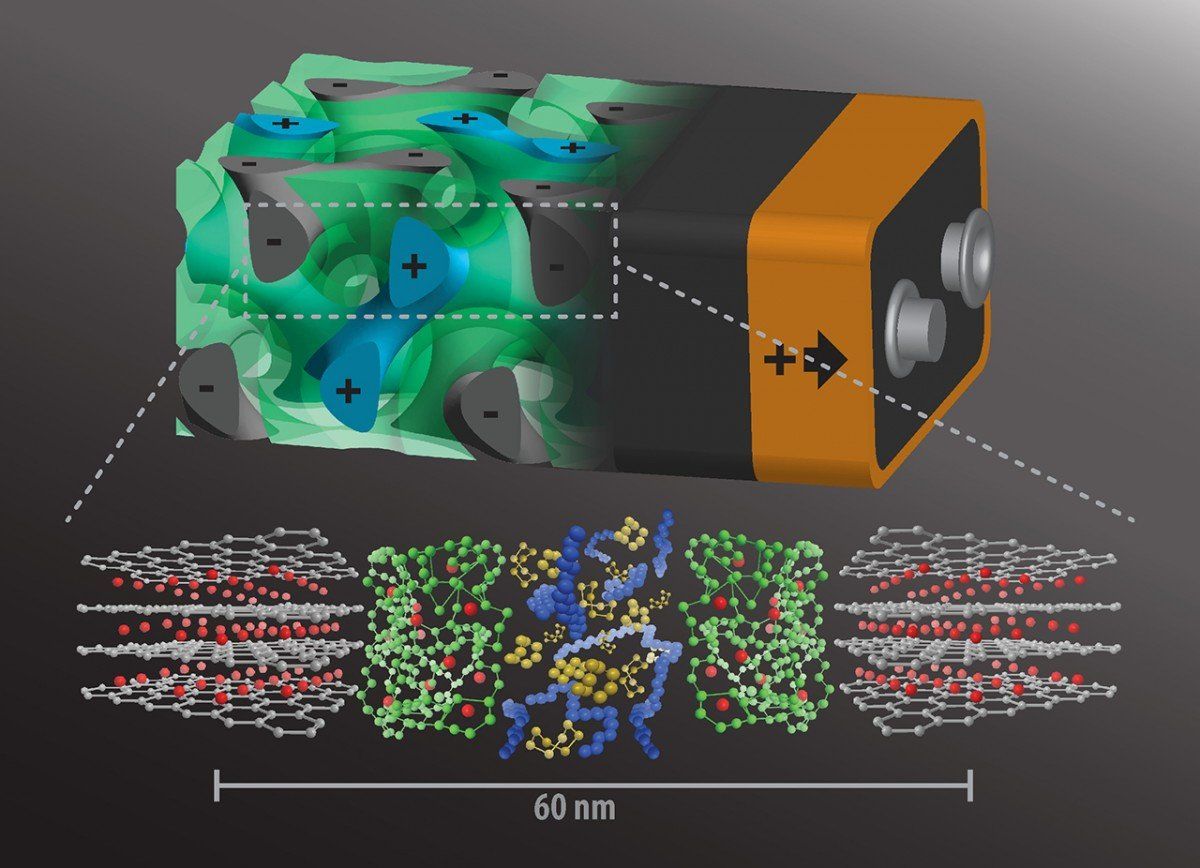
The world is a big place, but it’s gotten smaller with the advent of technologies that put people from across the globe in the palm of one’s hand. And as the world has shrunk, it has also demanded that things happen ever faster—including the time it takes to charge an electronic device.
A cross-campus collaboration led by Ulrich Wiesner, professor of engineering in the at Cornell University, addresses this demand with a novel energy storage device architecture that has the potential for lightning-quick charges.
The group’s idea: Instead of having the batteries’ anode and cathode on either side of a nonconducting separator, intertwine the components in a self-assembling, 3D gyroidal structure, with thousands of nanoscale pores filled with the elements necessary for energy storage and delivery.
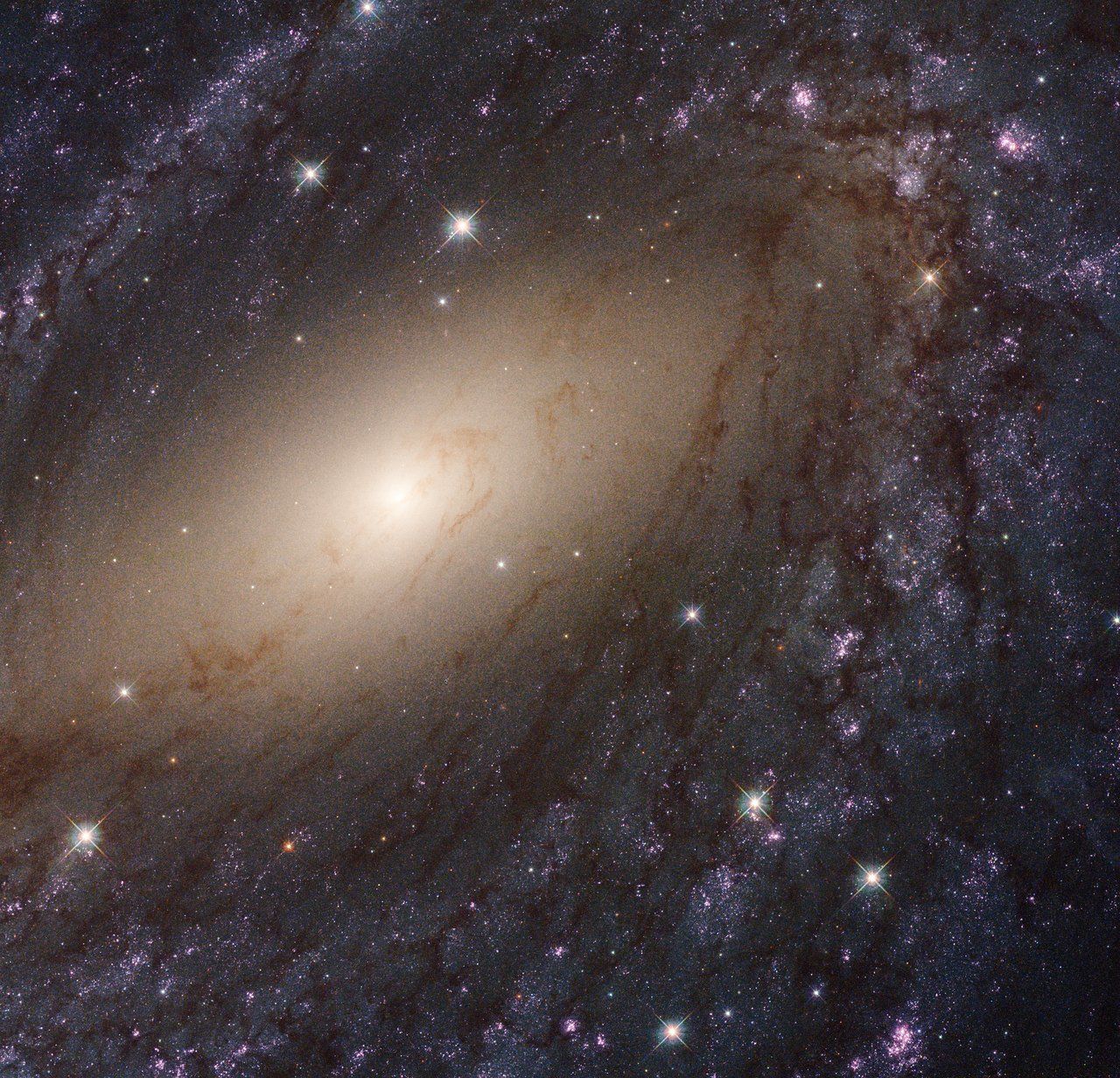


Capitalizing on the unparalleled sharpness and spectral range of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, an international team of astronomers is releasing the most comprehensive, high-resolution ultraviolet-light survey of nearby star-forming galaxies.
The researchers combined new Hubble observations with archival Hubble images for 50 star-forming spiral and dwarf galaxies in the local universe, offering a large and extensive resource for understanding the complexities of star formation and galaxy evolution. The project, called the Legacy ExtraGalactic UV Survey (LEGUS), has amassed star catalogs for each of the LEGUS galaxies and cluster catalogs for 30 of the galaxies, as well as images of the galaxies themselves. The data provide detailed information on young, massive stars and star clusters, and how their environment affects their development.
“There has never before been a star cluster and a stellar catalog that included observations in ultraviolet light,” explained survey leader Daniela Calzetti of the University of Massachusetts, Amherst. “Ultraviolet light is a major tracer of the youngest and hottest star populations, which astronomers need to derive the ages of stars and get a complete stellar history. The synergy of the two catalogs combined offers an unprecedented potential for understanding star formation.”


Injecting minute amounts of two immune-stimulating agents directly into solid tumors in mice can eliminate all traces of cancer in the animals, including distant, untreated metastases, according to a study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine.
The approach works for many different types of cancers, including those that arise spontaneously, the study found.
The researchers believe the local application of very small amounts of the agents could serve as a rapid and relatively inexpensive cancer therapy that is unlikely to cause the adverse side effects often seen with bodywide immune stimulation.