In an era of artificial eggs and Crispr, anyone could become a biological parent to the healthiest baby.


Elevation — How Drones Will Change Cities
Drones will transform cities, revolutionising how people travel, how goods are delivered and how buildings look and are constructed, according to a documentary by Dezeen.
“Aerial highways” will relieve pressure on roads as deliveries and human transportation take to the skies in unmanned electric vehicles.
By Jessica Hamzelou
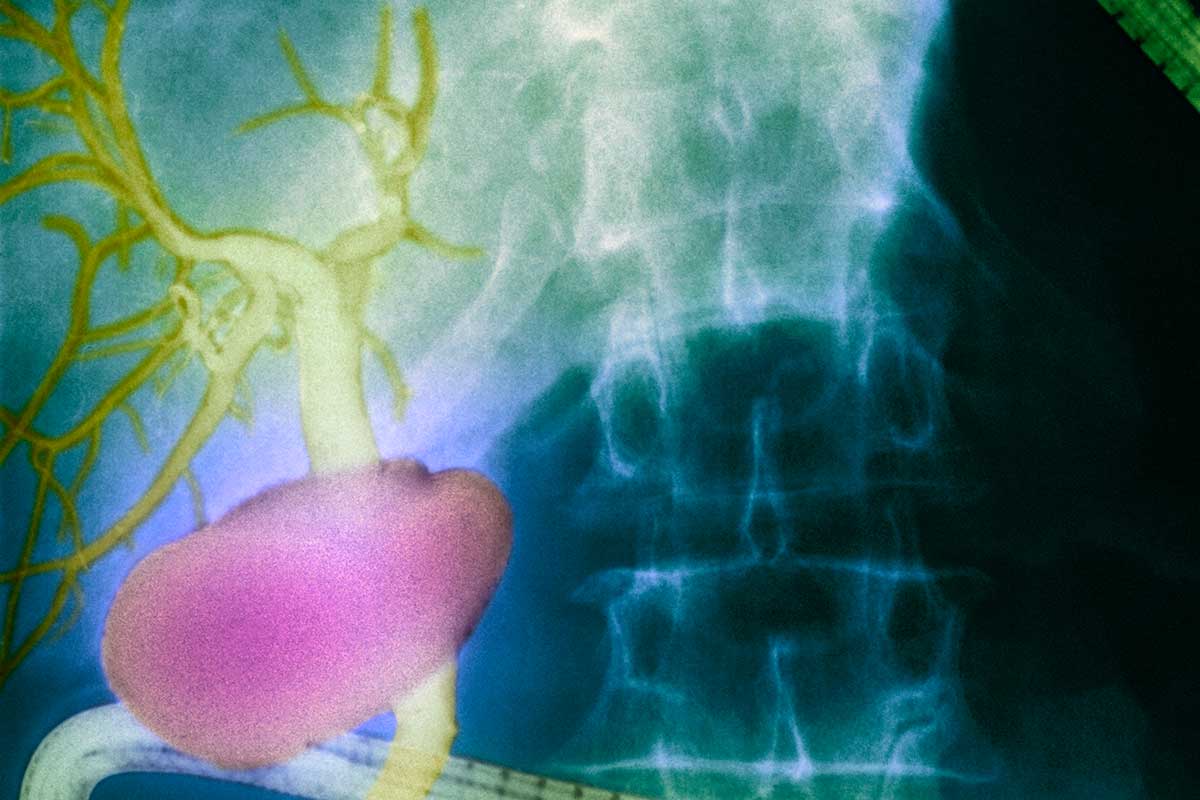
A newly discovered network of fluid-filled channels in the human body may be a previously-unknown organ, and it seems to help transport cancer cells around the body.
This discovery was made by chance, from routine endoscopies – a procedure that involves inserting a thin camera into a person’s gastrointestinal tract. Newer approaches enable doctors to use this procedure to get a microscopic look at the tissue inside a person’s gut at the same time, with some surprising results.
This is huge: Chinese scientists have successfully cloned monkeys (via NowThis Future)
Space Development Nexus will span 6 continents, and serve as the water cooler for the New Space industry as we all make our way to LEO and beyond, Networking individuals and companies from every aspect of the industry from launch vehicles to communications to astrogeology. Where social networking takes constant management, these meetups, Activities, workshops, seminars and other interactive activities will make our message available across the industry, and to the public, with one coherent voice – “Space is for everyone, and we’re bringing it down to Earth.”

Transhumanist thinking has gained a remarkable amount of traction and publicity this year. Powerful Silicon Valley interests have been mounting a charm offensive designed to persuade us of both the value and the inevitability of this transformation.
In a startling leap towards a future that many thought only existed in sci-fi, a Wisconsin high-tech company, Three Square Market, started microchipping its employees last year.
The announcement followed on the heels of a similar move by Swedish company Epicenter, the first to begin this practice. While Three Square Market’s approach is voluntary, the company is financially subsidizing the procedure.
Transhumanist agenda
There is a name of this kind of cultural weirdness: Transhumanism, a strange agglomeration of technology, politics, and even aspects of religion. The Transhumanist view of the future features a fully mechanized simulacrum of society teeming with visible and invisible robots and robotic functions that will engineer the minutia of life at every turn, presumably to make life easier and more fulfilling.
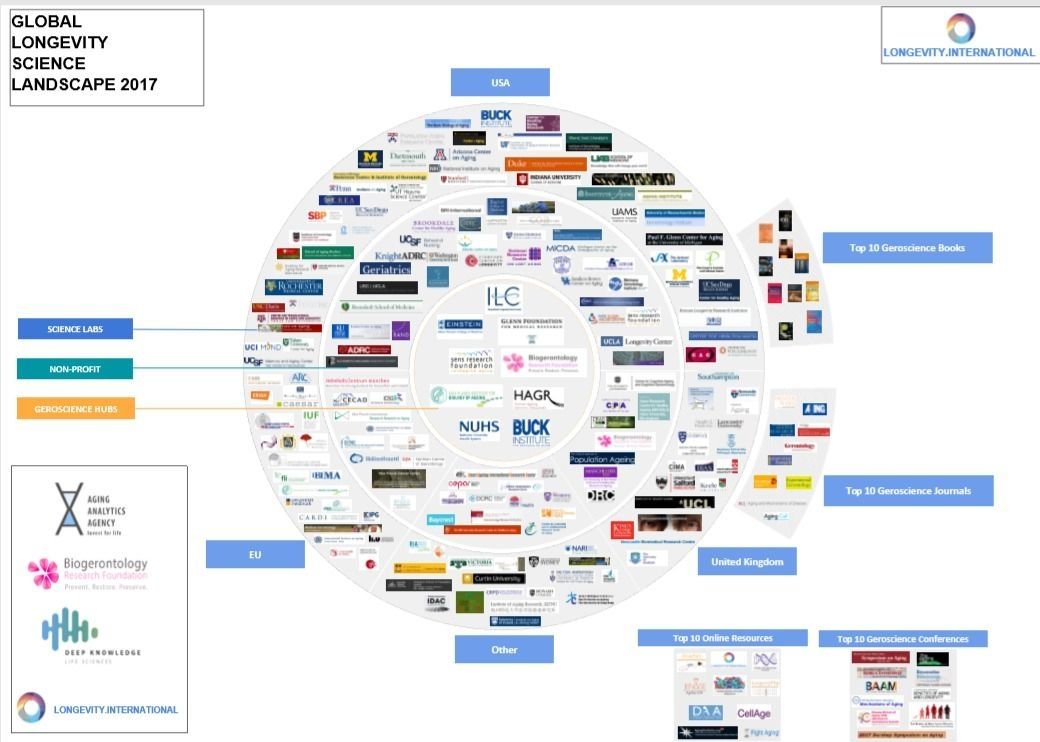
See a close-up of the above image!
UK aging research foundation produces roadmap for the emerging longevity industry in a series of reports to be published throughout the year
Friday, Feb. 2, 2017, London, UK: The Biogerontology Research Foundation has embarked on a year-long mission to summarise in a single document the various emerging technologies and industries which can be brought to bear on aging, healthy longevity, and everything in between, as part of a joint project between The Global Longevity Consortium, consisting of the Biogerontology Research Foundation, Deep Knowledge Life Sciences, Aging Analytics Agency and Longevity. International platform.
For scientists, policy makers, regulators, government officials, investors and other stakeholders, a consensus understanding of the field of human longevity remains fragmented, and has yet to be systematized by any coherent framework, and has not yet been the subject of a comprehensive report profiling the field and industry as a whole by any analytical agency to date. The consortium behind this series of reports hope that they will come to be used as a sort of Encyclopedia Britannica and specialized Wikipedia of the emerging longevity industry, with the aim of serving as the foundation upon which the first global framework of the industry will be built, given the significant industry growth projected over the coming years.
This pen can detect cancer in patients with 96.5% accuracy.
Today, we wanted to bring your attention to a new open access paper. The authors here review the role of cellular senescence in the context of the cardiovascular and metabolic diseases of aging. This paper puts special focus on the aging of the vascular system and the role that accumulating numbers of senescent cells play in that process.
What is cellular senescence?
As the body ages, increasing amounts of cells enter a state of senescence. Senescent cells do not divide or support the tissues of which they are a part; instead, they emit a range of potentially harmful signals known collectively as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). Senescent cells normally destroy themselves via a programmed process called apoptosis, and they are removed by the immune system; however, as the immune system weakens with age, increasing numbers of these senescent cells escape this process and build up.