Some market watchers have suggested $70,000 is a key level to watch and a break below that could lead bitcoin to decline further.


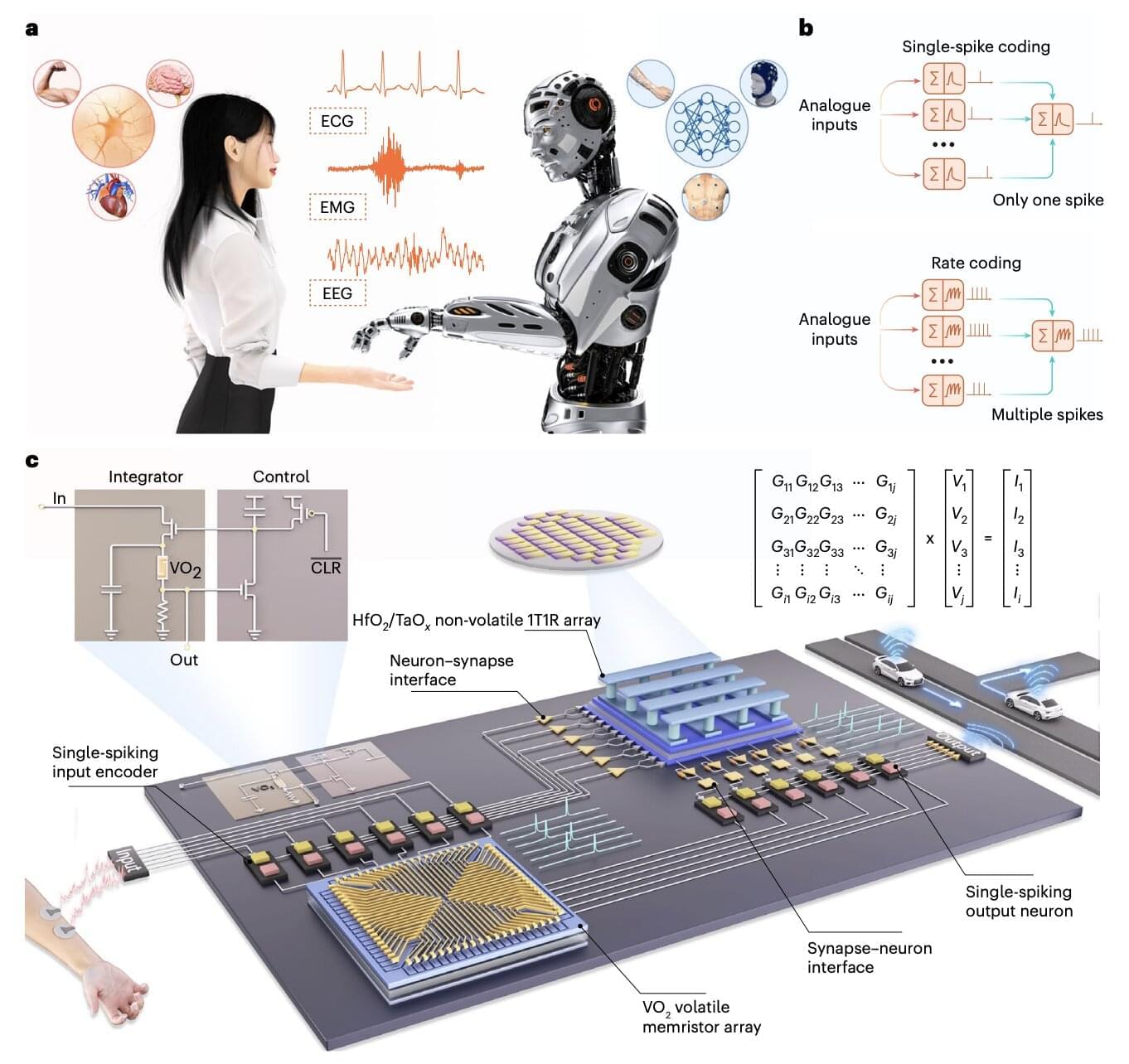
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) systems, such as the models underpinning the functioning of ChatGPT and various other online platforms, has grown exponentially over the past few years. Current hardware and electronic devices, however, might not be best suited for running these systems, which are computationally intensive and can drain huge amounts of energy.
Electronics engineers worldwide have thus been trying to develop alternative hardware that better reflects how the human brain processes information and could thus run AI systems more reliably, while consuming less power. Many of these brain-inspired hardware systems rely on memristors, electronic components that can both store and process information.
Researchers at Peking University and Southwest University recently introduced a new neuromorphic hardware system that combines different types of memristors. This system, introduced in a paper published in Nature Electronics, could be used to create new innovative brain-machine interfaces and AI-powered wearable devices.
Joscha Bach explores the nature of consciousness, free will, and reality through the lens of computation, cognitive science, and philosophy. Rather than treating the mind as a mystical entity, Joscha frames consciousness as a constructed dream—a model generated by the brain to make sense of the world and coordinate behavior.
We examine why beliefs should remain provisional, how the self functions as a useful fiction, and why suffering emerges when internal learning signals misfire. Joscha explains why free will feels real even if decisions arise before awareness, how meaning exists beyond the individual ego, and why wisdom is not simply knowledge but the ability to orient oneself within larger systems of value.
BON CHARGE — 15% off red light therapy products I personally use.
https://www.boncharge.com/knowthyself.
[Code: KNOWTHYSELF]
André’s Book Recs: https://www.knowthyselfpodcast.com/bo… 00:00 Intro: Joscha Bach 04:24 Agnosticism, Evidence, and Logical Alternatives 11:20 Reality as a Mental Simulation 13:00 What Physicalism Actually Claims 16:55 Telepathy, Rituals, and Distributed Minds 19:45 Consciousness Does Not Make Decisions 22:55 Free Will as a Post-Hoc Story 24:00 Consciousness as a Trance State 26:00 Meditation and the Illusion of Self 29:10 Out-of-Body Experiences Explained 31:07 Ad: BON CHARGE 36:30 Why the Brain Fills in Missing Reality 39:50 Dreams, Selves, and Narrative Identity 43:20 Intelligence, Models, and World-Building 47:10 Why Reality Feels Stable 51:00 Meaning, Agency, and Mental Compression 55:10 Why Consciousness Feels Central (But Isn’t) 59:30 The Psychological World vs Physical Reality 1:04:10 Intelligence Without Awareness 1:08:45 The Cost of Believing the Self Is Real 1:13:30 Waking Up From the Narrative 1:18:40 What a Cognitive Science View Really Implies 1:23:30 Final Thoughts: Living Inside the Dream ___________ Episode Resources: https://www.cimc.ai/ / andreduqum
/ knowthyself
/ @knowthyselfpodcast https://www.knowthyselfpodcast.com Listen to the show: Spotify: https://spoti.fi/4bZMq9l Apple: https://apple.co/4iATICX
___________
00:00 Intro: Joscha Bach.
04:24 Agnosticism, Evidence, and Logical Alternatives.
11:20 Reality as a Mental Simulation.
13:00 What Physicalism Actually Claims.
16:55 Telepathy, Rituals, and Distributed Minds.
19:45 Consciousness Does Not Make Decisions.
22:55 Free Will as a Post-Hoc Story.
24:00 Consciousness as a Trance State.
26:00 Meditation and the Illusion of Self.
29:10 Out-of-Body Experiences Explained.
31:07 Ad: BON CHARGE
36:30 Why the Brain Fills in Missing Reality.
39:50 Dreams, Selves, and Narrative Identity.
43:20 Intelligence, Models, and World-Building.
47:10 Why Reality Feels Stable.
51:00 Meaning, Agency, and Mental Compression.
55:10 Why Consciousness Feels Central (But Isn’t)
59:30 The Psychological World vs Physical Reality.
1:04:10 Intelligence Without Awareness.
1:08:45 The Cost of Believing the Self Is Real.
1:13:30 Waking Up From the Narrative.
1:18:40 What a Cognitive Science View Really Implies.
1:23:30 Final Thoughts: Living Inside the Dream.
___________
Episode Resources:
Philosopher, computer scientist, and AI developer Joscha Bach explains his interest in animist ideas about spirits governing reality and how they exist as’software patterns’.
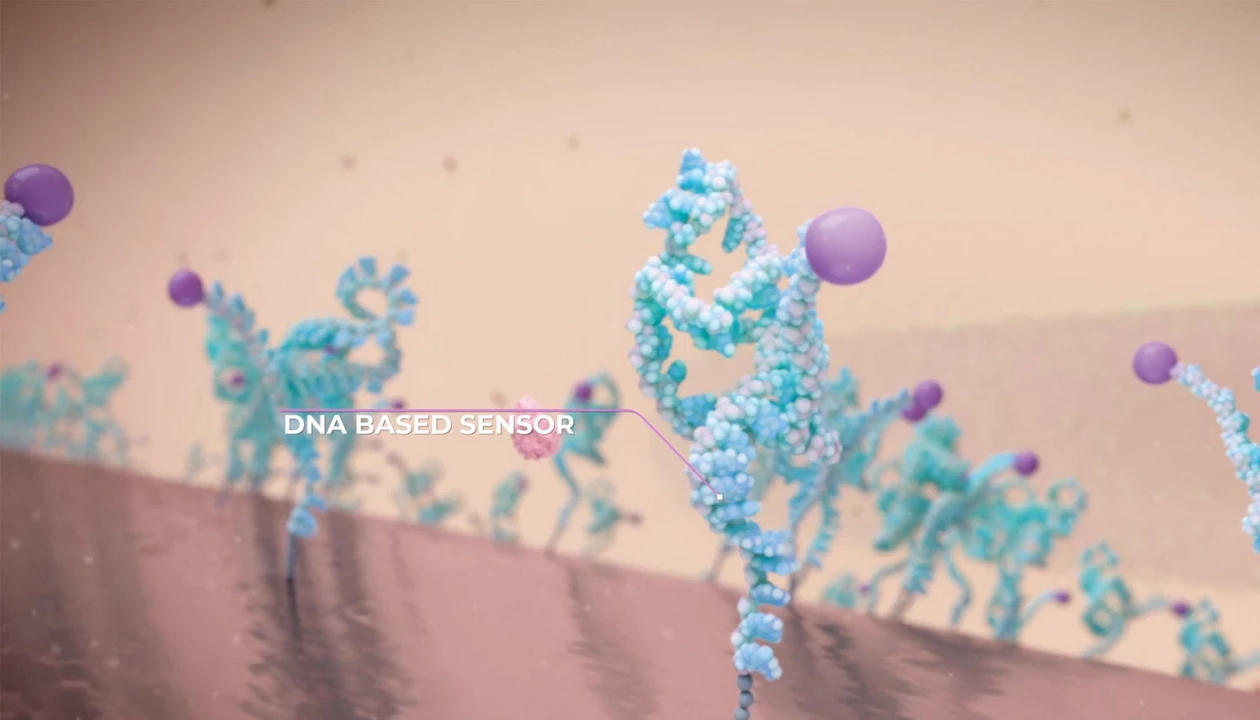
A wearable DNA-based sensor similar to a continuous glucose monitor can accurately and safely detect vancomycin concentrations in the body.
Aptamer-coated microneedle patch can detect amounts of the antibiotic vancomycin in real time for at least 12 hours by Helen Albert, special to C&EN.

Liu et al. reveal that BIW negatively regulates BR signaling by promoting BZR1 ubiquitination and degradation, while BIN2 enhances BIW’s stability and activity. Through the BZR1-dependent pathway, BIW inhibits lateral root development and chilling tolerance in tomato, providing a strategy for developing elite crop germplasm by targeted manipulation of BIW.

Here, Lintao Qu & team illuminate a neuroimmune mechanism in a mouse gout model involving MRGPRX2 signaling in synovial mast cells that drives pain and joint inflammation:
The figure: Mouse knee joint sections show treatment with an antibody against neuropeptide substance P (SP) decreases infiltration of neutrophils (Ly6G) and macrophages (CD68) into the synovium (S) in gout arthritis compared with control.
5Department of Endocrinology, Second Affiliated Hospital, University of South China, Hengyang, Hunan, China.
6College of Pharmacy, Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada.
7Center of Research Excellence in Allergy and Immunology, Research Department, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand.

Now online! Meningeal blood vessel blockage enhances anti-tumor immunity against GBM in preclinical models by expanding dural resident border-associated macrophages, which are equipped with an elevated antigen-presentation function and are poised for effective T cell activation, suggesting a surgical strategy for potentiating GBM immunotherapy.

NEUNew Maximizing Tumor Resection and Managing Cognitive Attentional Outcomes: Measures of Impact of Awake Surgery in Glioma Treatment by Zigiotto et al at “S. Chiara” University-Hospital, Azienda Provinciale per i Servizi Sanitari, Trento, Italy Congress of Neurological Surgeons (CNS)
including attention. Understanding how AwS and AsS affect attention is crucial, given its pivotal role in supporting various cognitive functions.
METHODS:
We conducted a retrospective analysis on 64 glioma patients treated with AwS or AsS. Attention was assessed with visual search tasks and Trail Making Test Part A before and 1 week and 1 month after surgery. Volumetric T1-weighted and T2/Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery MRI sequences before and after surgery were used to delineate the lesion and the surgical cavity. The extent of resection was calculated to determine supramaximal resection for both contrast-enhanced and non–contrast-enhanced tumor regions.
RESULTS:

The study findings also suggest approaches that enhance expression or activity of DMTF1 may have therapeutic potential in reversing or delaying aging-associated decline of neural stem cell function.
While the preliminary findings stemmed mainly from in vitro experiments, the researchers hope to explore if elevating DMTF1 expression can regenerate neural stem cell numbers as well as improve learning and memory under the conditions of telomere shortening and natural aging, without increasing the risk of brain tumors. The long-term objective is to discover small molecules that can enhance DMTF1 expression and activity to improve the function of aged neural stem cells.
“Our findings suggest that DMTF1 can contribute to neural stem cell multiplication in neurological aging,” Dr Liang said. “While our study is in its infancy, the findings provide a framework for understanding how aging-associated molecular changes affect neural stem cell behavior, and may ultimately guide the development of successful therapeutics.”