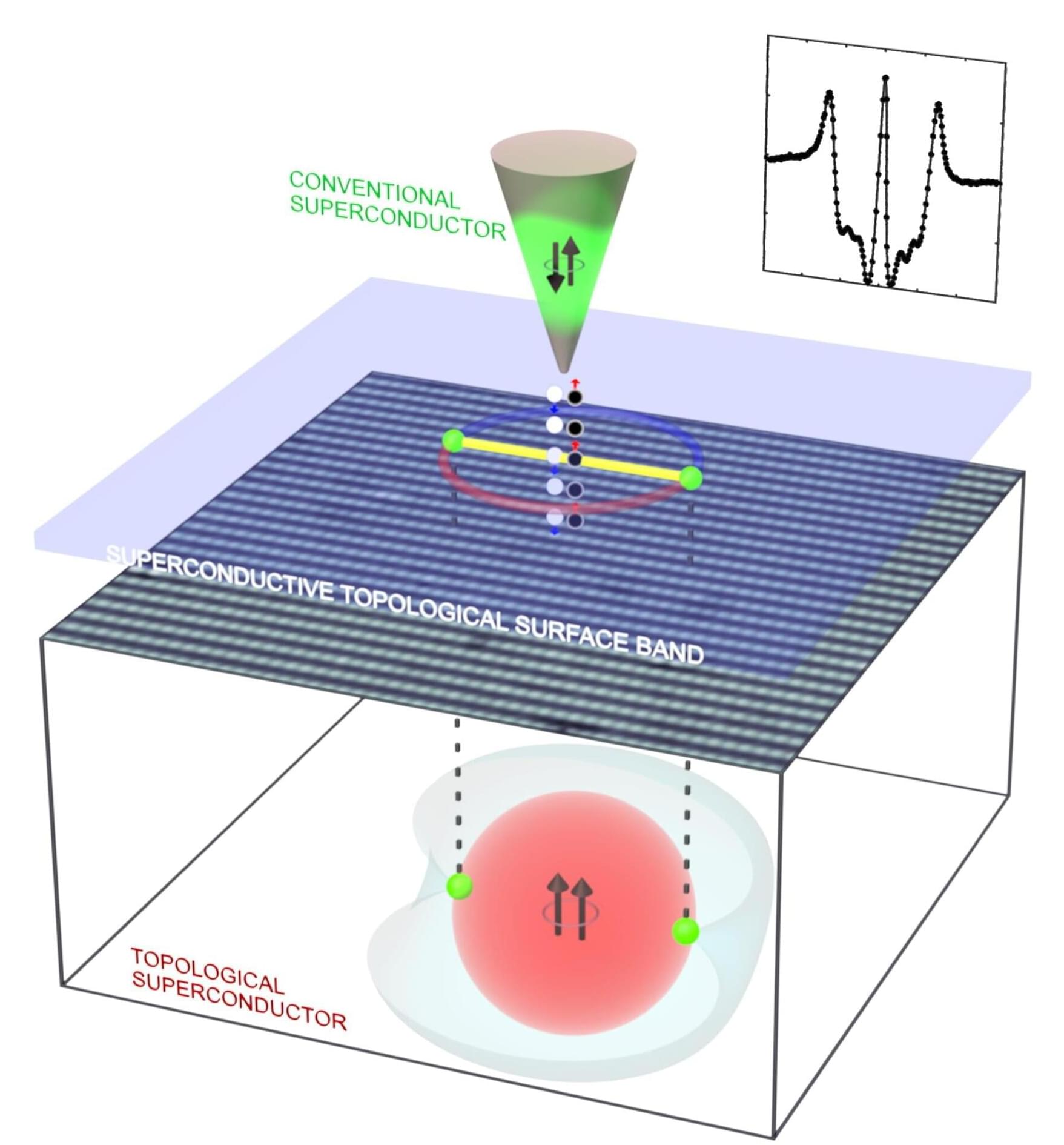
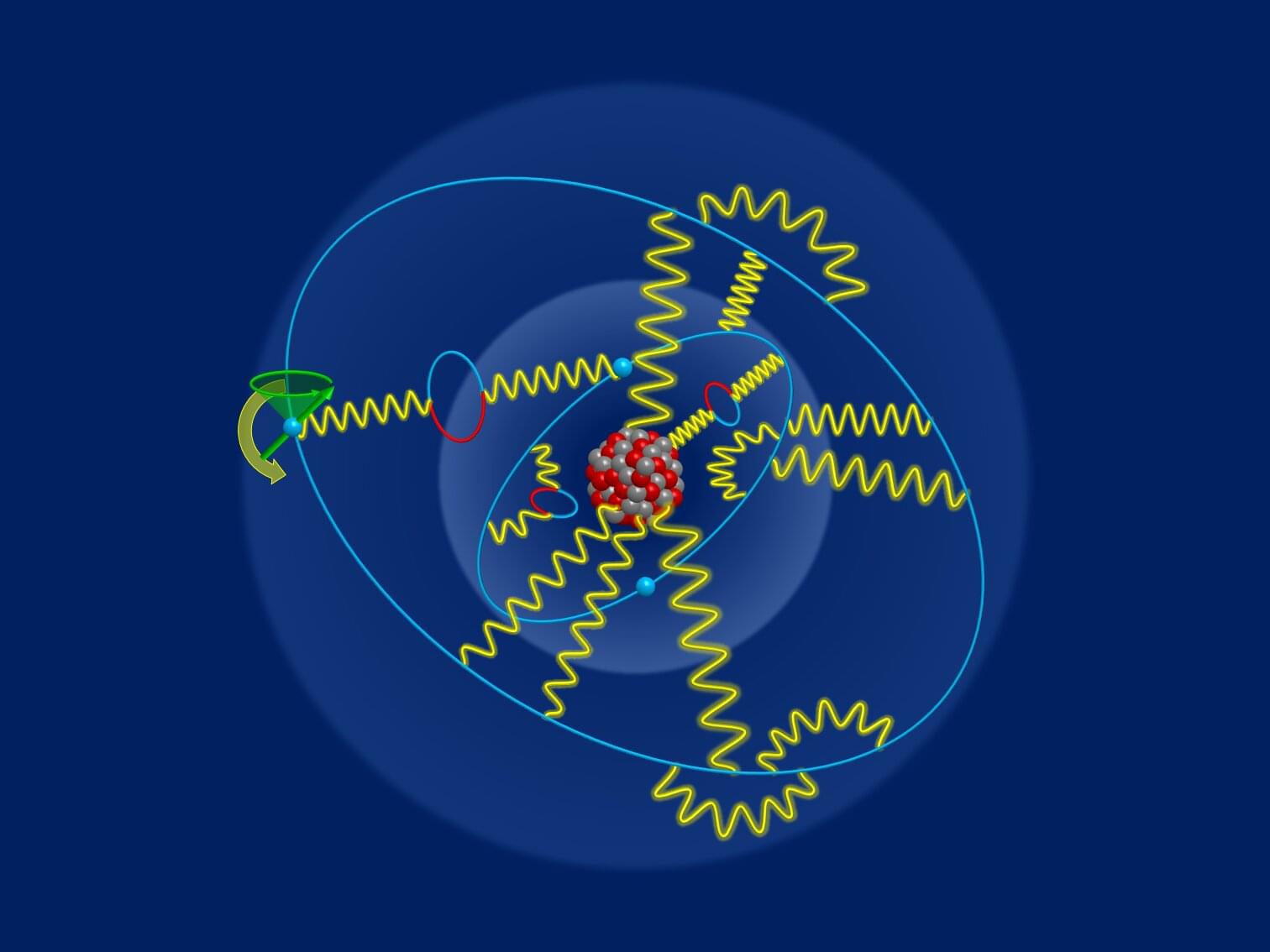
Scientists at University College Cork (UCC) in Ireland have developed a powerful new tool for finding the next generation of materials needed for large-scale, fault-tolerant quantum computing.
The significant breakthrough means that, for the first time, researchers have found a way to determine once and for all whether a material can effectively be used in certain quantum computing microchips.
The major findings have been published in Science and are the result of a large international collaboration which includes leading theoretical work from Prof. Dung-Hai Lee at the University of California, Berkeley, and material synthesis from professors Sheng Ran and Johnpierre Paglione at Washington University in St. Louis and the University of Maryland, respectively.