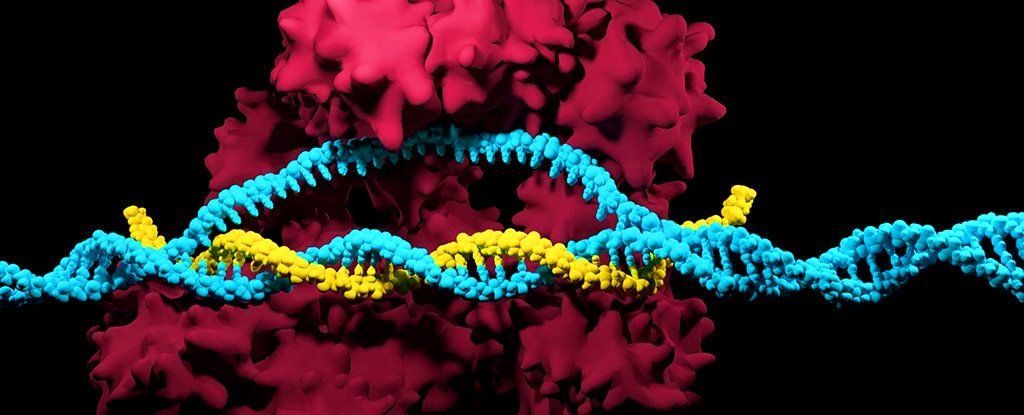
CRISPR has been heralded as one of the most important breakthroughs in modern science, but there could be a hidden and potentially dangerous side effect to the wonders of its genetic editing technology, a new study reveals.
A systematic investigation of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in mouse and human cells has discovered that the technique appears to frequently cause extensive mutations and genetic damage that the researchers say wouldn’t be detected by existing DNA tests.
“This is the first systematic assessment of unexpected events resulting from CRISPR/Cas9 editing in therapeutically relevant cells,” explains geneticist Allan Bradley from the Wellcome Sanger Institute in the UK.