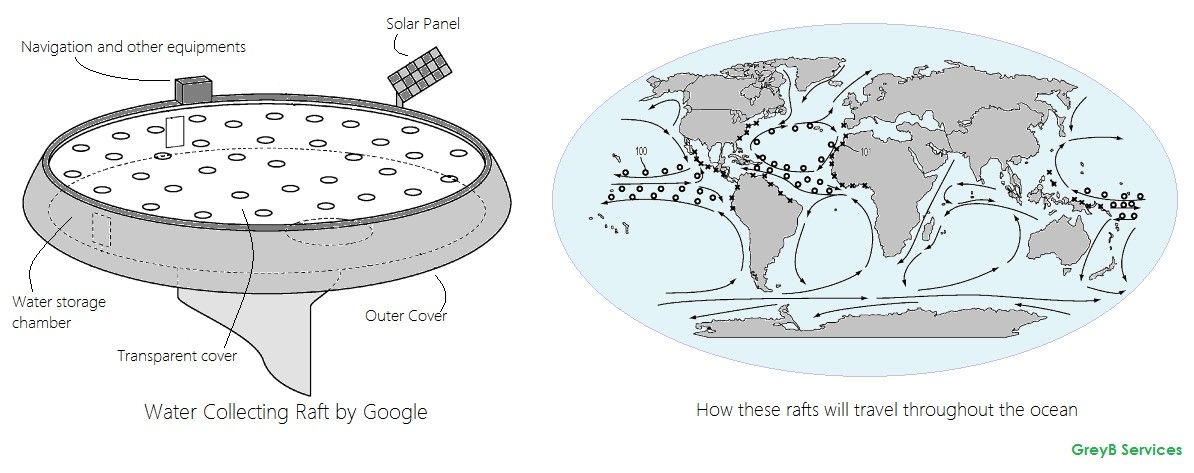
Harsh environment, less rain, and lack of infrastructure are among the many problems African countries face. Water scarcity and the lack of drinkable water, however, is a grave problem among all. It makes people use water from contaminated bodies which is the sole reason of water borne diseases like, diarrhea and typhoid.
Hundreds of organizations around the globe have taken this issue head-on. And Google, one of the most innovative companies of the planet, is in the league, too.
Google has launched multiple projects including Project Makani and Project Loon to resolve the power outages and connectivity issues in areas where they are most needed. Since the power and connectivity issues are already being worked upon, Google took another step to help these countries fight the water scarcity problem.