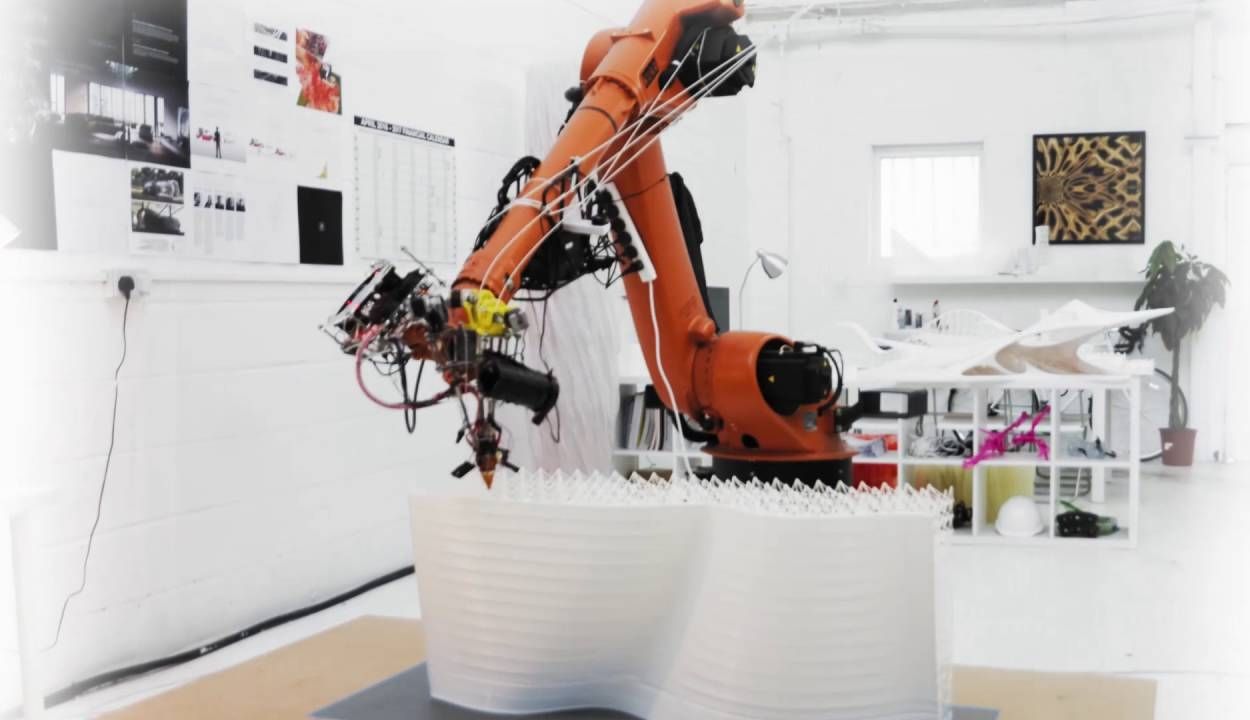
A London-based startup has combined some of today’s most disruptive technologies in a bid to change the way we’ll build the future. By retrofitting industrial robots with 3D printing guns and artificial intelligence algorithms, Ai Build has constructed machines that can see, create, and even learn from their mistakes.
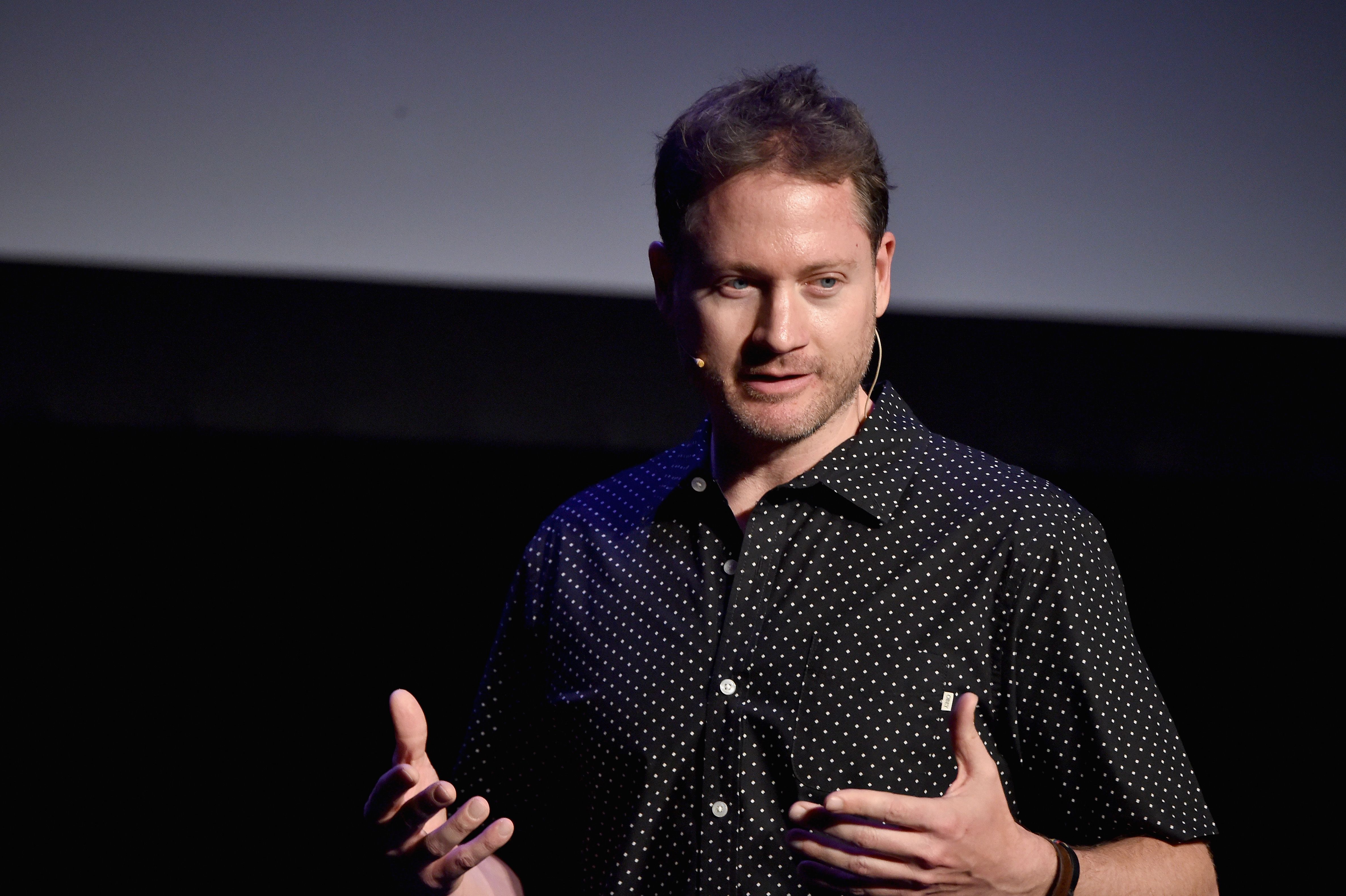
When CEO and founder Daghan Cam was studying architecture, he noticed a disconnect between small-scale manufacturing and large-scale construction. “On one side we have a fully automated production pipeline,” Cam explained at a recent conference in London. “On the other side we’re completely dependent on human labor.” With the emergence of more efficient printing technologies, he thought there must be a better way.
“We wanted to push the boundaries of how intricate we could design things through computation and how we could create them through 3D printing,” Cam said.