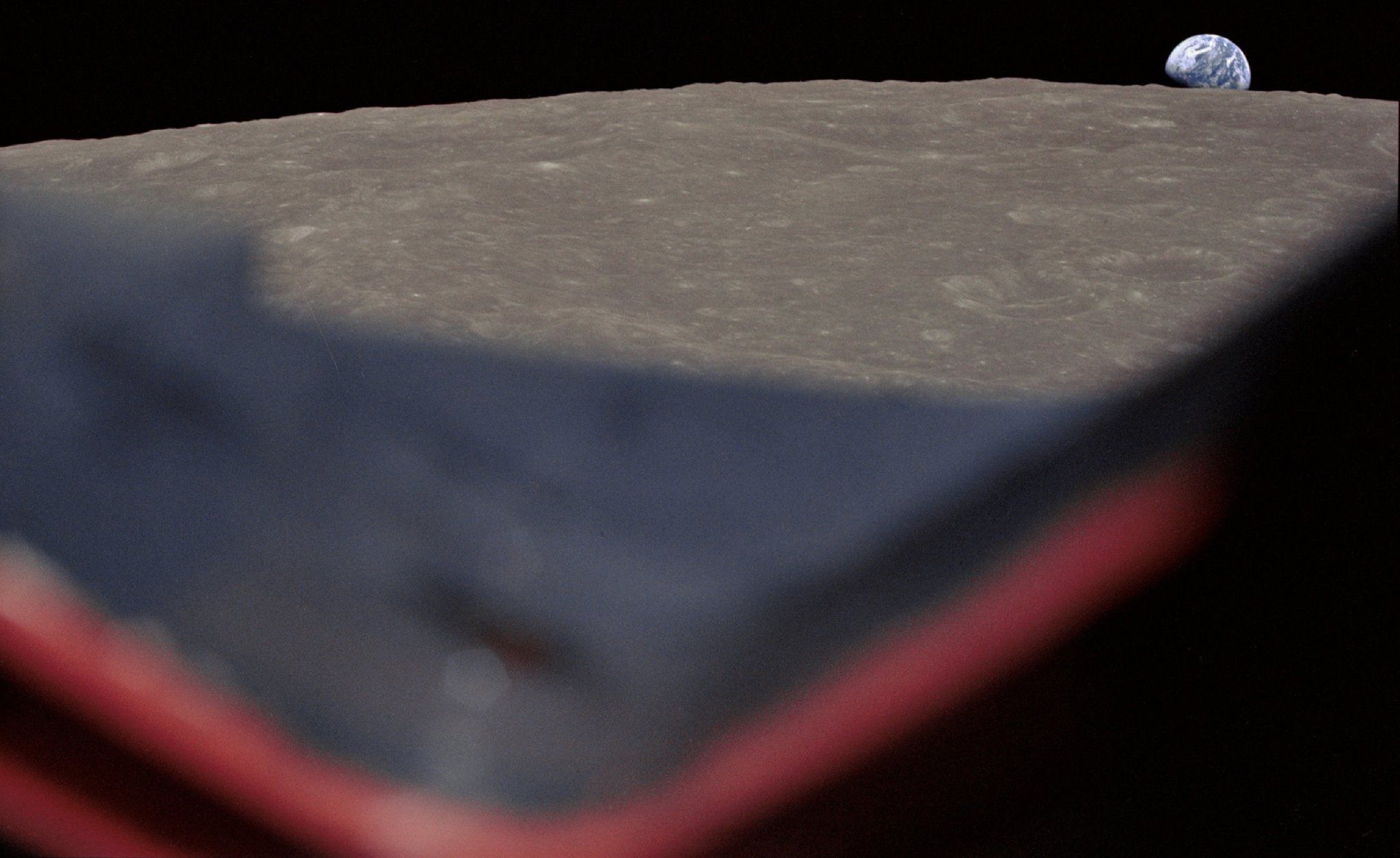
They glimpsed Earth outside their windows. “It’s a beautiful, beautiful view,” Frank Borman said to Mission Control. That Christmas Eve broadcast ended 1968 on a hopeful note, bringing a reminder of the all encompassing curiosity stitched into the fabric of all humans. Sink into the far side by celebrating our #Apollo50 Anniversary here: https://go.nasa.gov/2EGQJJX