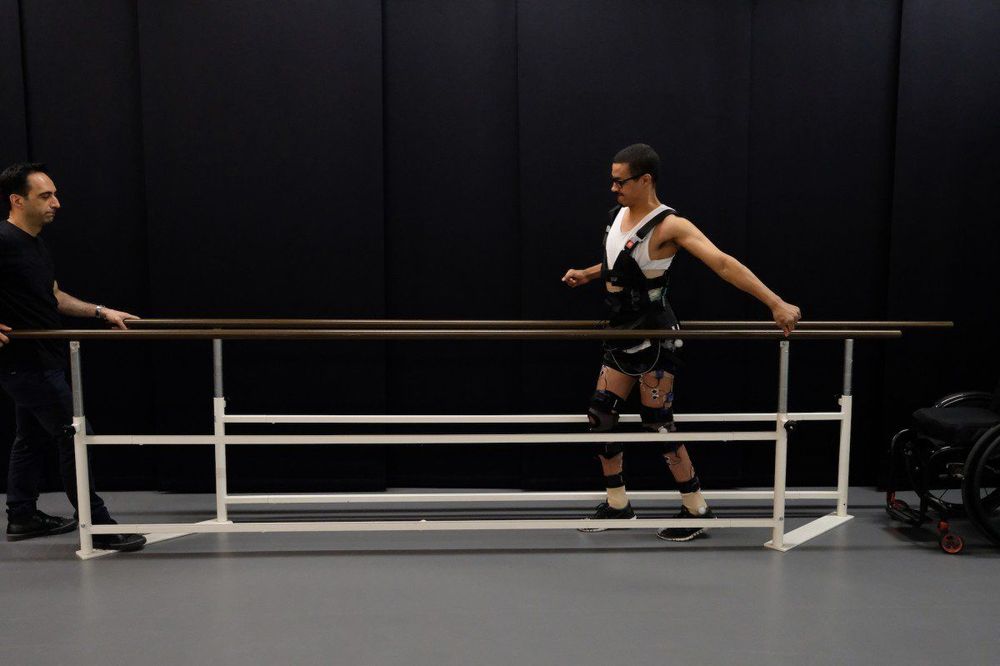
Three men with severe spinal cord injuries have walked for the first time in years after receiving targeted electrical stimulation of the spinal cord.
Breakthrough: Spinal cord injuries can severely reduce a person’s range of motion or lead to complete leg paralysis. In two new papers published in Nature and Nature Neuroscience, researchers describe implanting electrical stimulators into the damaged spinal cords of three men who all had partial or complete lower-leg paralysis. The stimulators then delivered targeted electric pulses in time with the patients’ walking gait.
The patients wore a series of sensors on their legs and feet that wirelessly communicated to the stimulators as they began to walk. Within a week, the men were able to leave the treadmill and walk on the ground with continued electrical stimulation. After a few months, they regained the ability to walk without any electrical stimulation at all.