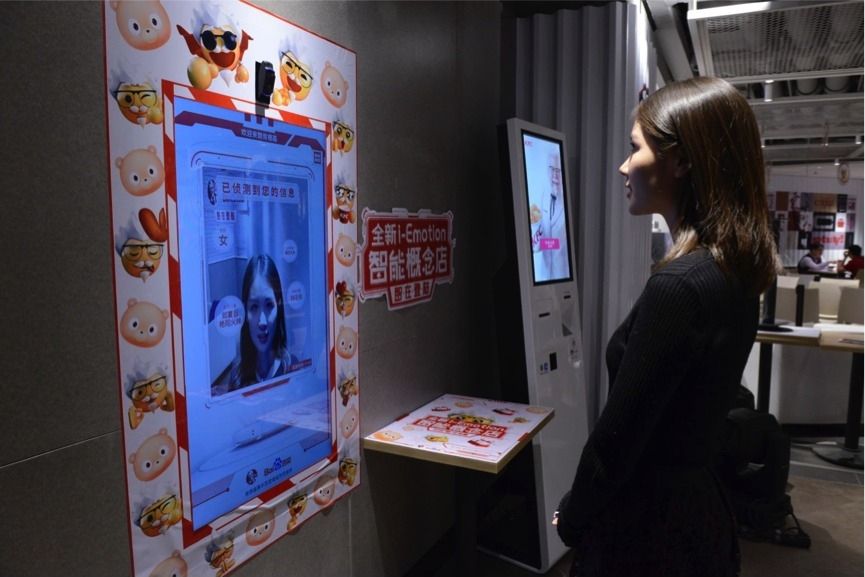
If you loathe having to talk out loud when ordering a meal at a fast-food restaurant, and you happen to love KFC, then you might want to start considering packing it up and moving to China where Baidu has just teamed up with the major chicken brand to create a more automated restaurant. The venture aims to use the company’s latest technologies to bring novel ways of providing service to KFC customers.
As an added feature, the outlet also offers augmented reality games via table stickers, a concept also made available to 300 other KFC locations in Beijing.
Baidu’s tech in this new restaurant, however, is all about guessing what you want before you can even ask; image recognition hardware installed at the KFC will scan customer faces, seeking to infer moods, and guess other information including gender an age in order to inform their recommendation.