Growing up in Jakarta’s polluted slums, Vera Mulyani loved building things. As a child, she dreamed of becoming an architect.
More than two decades later, Mulyani is a self-proclaimed “Marschitect,” and spends her time brainstorming how human life might be sustained on the red planet. After studying at École d’Architecture de Nantes in France and at New York Film Academy, in January 2015 she founded Mars City Design, a think tank of sorts aimed at developing blueprints for the first self-sustaining city on Mars.
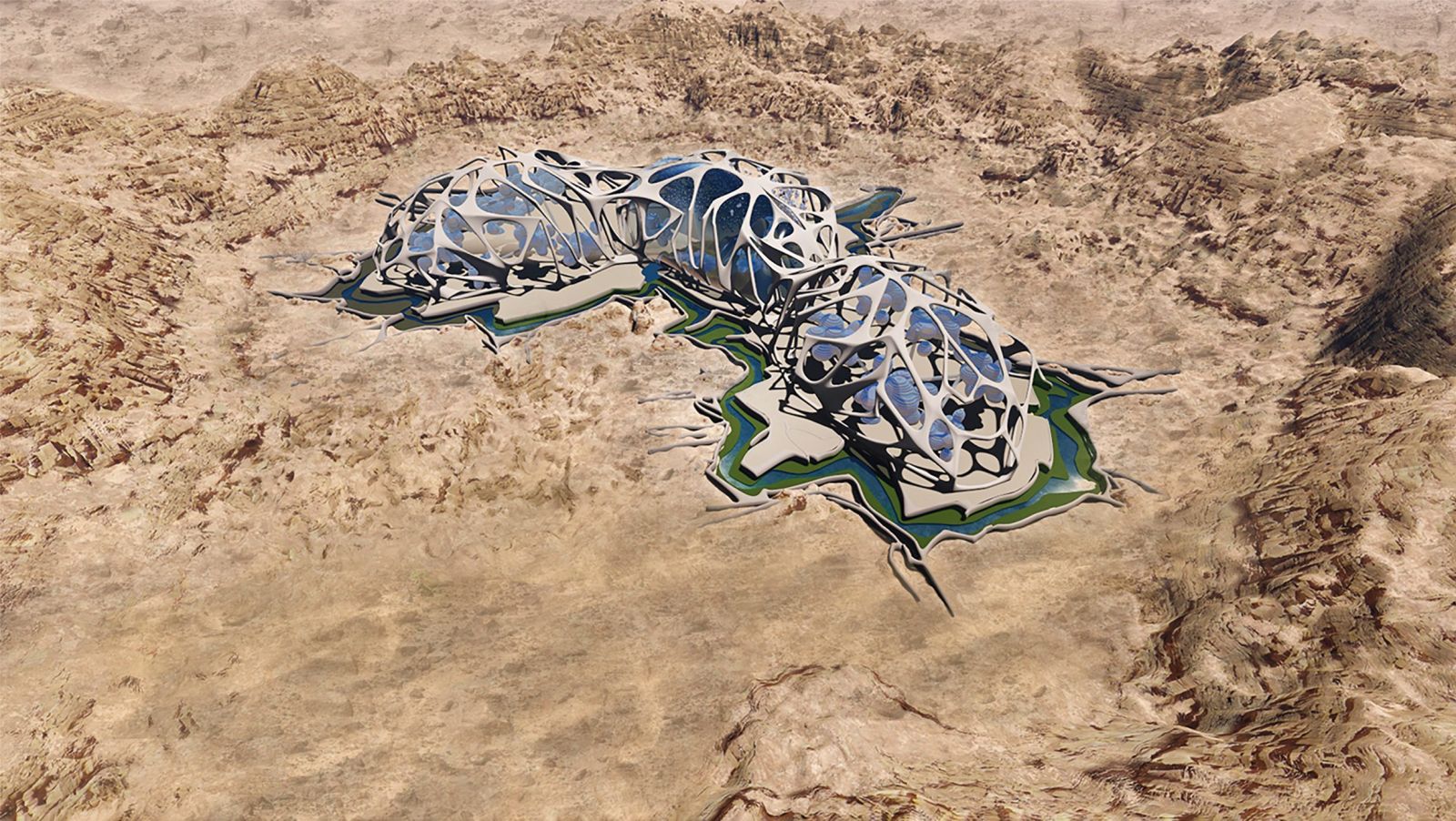
Earlier this month, Mars City Design raised $30,382 on Kickstarter to realize the next phase of its mission: Within the next three years, the group wants to 3D-print three to-scale habitat prototypes of Martian cities at Reaction Research Society’s test area in the Mojave Desert.