Liftoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 for Demo-1, the first flight test of the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft, is targeted for Saturday, March 2, at 2:49 a.m. EST from historic Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Join us at 2 a.m. EST for countdown coverage. Watch:
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
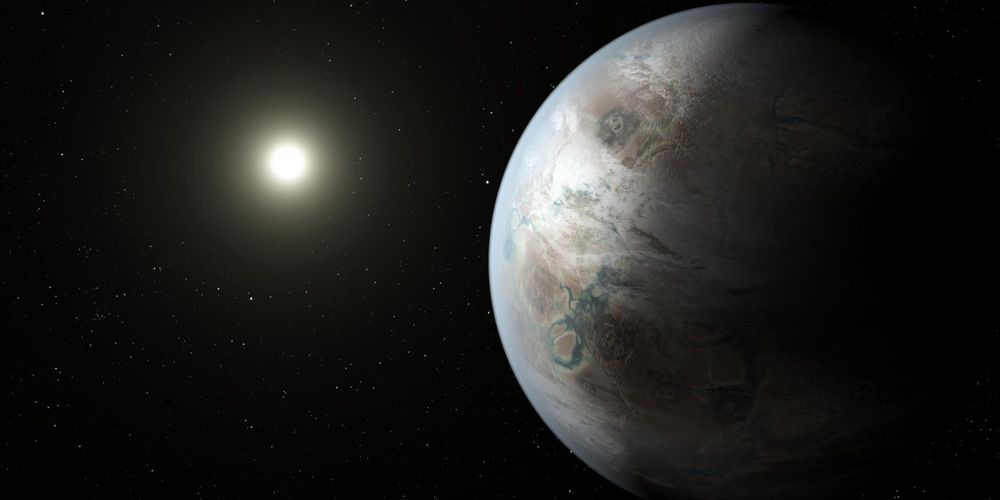

Scientists have found two planets outside our solar system that could host extra-terrestrial life
Are we alone in the universe?
Using data on the UV levels required to make the molecular structures needed within a functioning cell, scientists may have just found a pair of planets capable of supporting life — both exo-planets receive similar UV levels from stars needed to promote cell function, one of which is Kepler-452b.

Today in Space History: A space Pioneer embarks on a historic mission
As it travels through space, Pioneer 10 carries a unique payload: a 6.0 × 9.0 in gold-anodized aluminum plaque with images of two nude human figures (one male and one female) and information on the probe’s origin. It was designed by astronomers Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, just in case intelligent life finds the spacecraft. #FlipFacts


Prospects for Bioinspired Single-Photon Detection Using Nanotube-Chromophore Hybrids
The human eye is an exquisite photodetection system with the ability to detect single photons. The process of vision is initiated by single-photon absorption in the molecule retinal, triggering a cascade of complex chemical processes that eventually lead to the generation of an electrical impulse. Here, we analyze the single-photon detection prospects for an architecture inspired by the human eye: field-effect transistors employing carbon nanotubes functionalized with chromophores. We employ non-equilibrium quantum transport simulations of realistic devices to reveal device response upon absorption of a single photon. We establish the parameters that determine the strength of the response such as the magnitude and orientation of molecular dipole(s), as well as the arrangements of chromophores on carbon nanotubes. Moreover, we show that functionalization of a single nanotube with multiple chromophores allows for number resolution, whereby the number of photons in an incoming light packet can be determined. Finally, we assess the performance prospects by calculating the dark count rate, and we identify the most promising architectures and regimes of operation.
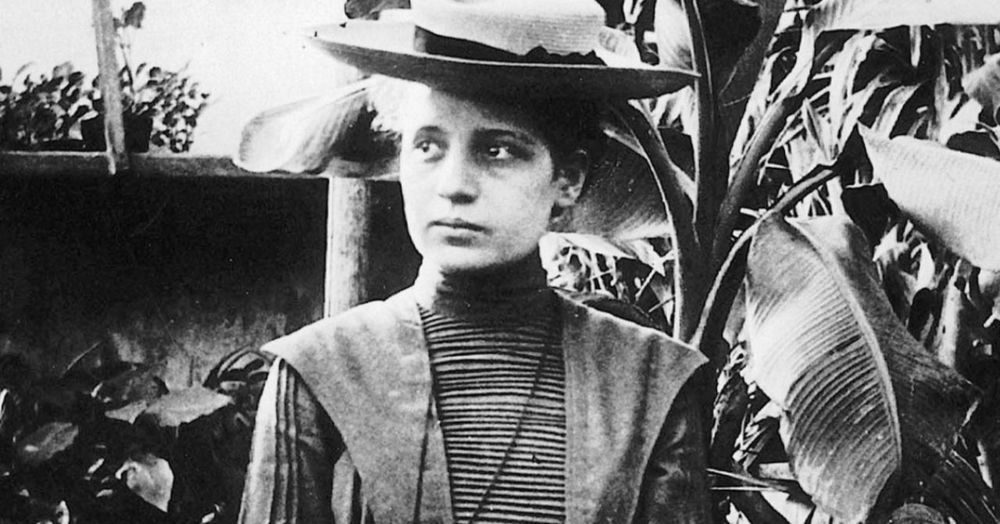


Lise Meitner Is the Forgotten Female Physicist Who Deserved a Nobel Prize
Nuclear fission — the physical process by which very large atoms like uranium split into pairs of smaller atoms — is what makes nuclear bombs and nuclear power plants possible. But for many years, physicists believed it energetically impossible for atoms as large as uranium (atomic mass = 235 or 238) to be split into two.
That all changed on Feb. 11, 1939, with a letter to the editor of Nature — a premier international scientific journal — that described exactly how such a thing could occur and even named it fission. In that letter, physicist Lise Meitner, with the assistance of her young nephew Otto Frisch, provided a physical explanation of how nuclear fission could happen.
It was a massive leap forward in nuclear physics, but today Lise Meitner remains obscure and largely forgotten. She was excluded from the victory celebration because she was a Jewish woman. Her story is a sad one.
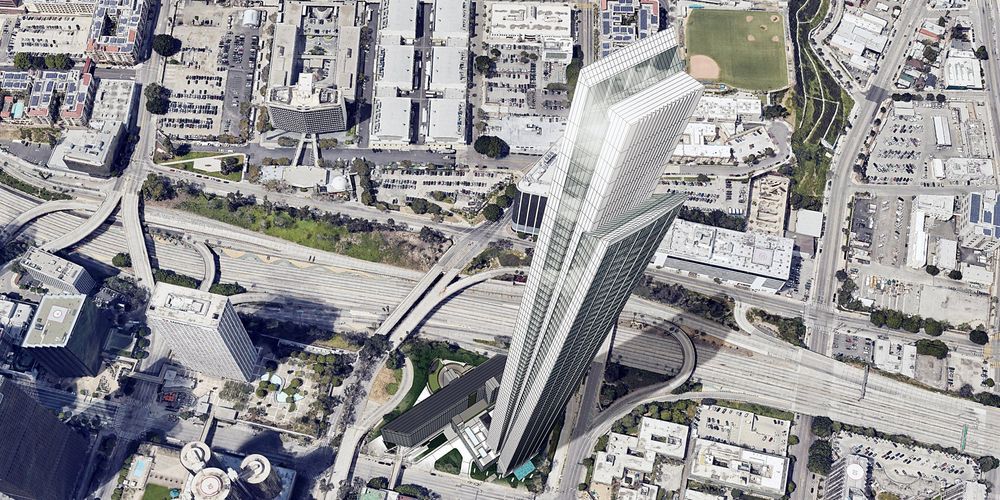

The tallest building in California will be a 77-story ‘supertall’ skyscraper in Los Angeles
- Los Angeles could be getting a brand-new skyscraper that’s taller than the Wilshire Grand — the tallest tower in California.
- The planned skyscraper is 77 stories high and features a mixture of condos, hotel rooms, and commercial space.
- The future development represents a growing trend of supertall construction as cities compete to have the most impressive skylines.
Los Angeles has endured endless criticism for its low-lying slab buildings, flat-topped towers, and mismatched design aesthetics.
In 2013, the former architecture critic at Los Angeles magazine, Greg Goldin, lamented the city’s “dull” and “mediocre” landscape.
