Google and Amazon are on the forefront of AI innovation. But have they already gone too far?
 By John Brandon Contributing editor, Inc.com
By John Brandon Contributing editor, Inc.com

Google and Amazon are on the forefront of AI innovation. But have they already gone too far?
 By John Brandon Contributing editor, Inc.com
By John Brandon Contributing editor, Inc.com

WASHINGTON — The U.S. military got is first big taste of artificial intelligence with Project Maven. An Air Force initiative, it began more than a year ago as an experiment using machine learning algorithms developed by Google to analyze full-motion video surveillance.
The project has received high praise within military circles for giving operators in the field instant access to the type of intelligence that typically would have taken a long time for geospatial data analysts to produce.
Project Maven has whetted the military’s appetite for artificial intelligence tools. And this is creating pressure on the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency to jump on the AI bandwagon and start delivering Maven-like products and services.


While you can’t teach an old dog new tricks, you may be able to make your pup young again.
A Harvard startup has begun preliminary experiments on beagles and claims it can make animals ‘younger’ by adding new DNA instructions to their bodies.
And, the firm says it could one day work for humans, too.
And inflammation is one of the three primary ageing processes.
Scientists have discovered a new metabolic process in the body that can switch off inflammation. They have discovered that ‘itaconate’—a molecule derived from glucose—acts as a powerful off-switch for macrophages, which are the cells in the immune system that lie at the heart of many inflammatory diseases including arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and heart disease.
The scientists, working in the School of Biochemistry and Immunology in the Trinity Biomedical Sciences Institute at Trinity College Dublin, hope their discovery will have relevance for inflammatory and infectious diseases—and that their findings may also help to develop much-needed new drugs to treat people living with these conditions.
Professor of Biochemistry at Trinity, Luke O’Neill, was, along with Dr. Mike Murphy of the University of Cambridge, the joint leader of the work just published in leading international journal Nature. The discoveries were made using both human cells and mice as a model organism.
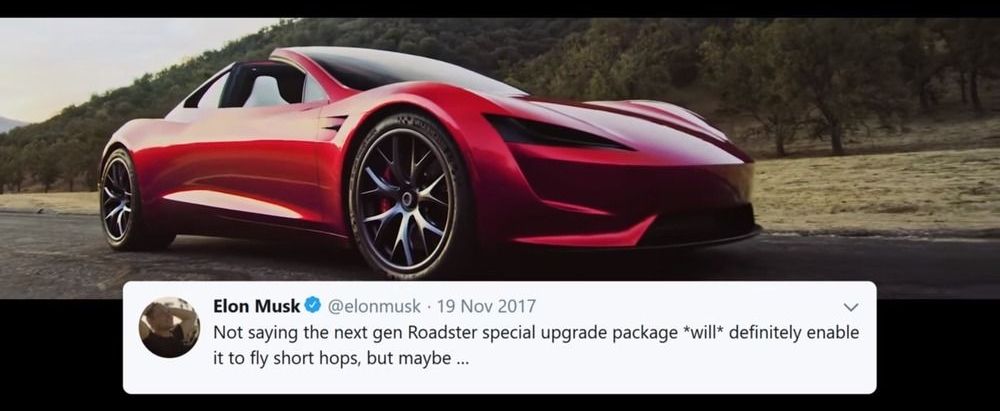
We’ve all dreamed of owning, or at the very least being a passenger of, a flying car. It’s the sci-fi dream that never transpired — until recently, that is. With a growing emphasis of developing flying taxis among several different companies, one wonders if the revolutionary Tesla Motors has plans to join in on this new venture.
Could Elon Musk’s random tweet from late last year be an indicator of Tesla’s interest in flying cars and their joining of this brand new “space race?”
This cool new tech will help you blow off your parents like never before!
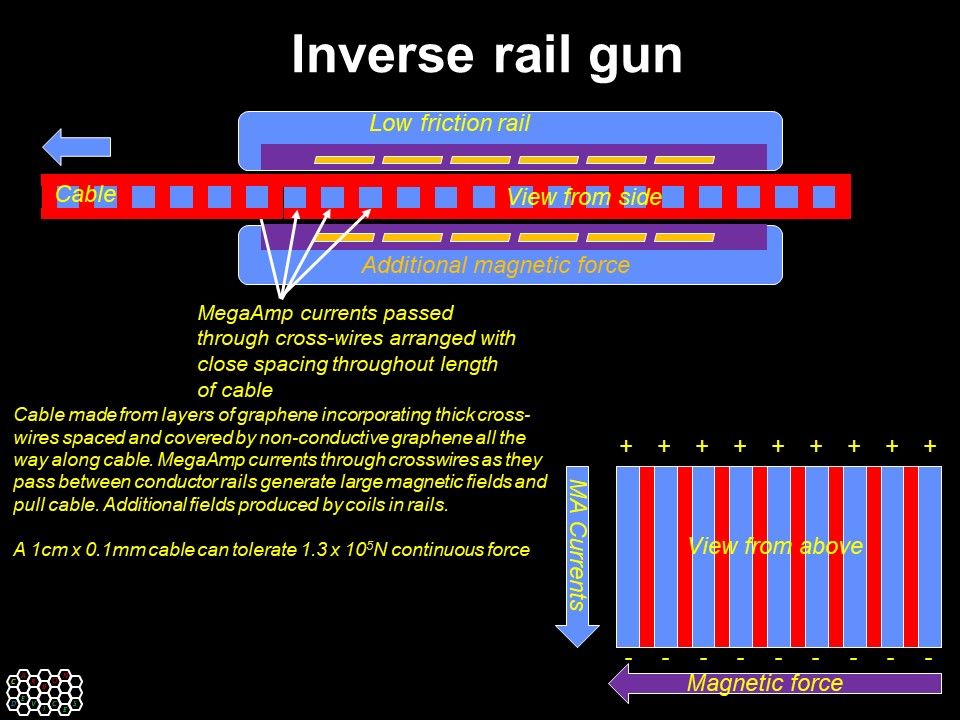
Future wars could be much more fierce with weapons even more powerful than nukes:
The world is progressing in many ways, but tribalism isn’t going away, so new arms races in AI, drones, bio-weapons and space weapons are already under way. Forewarned is forearmed. What sort of weaponry should we expect? I’ve discussed AI and bio approaches before on other blogs, so this one looks just at kinetic weaponry using advanced materials, coupled to EM acceleration systems.
https://carbondevices.com/2017/08/31/using-inverse-rail-guns…ce-launch/ shows a crude illustration of my invention, the inverse rail gun, which inverts the idea of using a slug on a short rail gun and uses the short rail gun to accelerate a long tape instead.