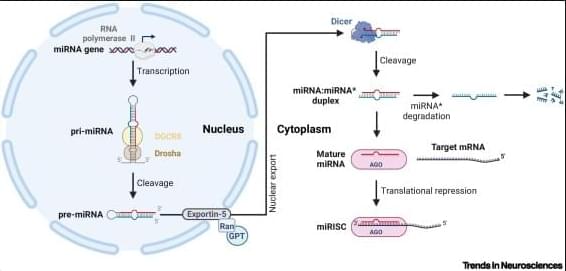
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) serve as key regulators of enteric nervous system development, orchestrating migration, proliferation, and differentiation of enteric nervous system progenitors.
Aberrant miRNA expression underpins the pathogenesis of several enteric neuropathies, including Hirschsprung’s disease.
A convergence of miRNA activity across distinct enteric neuropathies highlights shared molecular pathways, exemplified by the miR-200 family.
Modulating the expression of miRNAs to influence their associated gene expression networks has therapeutic potential for enteric neuropathies. https://sciencemission.com/MicroRNA-regulation-of-enteric-ne…nd-disease
The enteric nervous system (ENS), an elaborate network of neurons and glia woven through the gastrointestinal tract, is integral for digestive physiology and broader human health. Commensurate with its importance, ENS dysfunction is linked to a range of debilitating gastrointestinal disorders. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), with their pleiotropic roles in post-transcriptional gene regulation, serve as key developmental effectors within the ENS. Herein, we review the regulatory dynamics of miRNAs in ENS ontogeny, showcasing specific miRNAs implicated in both congenital and acquired enteric neuropathies, such as Hirschsprung’s disease (HSCR), achalasia, intestinal neuronal dysplasia (IND), chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO), and slow transit constipation (STC).