Sep 2, 2015
6 billionaires who want to live forever
Posted by Zoltan Istvan in category: life extension
Cool article on longevity science:
The search for the fountain of youth continues in Silicon Valley.
Cool article on longevity science:
The search for the fountain of youth continues in Silicon Valley.
When it comes to growing food, the sky’s the limit thanks to innovations like the Sky Urban Vertical Farming System. Designed and pioneered by the Singapore-based company Sky Greens, the vertical farming system is a revolutionary modern spin on the ancient practice of agriculture. Using cutting edge technology, the system demonstrates an energy efficient, environmentally friendly method of producing food that could be a powerful tool in feeding the ever-growing, increasingly urbanized, global population.
California researchers opened the world’s largest publicly available stem cell bank Tuesday, which will aid in the search for cures for genetic diseases such as Alzheimer’s, epilepsy and autism.
Universities from around the state will contribute adult skin samples to the bank, while the Buck Institute for Research in Novato will store the material.
The Stem Cell Bank is funded through a $32 million grant awarded in 2013 by the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine, which itself was established in 2004 through voter approval of Proposition 71. That measure provided an initial $3 billion in state bonds to the institute.
If you wanted an insane looking router with an almost as-insane boast, then say hello to ASUS’ new router. Touting it as the best for gaming, 4K streaming and smart home networking, the RT-AC5300 router will apparently give speeds that are 67 percent faster than first-gen, tri-band routers. It’s calling it the world’s fastest WiFi. ASUS is promising up to 1Gbps connections over 2.4GHz and up to 2.167Gbps on each of the two 5GHz bands — that’s a lot of data. Google just got a new router challenger.
A group of Japanese researchers have managed to improve the design of a transparent lithium-ion battery so that it’s now able to recharge itself when exposed to sunlight without the need for a separate solar cell.
The transparent battery was first developed by the researchers, led by Kogakuin University president and professor Mitsunobu Sato, back in 2013. The electrolyte used for the battery’s positive electrode is made mostly from lithium iron phosphate, while the electrolytes used for the negative electrode include lithium titanate, and lithium hexafluorophosphate.
Those are all common ingredients used in Li-ion rechargeable batteries, but the thickness of these electrodes are just 80 to 90 nanometers, which allows a lot of light to pass through and makes these batteries almost completely transparent.
.
NASA Glenn Research Center, GRC, currently has several programs to advance near-term photovoltaic array development. One project is to design, build, and test two 20 kW-sized deployable solar arrays, bringing them to technology readiness level (TRL) 5, and through analysis show that they should be extensible to 300 kW-class systems (150 kw per wing). These solar arrays are approximately 1500 square meters in total area which is about an order-of-magnitude larger than the 160 square meters solar array blankets on the International Space Station (ISS).
The ISS has the four (pair) sets of solar arrays that can generate 84 to 120 kilowatts of electricity. Each of the eight solar arrays is 112 feet long by 39 feet wide and weighs 2400 pounds. There were space missions involving astronauts working in space to install and deploy the ISS solar panels.
This is a link to the video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hptgw_-59YY
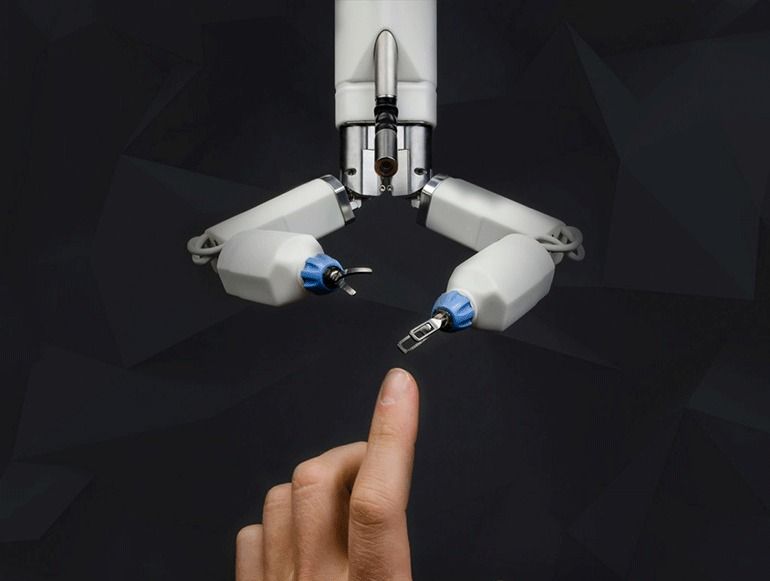

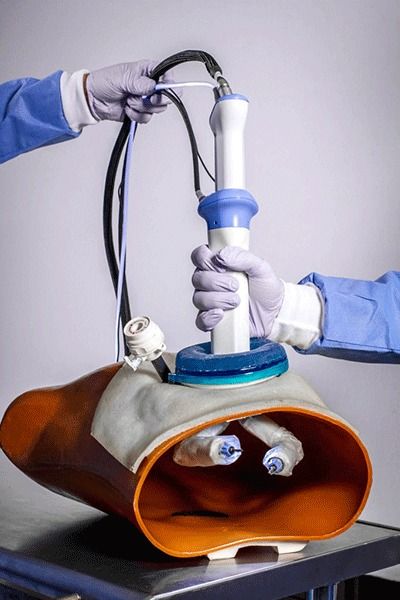
Thanks to MassDevice, we learned of a new company that’s developed a small surgical robot for performing laparoscopic procedures that may lower the cost and offer robotic capability to clinics that don’t have millions of dollars in discretionary funds. Virtual Incision Corporation is a spin-off out of the University of Nebraska and the company just raised $11.2M in equity financing to sponsor a feasibility study of its robotic technology.
The system was designed to fit almost completely into the abdominal cavity via a single incision, with only the handle and cables staying on top. It’s intended for surgeries that are often performed in an open fashion that can benefit from robotic laparoscopy, such as colon resections.
A device that reanimates organs taken from dead patients has shown promise in heart transplant surgeries, though it’s raising some ethical concerns, as well. As MIT Technology Review reports, the so-called “heart in a box” uses tubing and oxygen to pump blood and electrolytes into hearts from recently deceased patients, allowing the organs to continue functioning within a chamber. The system, developed by Massachusetts-based Transmedics, has been successfully deployed in at least 15 heart transplants in the UK and Australia, and is awaiting regulatory approval in the US.
Until now, hearts used for transplants have usually been extracted from brain-dead patients; those from dead patients have been considered too damaged. Once removed, the hearts are also stored and transported in cold temperatures to avoid rapid deterioration, though scientists have begun using devices like the heart in a box to keep the organs warm and functioning. That, doctors say, could increase the pool of donated hearts by between 15 and 30 percent.
Some say the $250,000 device is still too expensive to be deployed widely, and that it needs greater automation. For medical ethicists, the question is how long surgeons should wait before removing a heart that has stopped. “How can you say it’s irreversible, when the circulatory function is restored in a different body?” Robert Truog, an ethicist at Harvard University, tells MIT Technology Review. “We tend to overlook that because we want to transplant these organs.” Truog says he believes those patients can be considered dead, though it’s ultimately a decision for family members to make. “They are dying and it’s permissible to use their organs. The question is whether they are being harmed, and I would say they are not.”
A key mystery of the DNA replication process has been unraveled by researchers from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST).
Before a bacterium can divide, it must make a copy of its genetic material, the circular DNA molecules that resemble bunched rubber bands, through a process called DNA replication. In this process, the two strands of DNA making up the circular DNA molecule unwind and separate to become templates for generating new strands.
To ensure the process is well regulated, the bacterium has set a number of “roadblocks,” or termination sites on the DNA, to ensure the permanent stoppage of replication forks, Y-shaped structures formed between the strands as the DNA molecule splits.
A UCSF-led team has developed a technique to build tiny models of human tissues, called organoids, more precisely than ever before using a process that turns human cells into a biological equivalent of LEGO bricks. These mini-tissues in a dish can be used to study how particular structural features of tissue affect normal growth or go awry in cancer. They could be used for therapeutic drug screening and to help teach researchers how to grow whole human organs.
The new technique — called DNA Programmed Assembly of Cells (DPAC) and reported in the journal Nature Methods on August 31, 2015 — allows researchers to create arrays of thousands of custom-designed organoids, such as models of human mammary glands containing several hundred cells each, which can be built in a matter of hours.
There are few limits to the tissues this technology can mimic, said Zev Gartner, PhD, the paper’s senior author and an associate professor of pharmaceutical chemistry at UCSF. “We can take any cell type we want and program just where it goes. We can precisely control who’s talking to whom and who’s touching whom at the earliest stages. The cells then follow these initially programmed spatial cues to interact, move around, and develop into tissues over time.”
