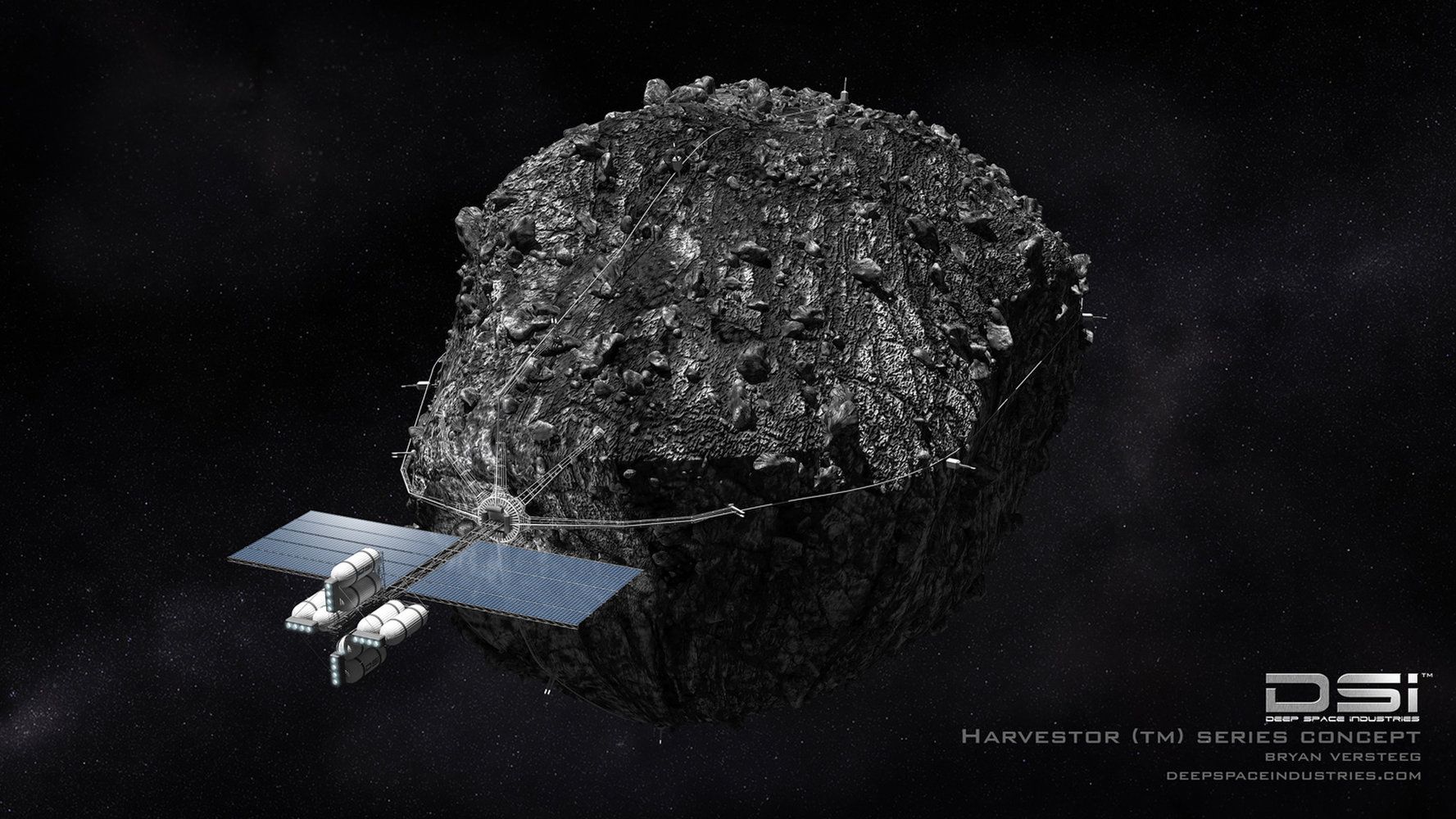
Astronomers could help asteroid miners identify the most promising targets, potentially slashing the cost of off-Earth resource extraction, Harvard astrophysicist Martin Elvis said.
I’ll be on a panel and also doing an author’s roundtable (The Transhumanist Wager) at FreedomFest in Las Vegas on July 21. It’s one of the largest gatherings of free minds in the world and this year is the 10th anniversary. If you’re there, please say hello! Others are speaking on life extension and AI. Here’s my speaker’s page:
Check out what Zoltan Istvan will be attending at FreedomFest 2017.
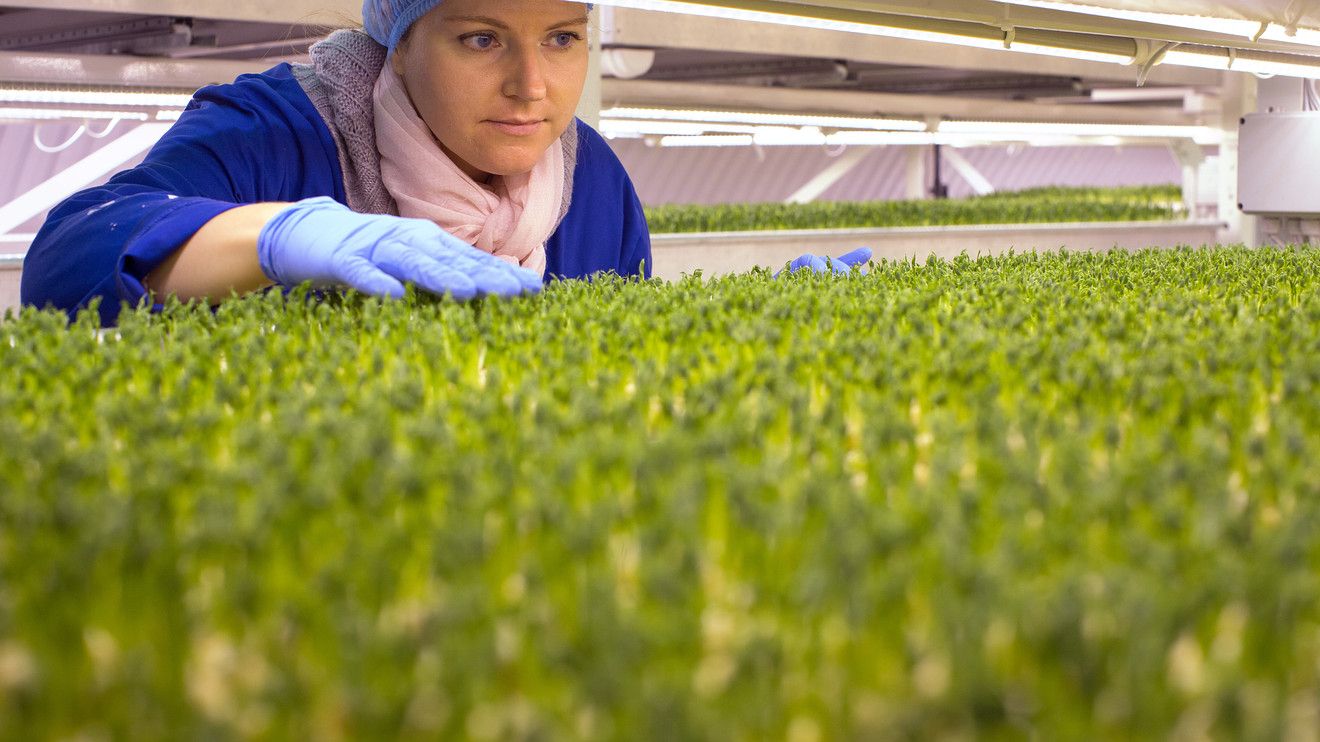
NASA has revealed plans to grow bioprinted cancer cells in space in a bid to advance cancer research.
Utilizing the microgravity environment, NASA hopes to the cell structures will grow in a more natural spherical shape. Since, back on earth in vitro the cells have only able been able to grow in two-dimensional layers. However to harness the cells without the presence of gravity, NASA is hoping to employ magnets.
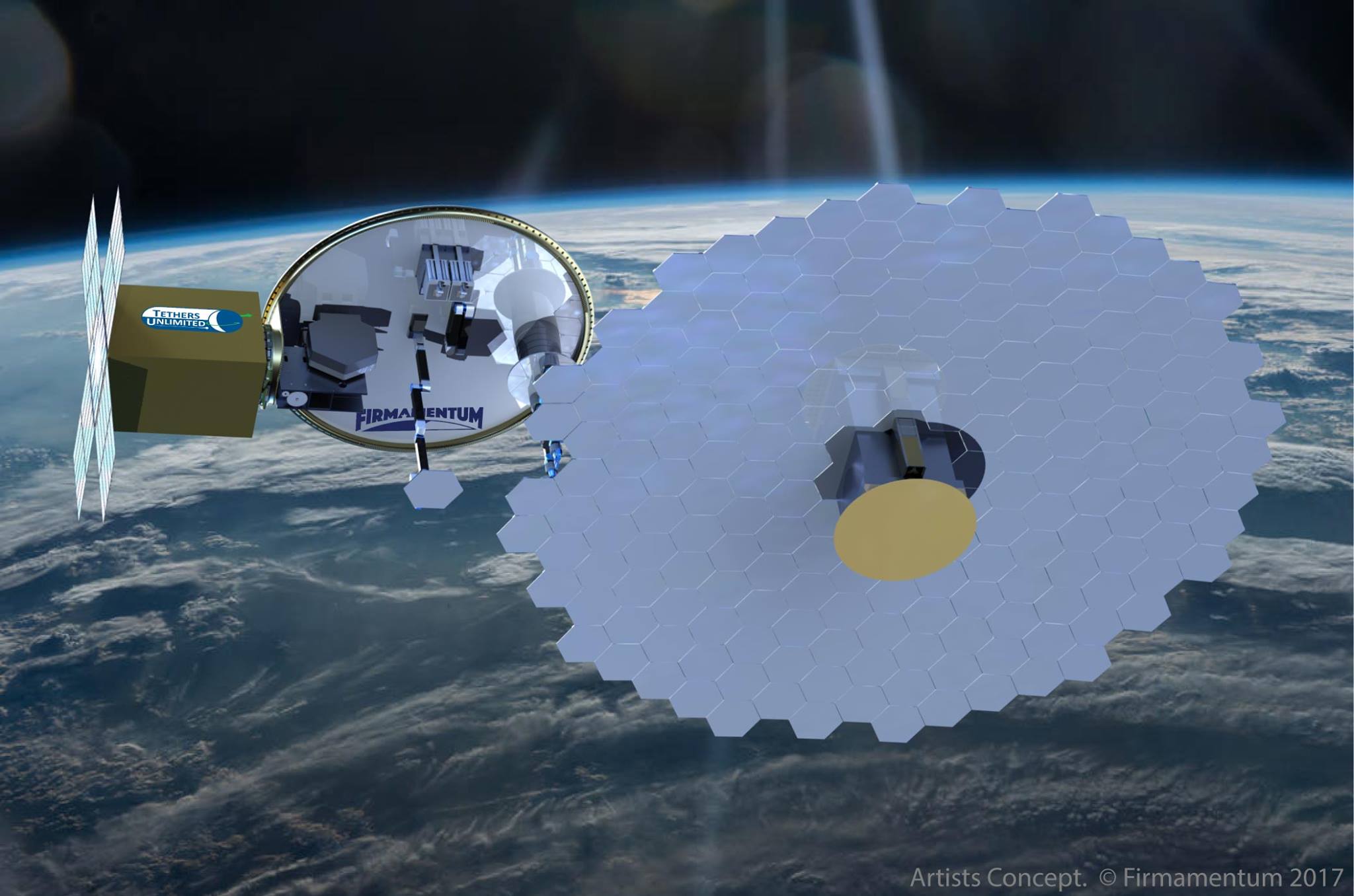
We are incredibly excited to announce that Firmamentum, a division of Tethers Unlimited, Inc. (TUI), has signed a contract with the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) to develop a system that will use in-space manufacturing and robotic assembly technologies to construct on orbit a small satellite able to provide high-bandwidth satellite communications (SATCOM) services to mobile receivers on the ground.
Under the OrbWeaver Direct-to-Phase-II Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) effort, Firmamentum aims to combine its technologies for in-space recycling, in-space manufacturing, and robotic assembly to create a system that could launch as a secondary payload on an Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV). This system would recycle a structural element of that rocket, known as an EELV Secondary Payload Adapter (ESPA) ring, by converting the ring’s aluminum material into a very large, high-precision antenna reflector. The OrbWeaver™ payload would then attach this large antenna to an array of TUI’s SWIFT® software defined radios launched with the OrbWeaver payload to create a small satellite capable of delivering up to 12 gigabits per second of data to K-band very small aperture terminals (VSAT) on the ground.
The concept of repairing age-related damage to prevent diseases is now mainstream and openly talked about by most acadmics.
Earlier this year the second Scripps Florida Symposium was held and now this open access paper reports on the event. The title of of the event was ‘Advances in Therapeutic Approaches to Extend Healthspan’ and was held on January 22nd–25th, 2017 at The Scripps Research Institute in Jupiter, Florida.
It is once again very refreshing to see that the focus of the researchers here is now firmly on intervening on the various aging processes in order to prevent or treat age-related diseases. Less than a decade ago suggesting addressing the aging processes to treat disease as a preventative form of medicine would have jepordised the chances of funding, or even damaged a researcher’s career prospects. Now the majority of researchers are engaged in exploring the potential of increasing healthspan (the period of life spent free of age-related disease) with the aim of delaying or preventing age-related diseases.
The taboo of talking about doing something about aging
Whilst there is still resistance in academia to talk in public about the potential of these therapies leading to not only healthier but also longer lives, it is nonetheless a step in the right direction. The discussion has changed dramatically in the last decade and the taboo of targeting the aging process has largely been banished, this in our view is a good thing. Only the most conservative scientists cling to the idea that nothing can be done about aging despite the mountains of evidence suggesting otherwise.
We teamed up the MMTP last week and did a special longevity live panel on Facebook with Dr. Aubrey de Grey, Dr. Alexandra Stolzing, Dr. Oliver Medvedik and guests. Check it out.
We teamed up with the MMTP for their “How to Promote Longevity?” Live Panel. Dr. Aubrey de Grey, Dr. Alexandra Stolzing and Dr. Oliver Medvedik and guests discuss the latest research and progess in rejuvenation biotechnology.
“For example, Hasan says, “we can test theoretical ideas in the early universe,” simulating how particles may have behaved just after the Big Bang, when Lorentz symmetry may not have been obeyed.”
It’s interesting how often I hear condensed matter physicists justify their work by saying “might be important for something with quantum gravity” while condensed matter physics by itself is much more likely than quantum gravity to be good for something.
The Evening Standard reviews the new book Radicals whose opening chapter is about transhumanism and my 2016 presidential campaign:
With the apparent collapse of Ukip and the defeat of Marine Le Pen, perhaps those of us fretting about the decline of liberal democracy may breathe easier. Still, many established Western parties remain in decline. And we have yet to deal with the consequences of the “populist” spasms that gave us Brexit and the absurd President Trump. This is the climate that impels Jamie Bartlett, of think tank Demos, to examine some of the new “radicals”.
Radicalism is important, he believes, because it is a source of new ideas: even if liberal democracy is forced to argue with racists or anti-democratic radicals, that should help make it stronger.
He is inevitably selective in his choice of seven different figures or movements, plus the anti-radicalisation work of the Prevent programme: there is an uneasy bracketing of political radicals and wacky futurists.
Thus in the latter group we meet US transhumanist presidential candidate Zoltan Istvan, leader of assorted “biohackers” attempting to merge humans and machines. Bartlett spends time with the Psychedelic Society, organising supervised psilocybin trips; with the German Tamera commune in Portugal, practising free love; and with the scarcely less loopy Vit Jedlicka, founder of a putative libertarian state on the Serbian/Croatian border.