The emirate believes using the technology to conduct its business will make it more efficient and burnish its business-friendly image.
Pocket Doctor
Posted in biotech/medical
Story highlights
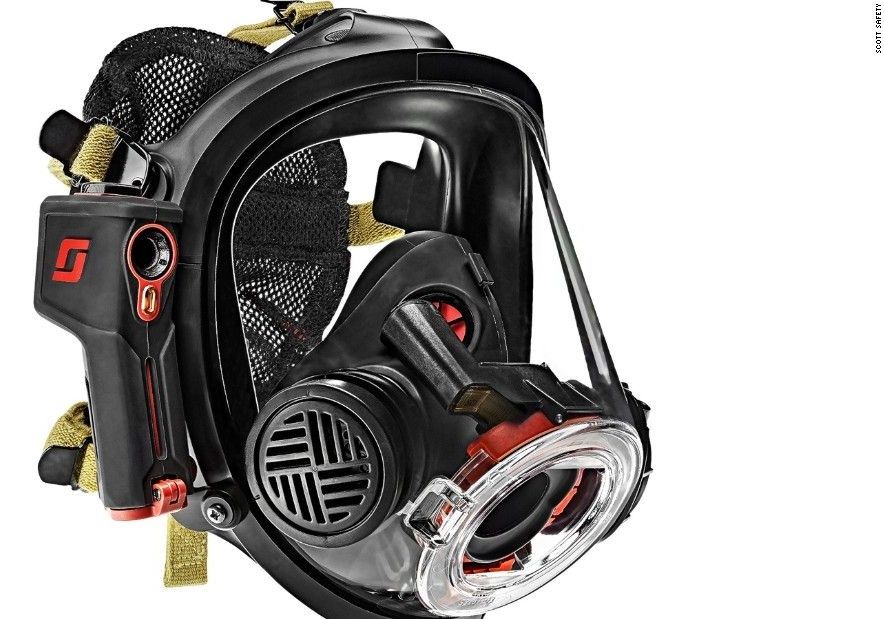
- Smoke can hide unconscious victims from firefighters
- Firefighters have used thermal cameras to locate victims
- New device projects thermal image into firefighters’ masks
What’s the most dangerous thing in a fire?
If you think it’s the flames or the heat, that’s understandable: those are dangerous, too. But both from a victim’s and a firefighter’s perspective, the deadliest enemy is smoke.
Read more
Solar System Size Comparison
Posted in space
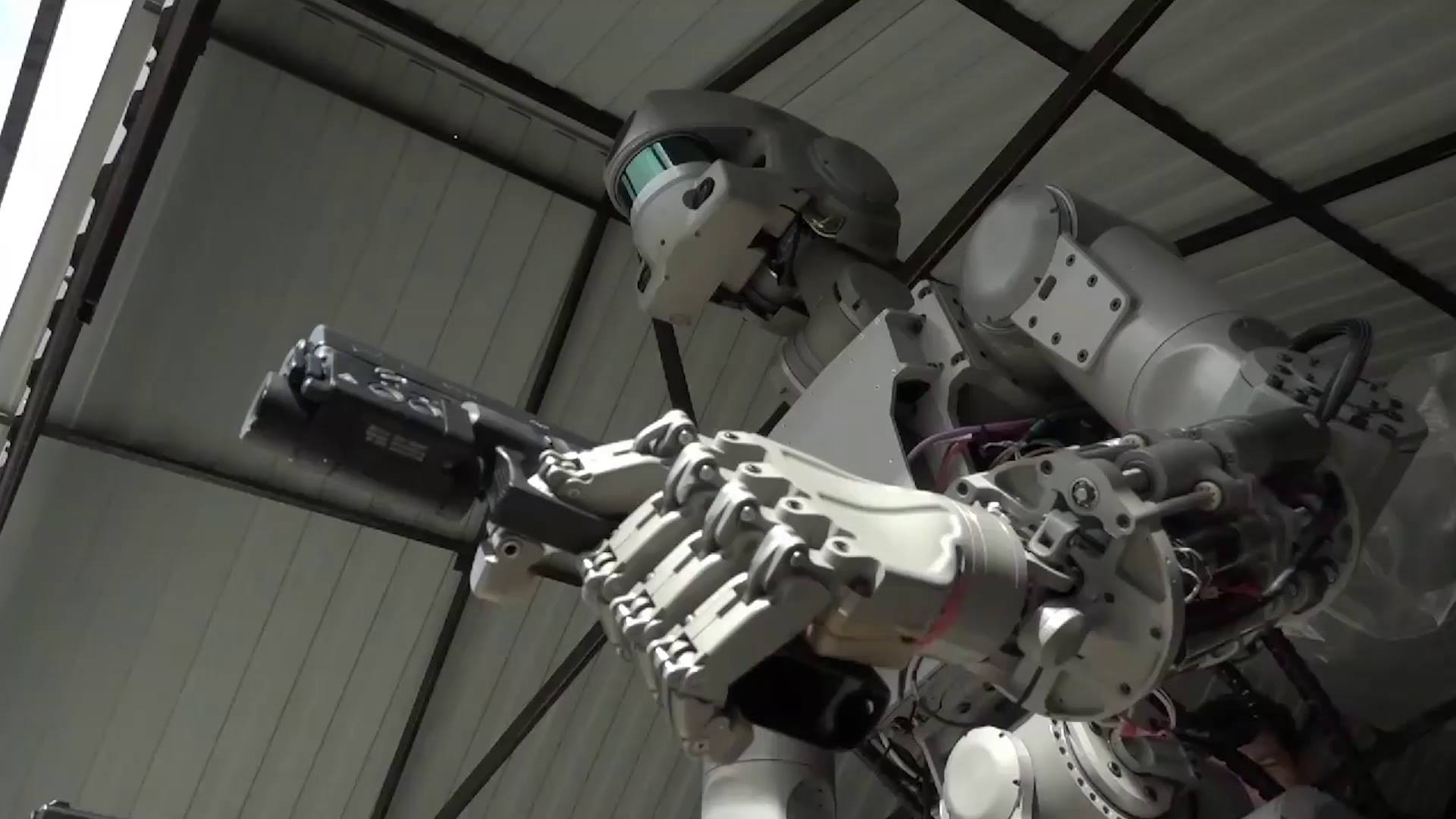
This Russian robot shoots guns
Posted in robotics/AI
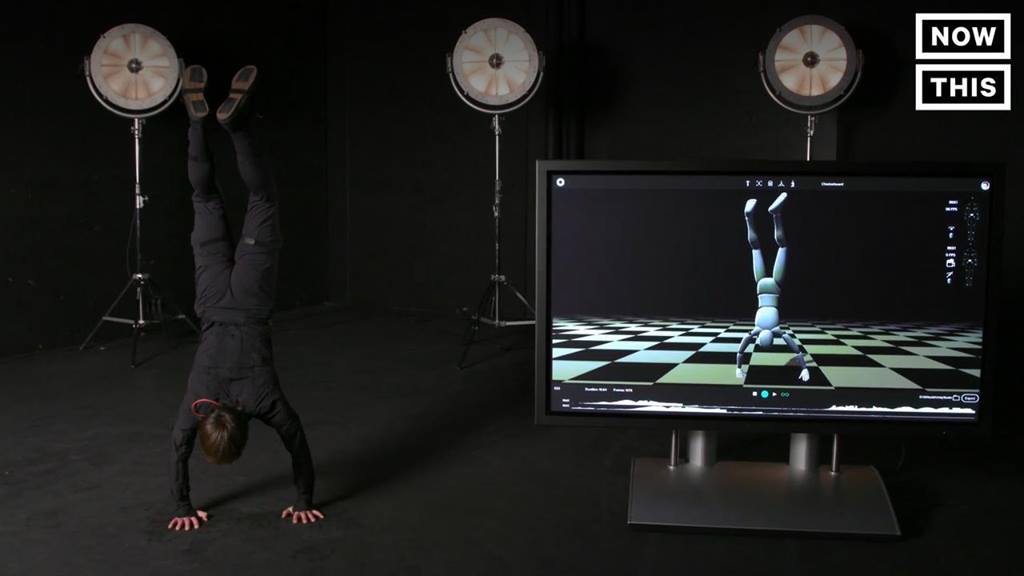
Motion Capture Jumpsuit
Posted in entertainment
Apple Dubai windows
Posted in futurism