Aether collaborating with University College London and Loughborough University to develop 3D printing nanotechnology at a revolutionary low cost.
Erin Abbott [email protected]
Aether collaborating with University College London and Loughborough University to develop 3D printing nanotechnology at a revolutionary low cost.
Erin Abbott [email protected]
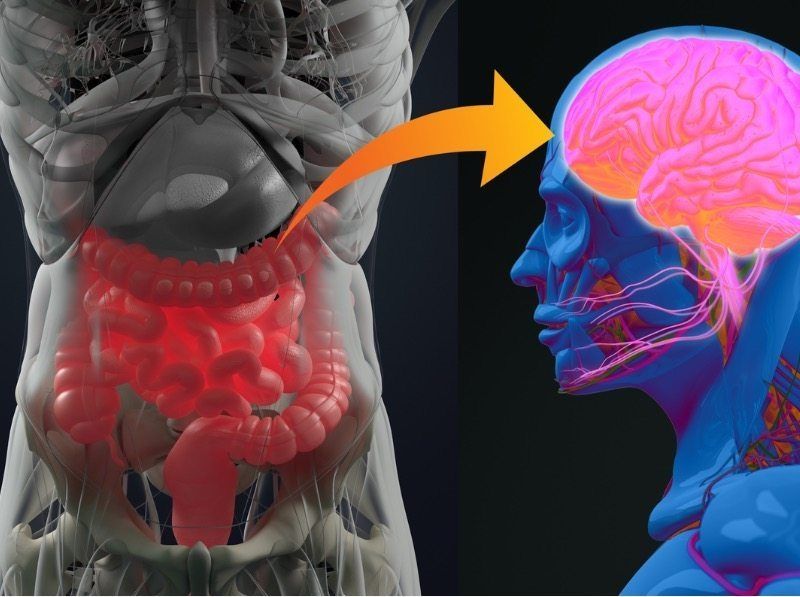
Food additives known as dietary emulsifiers, commonly found in processed foods to improve texture and extend shelf life, may adversely affect anxiety-related and social behaviors in mice, Georgia State researchers have found.
The scientists also observed sex differences in the mice’s behavioral patterns, suggesting that emulsifiers affect the brain via distinct mechanisms in males and females.
The study, published in Scientific Reports, was led by Geert de Vries, professor of neuroscience and associate vice president for research at Georgia State, and Benoit Chassaing, assistant professor of neuroscience. Andrew T. Gewirtz, professor in the Institute for Biomedical Sciences, also contributed.

Few people remember that the Panama Canal started out as a world-cringing disaster, with the French Company spending over $287 million and causing more than 20,000 deaths, before throwing in the towel and filing for bankruptcy. Again, this set the stage for a far more successful effort led by the U.S. that followed.
But what happens when we no longer fail forward? Or what if there are too many failures all at once?
We are more dependent on technology today, than ever before in history. And it’s rather obvious, as this trend continues, that we will use more technology in the future than we do today.


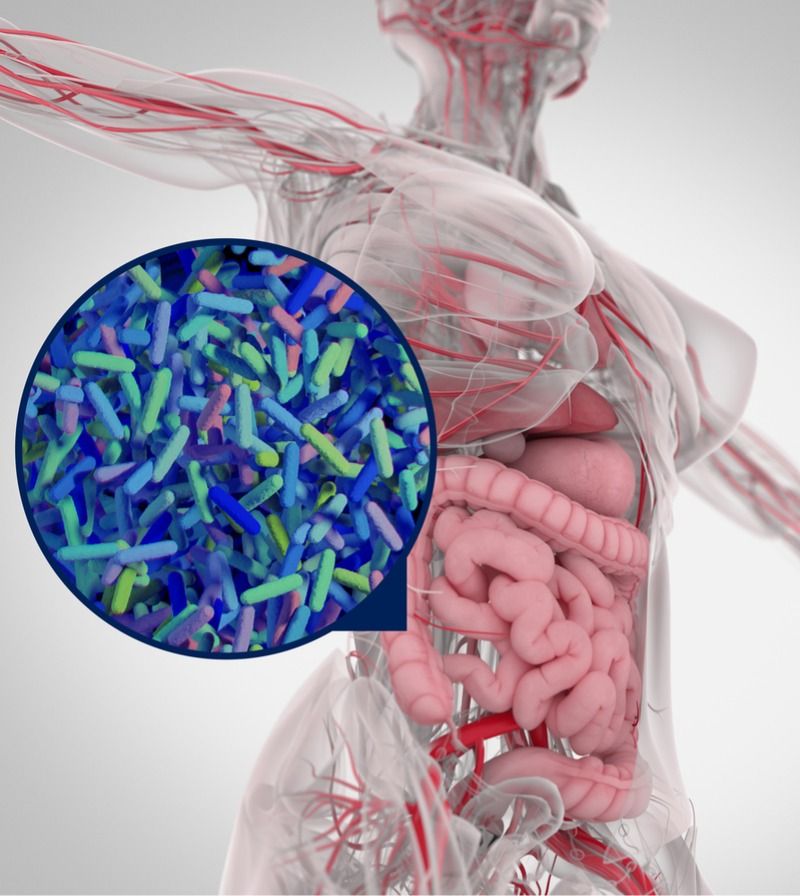
A new study has outlined the age-related changes of the gut microbiome, showing a correlation between the microbiome’s composition and overall health.
The gut microbiome
The microbiome describes a varied community of bacteria, archaea, eukarya, and viruses that inhabit our gut. The four bacterial phyla of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria comprise 98% of the intestinal microbiome.

https://paper.li/e-1437691924#/
We’ll likely see a rise in internet blackouts in 2019, for two reasons: countries deliberately “turning off” the internet within their borders, and hackers disrupting segments of the internet with distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Above all, both will force policymakers everywhere to reckon with the fact that the internet itself is increasingly becoming centralized — and therefore increasingly vulnerable to manipulation, making everyone less safe.
From a report: The first method — states deliberately severing internet connections within their country — has an important history. In 2004, the Maldivian government caused an internet blackout when citizens protested the president; Nepal similarly caused a blackout shortly thereafter. In 2007, the Burmese government apparently damaged an underwater internet cable in order to “staunch the flow of pictures and messages from protesters reaching the outside world.” In 2011, Egypt cut most internet and cell services within its borders as the government attempted to quell protests against then-President Hosni Mubarak; Libya then did the same after its own unrest.
In 2014, Syria had a major internet outage amid its civil war. In 2018, Mauritania was taken entirely offline for two days when undersea submarine internet cables were cut, around the same time as the Sierra Leone government may have imposed an internet blackout in the same region. When we think about terms like “cyberspace” and “internet,” it can be tempting to associate them with vague notions of a digital world we can’t touch. And while this is perhaps useful in some contexts, this line of thinking forgets the very real wires, servers, and other hardware that form the architecture of the internet. If these physical elements cease to function, from a cut wire to a storm-damaged server farm, the internet, too, is affected. More than that, if a single entity controls — or can at least access — that hardware for a region or even an entire country, government-caused internet blackouts are a tempting method of censorship and social control.


Some people on his communications staff at the time were not pleased.
Sims writes that he was “getting antsy” in the room due to Trump’s abrupt question shortly before a televised phone call with the Space Station. NASA officials were believed to have gone to great lengths to coordinate with the Space Station, which could only be reached during a certain time due to “orbital mechanics.”
“All I could think about was that we had to be on camera in three minutes … And yet we’re in here casually chatting about shaving a full decade off NASA’s timetable for sending a manned flight to Mars,” Sims reportedly wrote. “And seemingly out of nowhere.”
Trump, who appeared “distracted,” reportedly asked Lightfoot: “But what if I gave you all the money you could ever need to do it?”

Last year, the FDA announced a whole bunch of recalls related to blood pressure medication over fears that an impurity created during the manufacturing process could lead to cancer. The compound in question was found in dozens of prescription medications that contained the active ingredient valsartan, prompting several distributors and manufacturers to issue voluntary recalls affecting countless heart patients.
Now, additional medications containing a similar blood pressure drug, irbesartan, have been found to contain the same impurity, and a new round of recalls is upon us. Solco Healthcare LLC is now asking anyone with potentially contaminated medication to stop taking the drug.