May 13, 2016
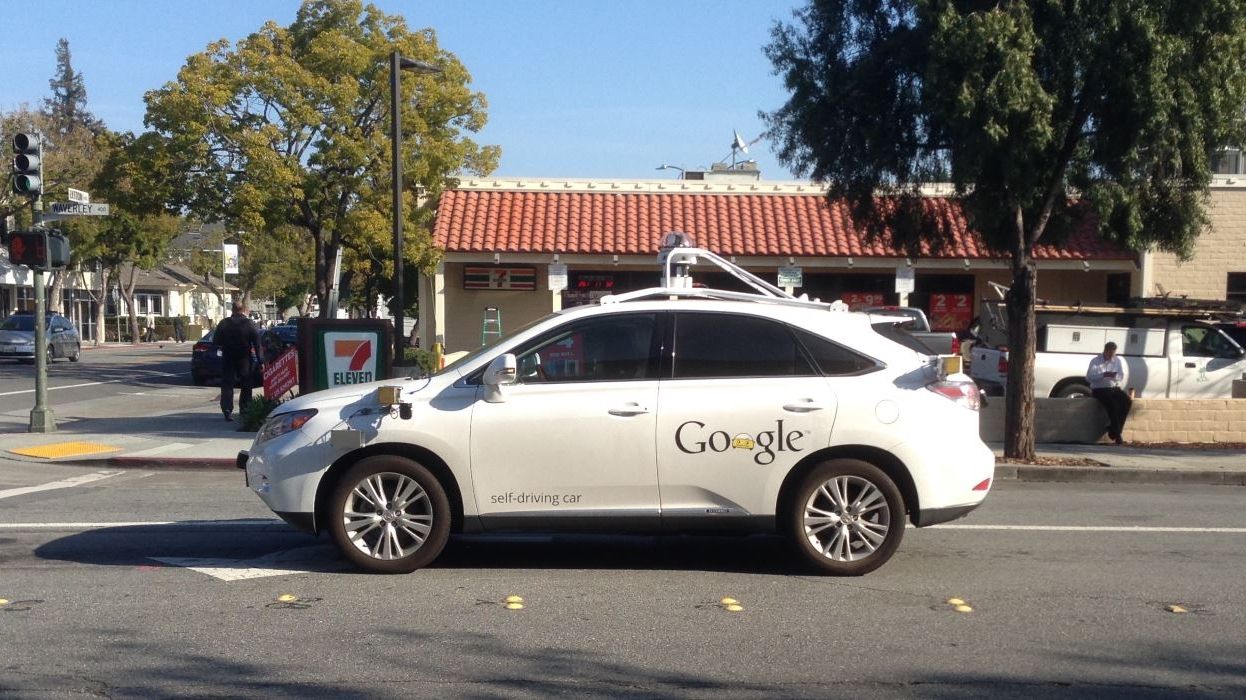
Google will pay people $40,000 a year not to drive their self driving cars
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: robotics/AI, transportation
Thinking about a change of career? Google’s got a heck of a job offer for you. They’ll potentially pay up to $40,000 a year for you to not drive one of their autonomous cars. That’s based on base pay for $20 per hour working full time hours (40 hours a week).
There has to be some kind of catch, you say? Of course there is. Google isn’t just planning on throwing money at people to ride around with an AI chauffeur while sucking on slurpees and binge-watching Netflix from the non-driver’s seat.
No, you’ll actually have to pay attention. Google’s cars have logged plenty of hours on real roads, but there are still going to be times when the car doesn’t know how to handle a situation — say, sharing a narrow section of road with an oncoming bus. Since there’s no way of knowing when you’ll need to lend a helping hand (or foot), you need to be ever vigilant behind the wheel.
Continue reading “Google will pay people $40,000 a year not to drive their self driving cars” »