I’m cheating.
Found this book. It was written in 1968.
Oh how things change.
4/5 down.

This technology may someday power spacecraft, satellites, high-flying drones, and pacemakers.
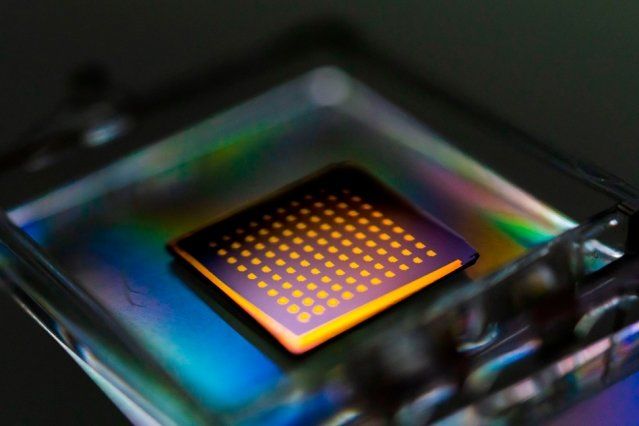

For businesses that want to maintain or increase their bottom line, this means re-engineering the fundamentals of their supply chain by developing or adopting new material solutions that achieve a lot more with a lot less.
“The smart companies, manufacturers and brands are the ones who are starting to invest in sustainable material innovation,” says Caroline Till, co-author of Radical Matter: Rethinking Materials for a Sustainable Future, adding, “There’s a thirst from consumers for this.” It’s clear that tomorrow’s leaders will be those who are brave enough to invest in this research today.
For The Future Laboratory’s new Material Far Futures report, we’ve compiled the most transformative case studies in material innovation into the 10 paradigms that we believe will disrupt industry in the coming decades, each with original visualisations from Studio Brasch. From fabrics that generate power through motion and new forms of kinetic architecture to bio-engineering’s impact on luxury fashion, the materials of tomorrow will be smarter, stronger, more dynamic and, crucially, less ecologically damaging.

United Launch Alliance, Northrup Grumman and Blue Origin, a company owned by Amazon-founder Jeff Bezos, were awarded major Air Force contracts Wednesday totaling more than $2 billion to develop next-generation rockets capable of boosting high-value national security payloads into orbit.
Two of the new rockets will be selected in a second competition, providing assured access to space through the next decade and beyond. In a surprise to some observers, SpaceX, the ambitious rocket company founded by Elon Musk, was not among the latest winners in the Pentagon’s Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle program.
The Launch Service Agreements “will facilitate the development of three domestic launch system prototypes and enable the future competitive selection of two National Security Space launch service providers for future procurements, planned for no earlier than fiscal year 2020,” the Air Force said in a statement.
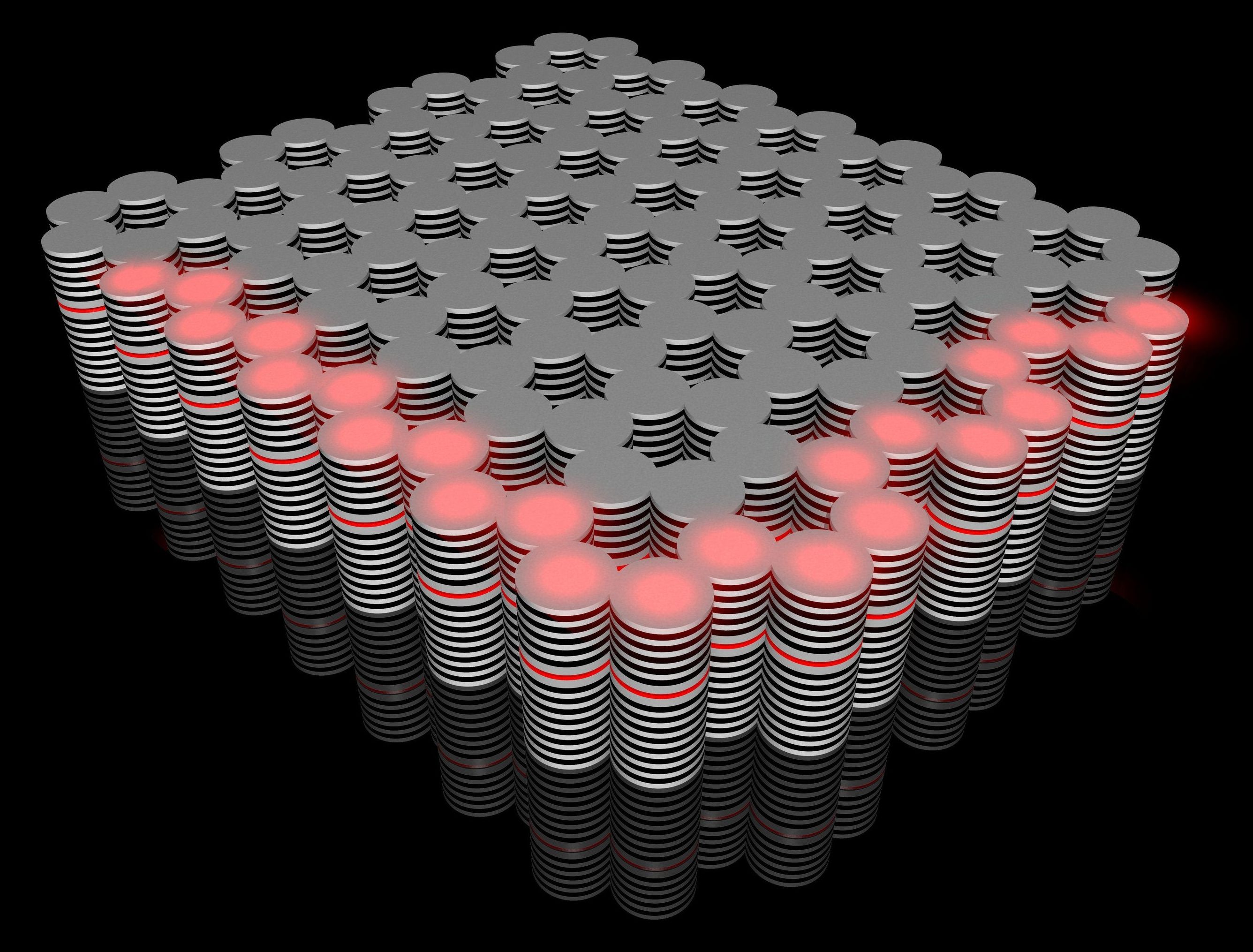
For the first time, physicists have built a unique topological insulator in which optical and electronic excitations hybridize and flow together. They report their discovery in Nature.
Topological insulators are materials with very special properties. They conduct electricity or light particles only on their surface or edges, not the interior. This unusual characteristic could provide technical innovations, and topological insulators have been the subject of intense global research for several years.
Physicists of Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU) in Bavaria, Germany, with colleagues from the Technion in Haifa, Israel, and Nanyang Technological University in Singapore have reported their discovery in the journal Nature. The team has built the first “exciton-polariton topological insulator,” a topological insulator operating with both light and electronic excitations simultaneously.
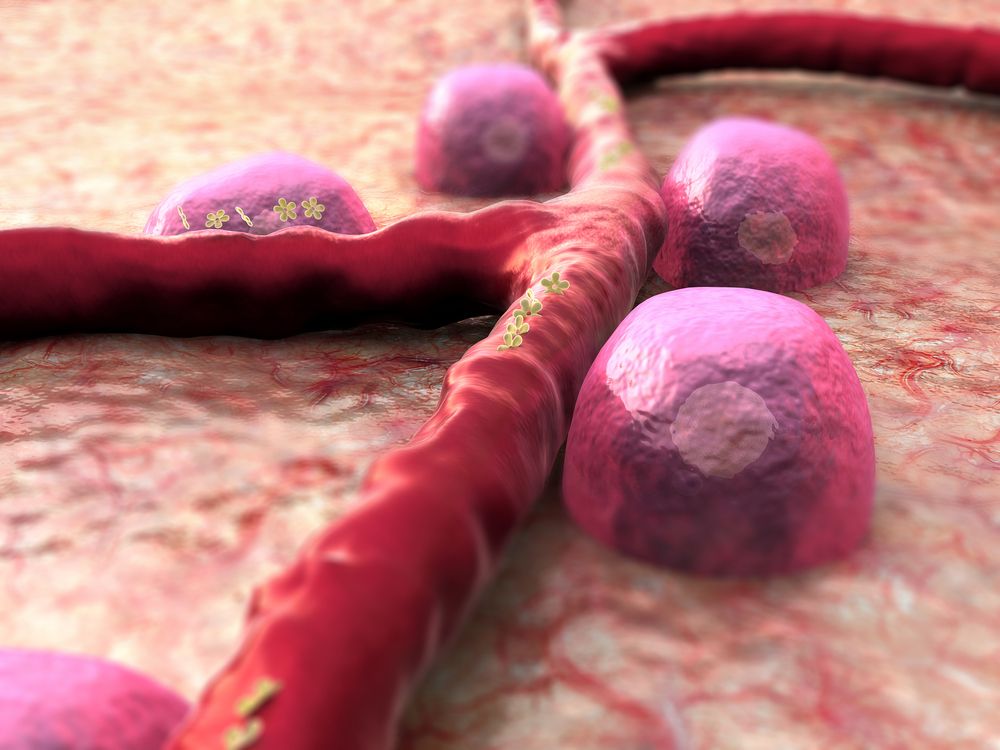
Scientists at Lund University, Sweden showed that it is possible to prevent type 2 diabetes in mice by inhibiting a protein known as VDAC1. This inhibitor might be employed in treating this disease in humans [1].
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) develops after years of prediabetes during which high glucose (glucotoxicity) impairs insulin secretion. We report that the ATP conducting mitochondrial outer membrane voltage dependent anion channel-1 (VDAC1) is upregulated in islets from T2D and non-diabetic organ donors under glucotoxic conditions. This is caused by a glucotoxicity-induced transcriptional program, triggered during years of prediabetes with suboptimal blood glucose control. Metformin counteracts VDAC1 induction. VDAC1 overexpression causes its mistargeting to the plasma membrane of the insulin secreting β cells with loss of the crucial metabolic coupling factor ATP. VDAC1 antibodies and inhibitors prevent ATP loss. Through direct inhibition of VDAC1 conductance, metformin, like specific VDAC1 inhibitors and antibodies, restores the impaired generation of ATP and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in T2D islets.

China has included 17 life-saving cancer drugs in its national public insurance after negotiations drastically cut their prices, in response to their cost fuelling the smuggling of cheap drugs from abroad in an echo of the popular Chinese film Dying to Survive.
Costs slashed by over half on average, in wake of hit movie featuring the plight of those unable to afford prohibitively priced medicines and forced to look abroad.
Don’t look now, but Boston Dynamics’ robot Atlas is back. And now it can do parkour: https://wired.trib.al/B2Aai5y