5G means faster video streaming… and stronger surveillance.


A growing number of devices are now connected to the internet and are capable of collecting, sending and receiving data. This interconnection between devices, referred to as the Internet of Things (IoT), poses serious security threats, as cyberattackers can now target computers and smartphones, but also a vast array of other devices, such as tablets, smart watches, smart home systems, transportation systems and so on.
For the time being, examples of large-scale IoT implementations (e.g. connected infrastructure, cities, etc.) are somewhat limited, yet they could soon become widespread, posing significant risks for businesses and public services that heavily rely on the internet in their daily operations. To mitigate these risks, researchers have been trying to develop security measures to protect devices connected to the internet from wireless network attacks.
To this end, two researchers at Baoji University of Arts and Sciences, in China, have recently developed a new method to defend devices in an IOT environment from wireless network attacks. Their approach, presented in a paper published in Springer’s International Journal of Wireless Information Networks, combines a deep neural network with a model based on game theory, a branch of mathematics that proposes strategies for dealing with situations that entail competition between different parties.
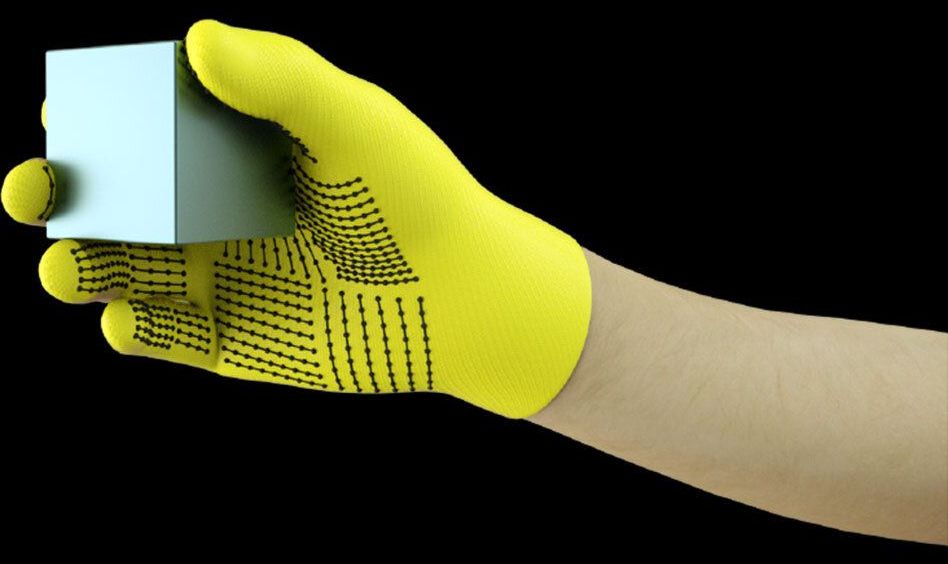
Wearing a sensor-packed glove while handling a variety of objects, MIT researchers have compiled a massive dataset that enables an AI system to recognize objects through touch alone. The information could be leveraged to help robots identify and manipulate objects, and may aid in prosthetics design.
The researchers developed a low-cost knitted glove, called “scalable tactile glove” (STAG), equipped with about 550 tiny sensors across nearly the entire hand. Each sensor captures pressure signals as humans interact with objects in various ways. A neural network processes the signals to “learn” a dataset of pressure-signal patterns related to specific objects. Then, the system uses that dataset to classify the objects and predict their weights by feel alone, with no visual input needed.
In a paper published in Nature, the researchers describe a dataset they compiled using STAG for 26 common objects—including a soda can, scissors, tennis ball, spoon, pen, and mug. Using the dataset, the system predicted the objects’ identities with up to 76 percent accuracy. The system can also predict the correct weights of most objects within about 60 grams.


A team of bioengineers has successfully 3D-printed tissues they believe doctors could one day implant into patients to help heal the knee, ankle, and elbow injuries that have ended the careers of countless athletes.
“I think this will be a powerful tool to help people with common sports injuries,” Rice University researcher Sean Bittner said in a press release — though the impact of the group’s work could extend far beyond the turf or pitch.
Neutron stars are born after supernovas, an implosion that compresses an object the size of the sun to about the size of Montreal, making them “a hundred trillion times denser than anything on earth.” Their immense gravity makes their outer layers freeze solid, making them similar to earth with a thin crust enveloping a liquid core.
This will help provide better understand gravitational waves like those detected last year when two neutron stars collided. The new results even suggest that lone neutron stars might generate small gravitational waves.

10(Z)-hexadecenoic acid, a fatty acid found in the soil based bacterium Mycobacterium vaccae, interacts with immune cells to inhibit pathways that drive inflammation and increases resilience to stress. Researchers say the findings could bring us one step closer to developing a microbe-based “stress vaccine”.
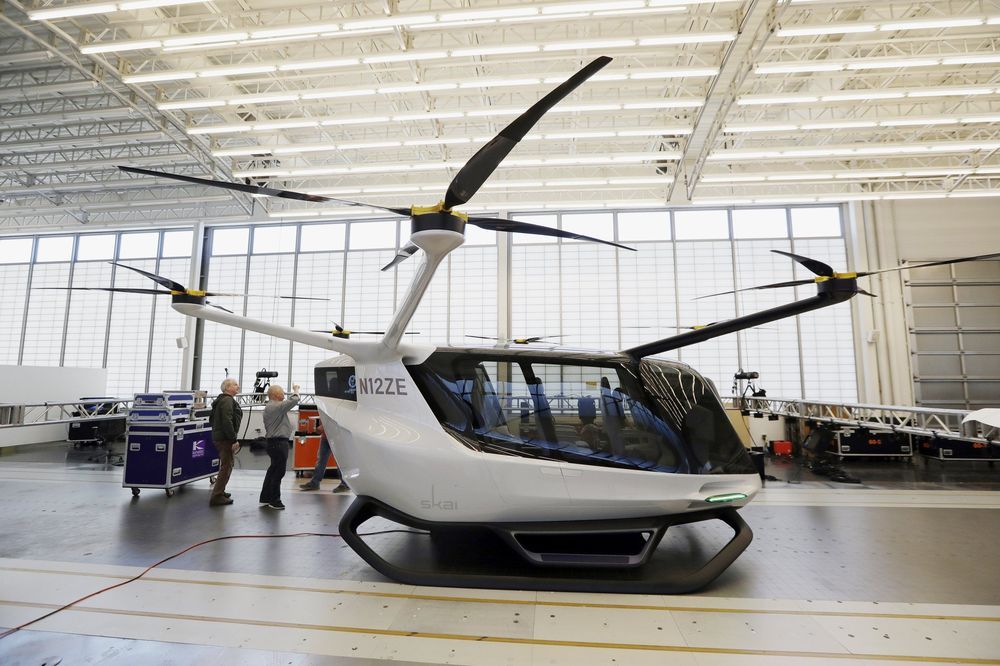


LOS ANGELES (AP) — A transportation company is betting its sleek new hydrogen-powered electric flying vehicles will someday serve as taxis, cargo carriers and ambulances of the sky, but experts say they will have to clear a number of regulatory hurdles before being approved for takeoff years in the future.
With six rotors on the roof and seats inside for five people, a passenger model of the Skai (pronounced “sky”) unveiled Wednesday near Los Angeles resembles an oversized drone crossed with a luxury SUV.
Like a drone, the vehicle from Alaka’i Technologies takes off and lands vertically. It’s one of many similar electric flying crafts in production, including prototypes from Boeing and Airbus that made successful test flights this year, according to Vertical Flight Society, an industry group.