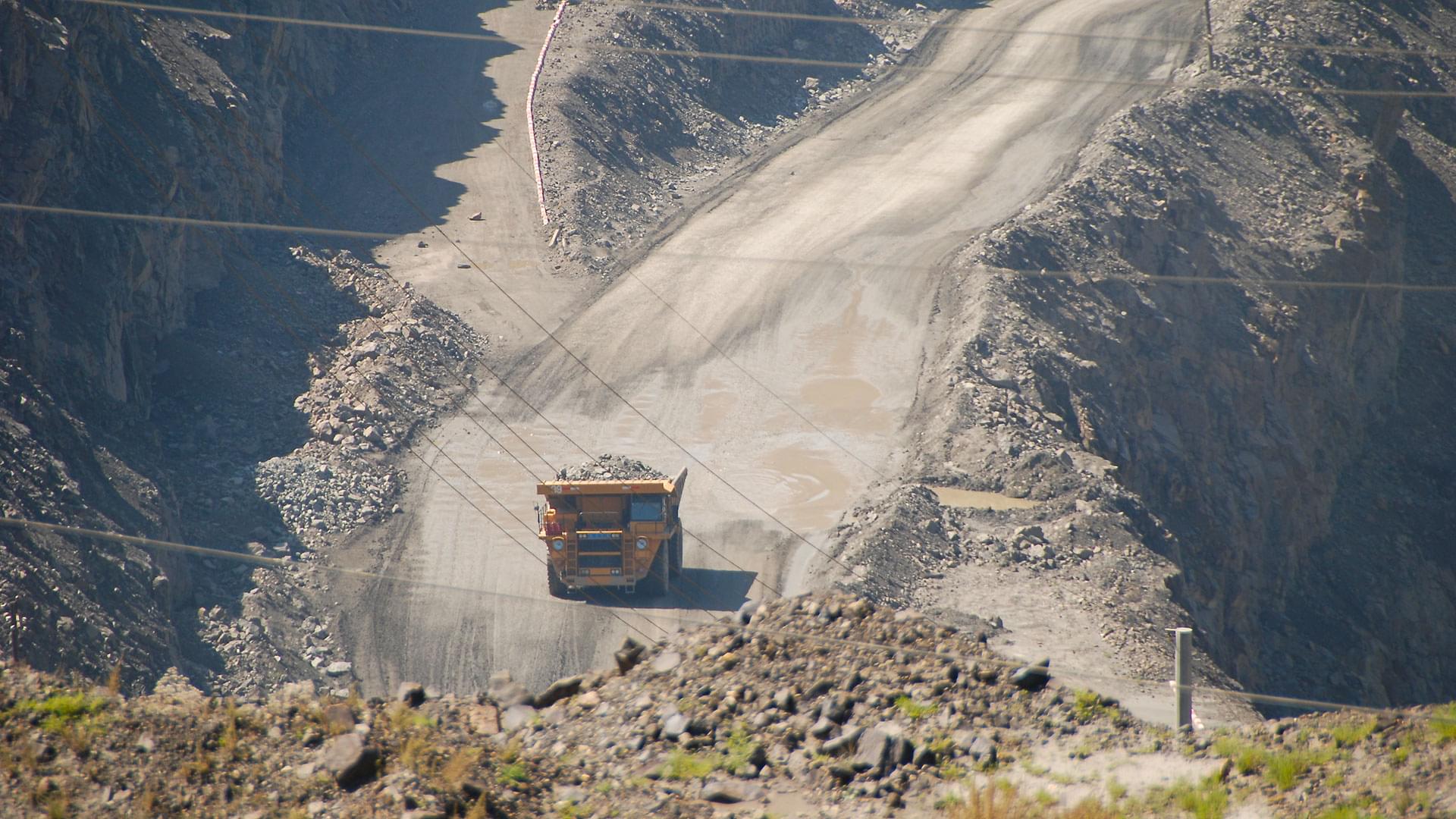
Previous measures meant all exporters faced lengthy approval processes.


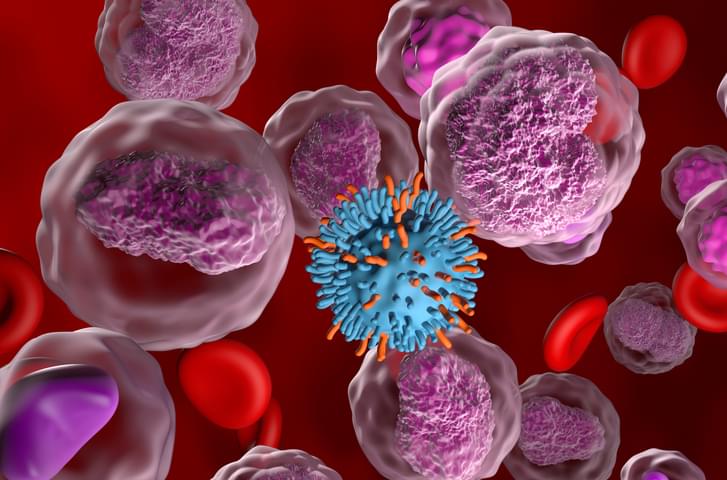
High manufacturing costs are limiting patient access to CAR T cell therapies, according to new research, which indicates that decentralization, vector-free modification technologies, and AI would help make production cheaper.
Making CAR T therapies is an expensive business. A recent study suggested that producing a single batch can cost anywhere between $170,000 and $220,000, depending on the logistical, processing, and distribution steps involved.
The fundamental problem is that CAR T production is not a good fit for centralized manufacturing, according to Martin Bonamino, PhD, leader of the experimental cancer immunotherapy group at Brazil’s National Cancer Institute (INCA).
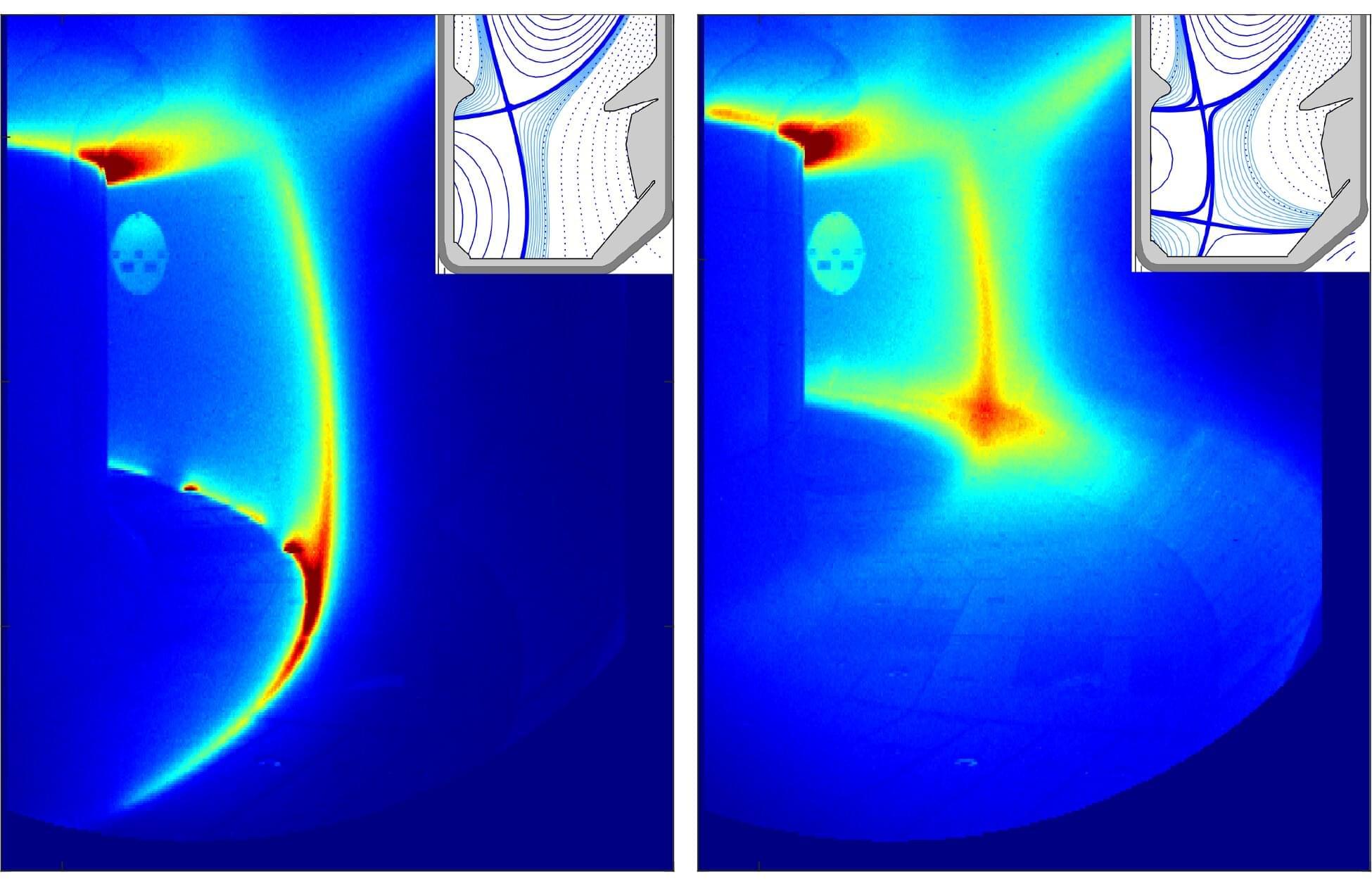
Nuclear fusion reactors are highly powerful technologies that can generate energy by fusing (i.e., joining) two light atomic nuclei to form a heavier nucleus. These fusion reactions release large amounts of energy, which can then be converted into electrical power without emitting greenhouse gases.
One of the most reliable and promising fusion reactor designs is the so-called tokamak. Tokamaks are devices that use a doughnut-shaped magnetic field to confine and heat plasma (i.e., superhot, electrically charged gas) for the time necessary for fusion reactions to take place.
Despite their potential for the generation of large amounts of clean energy, future reactor tokamaks may face huge challenges in managing the intense heat produced by fusion reactions. Specifically, some of the confined plasma can interact with the walls of the reactors, damaging them and adversely impacting both their durability and performance.
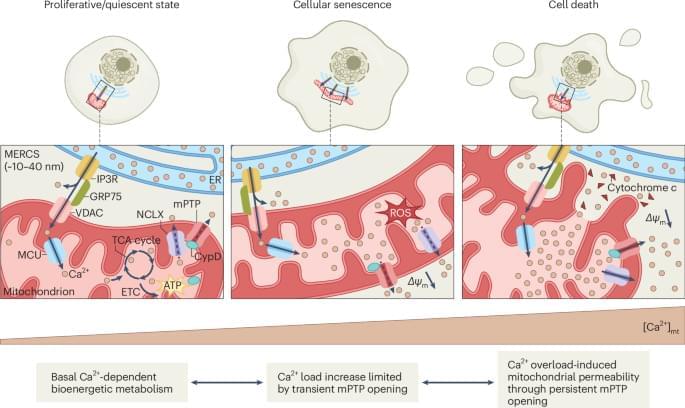
Manipulating senescent cells by eliminating them or by modifying their activity has attracted huge interest for its potential to delay or even treat many age-related diseases, and to improve healthy aging. Mitochondria, and in particular their calcium levels, have emerged as key regulators of cellular senescence, cell death and the balance between the two, and might constitute targets for novel strategies to stifle the viability or properties of senescent cells.
Click this link https://sponsr.is/bootdev_mattbatwings and use my code MATTBATWINGS to get 25% off your first payment for boot.dev.
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/mattbatwings.
Discord: https://discord.gg/V5KFaF63mV
My socials: https://linktr.ee/mattbatwings.
My texture pack: https://modrinth.com/resourcepack/mattpack.
World Download: (JAVA 1.21) https://www.planetminecraft.com/project/3d-maze-explorer/
Oscar’s 3D Maze Program: https://youtu.be/2hdc0Fn302w.
Thanks again to @captainluma7991 for working with me on this!
Want to get more involved in the logical redstone community?
Learn Logical Redstone! https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PL5LiOvrbVo8keeEWRZVaHfprU4zQTCsV4
Open Redstone Engineers (ORE): https://openredstone.org/
0:00 Intro.
0:32 Oscar91
1:48 Generalization.
2:59 Display.
4:53 Maze to Tilemap Conversion.
6:12 Maze Exploration.
7:51 Wireframe Display.
8:27 Random Generation.
Music (in order):
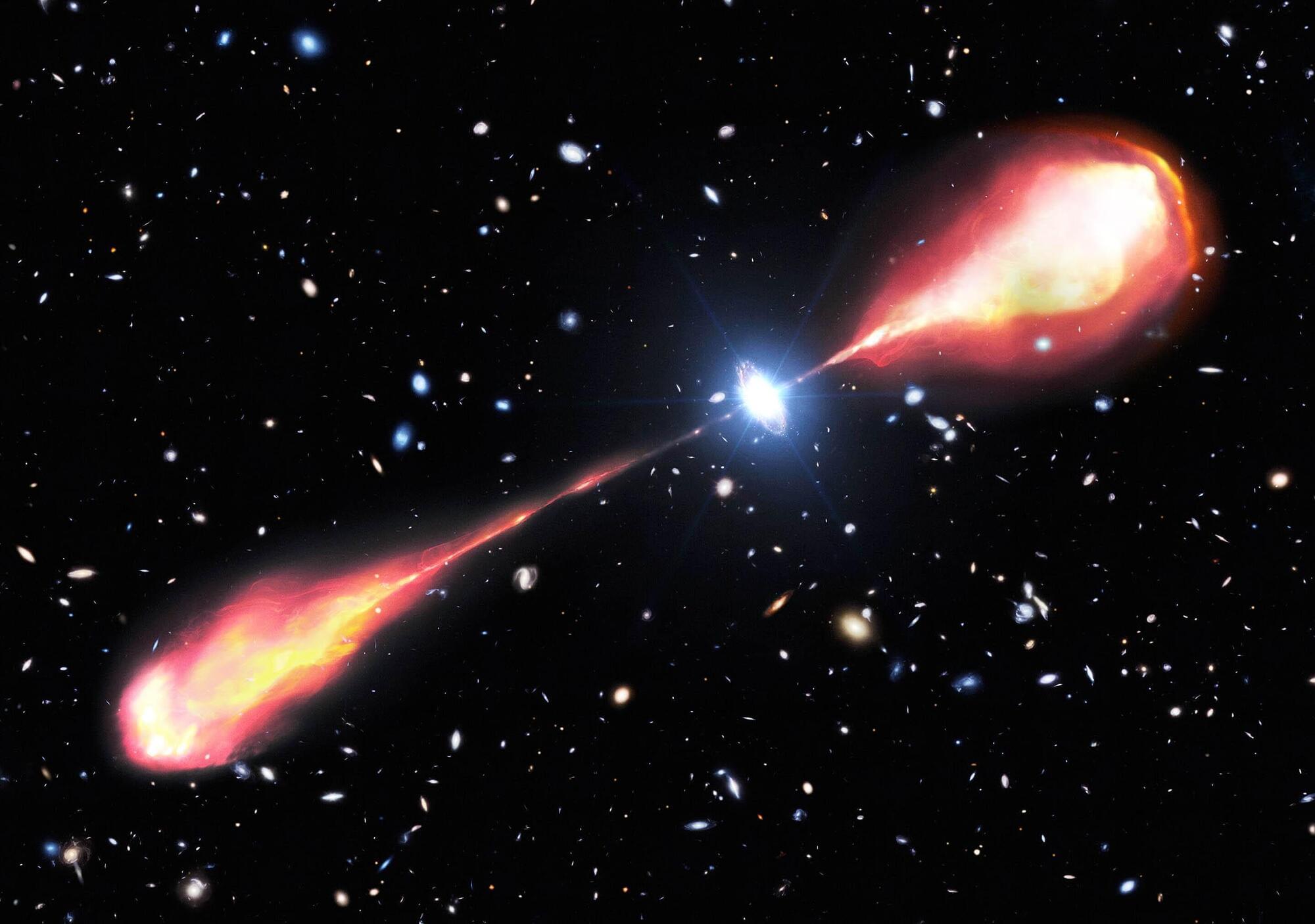




That hurdle has now been cleared. A newly analyzed radio image reveals twin lobes stretching roughly 66,000 light-years on each side of a quasar called J1601+3102.
Because the radio waves began their trip across space more than 12.1 billion years ago, the observation shows the quasar as it was when the universe had completed only about nine percent of its history.
This particular quasar, J1601+3102, belongs to a youthful universe – it flared into view when the cosmos was less than 1.2 billion years old.
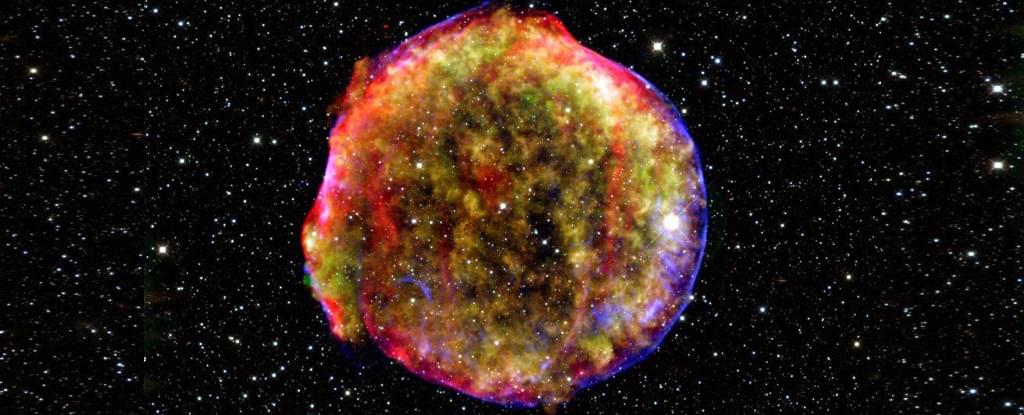

Somewhere in our galaxy are engines capable of driving atomic fragments to velocities that come within a whisker of lightspeed.
The explosive deaths of stars seems like a natural place to search for sources of these highly energetic cosmic bullets, yet when it comes to the most powerful particles, researchers have had their doubts.
Numerical simulations by a small international team of physicists may yet save the supernova theory of cosmic ray emissions at the highest of energies, suggesting there is a brief period where a collapsing star could still become the Universe’s most extreme accelerator.