From Academy Award-winning director Alex Gibney comes a documentary about the rise and fall of Theranos, the one-time multibillion-dollar healthcare company founded by Elizabeth Holmes. Premieres March 18 on HBO.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
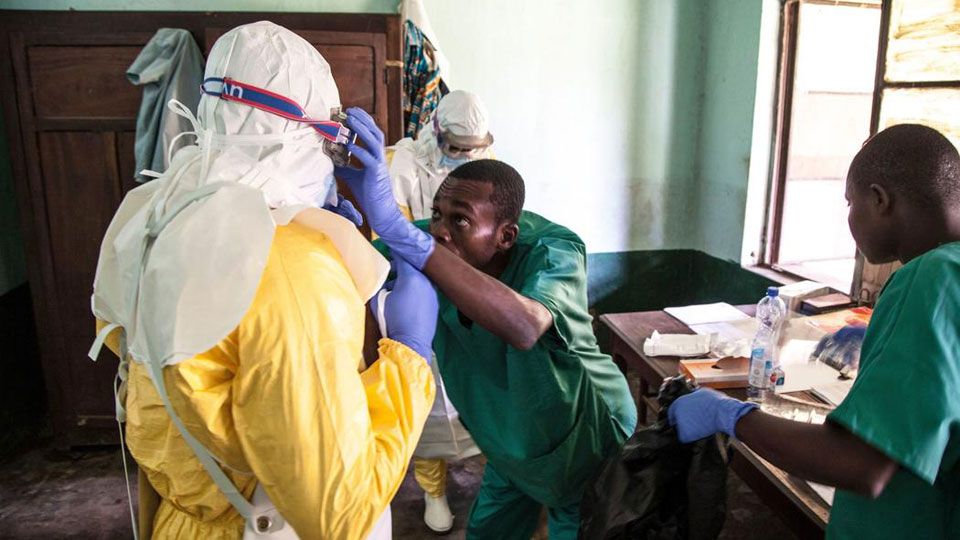
Ebola confirmed in a city of more than 1 million in Congo
JOHANNESBURG (AP) — The global health community gulped Thursday with the announcement that a case of Ebola had been confirmed in a city of more than 1 million in Congo, bringing the latest outbreak of the often deadly hemorrhagic fever out of remote rural areas. “Confirmation of urban #Ebola in #DRC is a game changer in this outbreak – the challenge just got much much tougher,” the World Health Organization’s emergencies chief, Dr. Peter Salama, said on Twitter. Here’s a look at the outbreak.
What is Ebola?
Ebola is a virus that without preventive measures can spread quickly between people and is fatal in up to 90 percent of cases. The symptoms include fever, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle pain and at times internal and external bleeding. Symptoms can start to occur between two and 21 days from infection, according to WHO.

TR-3B Anti-Gravity Spacecrafts
It doesn’t exist officially. It uses highly pressured mercury accelerated by nuclear energy to produce a plasma that creates a field of anti-gravity around the ship. Conventional thrusters located at the tips of the craft allow it to perform all manner of rapid high speed maneuvers along all three axes. Interestingly, the plasma generated also reduces radar signature significantly. So it’ll be almost invisible on radar & remain undetected. This literally means that it can go to any country it likes without being detected by air traffic control & air defence systems.



Effect of low-level laser therapy on mesenchymal stem cell proliferation: a systematic review
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) has been used in several in vitro experiments in order to stimulate cell proliferation. Cells such as fibroblasts, keratinocytes, lymphocytes, and osteoblasts have shown increased proliferation when submitted to laser irradiation, although little is known about the effects of LLLT on stem cells. This study aims to assess, through a systematic literature review, the effects of LLLT on the in vitro proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells. Using six different terms, we conducted an electronic search in PubMed/Medline database for articles published in the last twelve years. From 463 references obtained, only 19 papers met the search criteria and were included in this review. The analysis of the papers showed a concentration of experiments using LLLT on stem cells derived from bone marrow, dental pulp, periodontal ligament, and adipose tissue. Several protocols were used to irradiate the cells, with variations on wavelength, power density, radiation time, and state of light polarization. Most studies demonstrated an increase in the proliferation rate of the irradiated cells. It can be concluded that the laser therapy positively influences the in vitro proliferation of stem cells studied, being necessary to carry out further experiments on other cell types and to uniform the methodological designs.
New single vaccination approach to killer diseases
Scientists from the University of Adelaide’s Research Centre for Infectious Diseases have developed a single vaccination approach to simultaneously combat influenza and pneumococcal infections, the world’s most deadly respiratory diseases.
The researchers say a single vaccination—combining vaccines from the new class of vaccines they are developing—will overcome the limitations of current influenza and pneumococcal vaccines used around the world.
Published today in the prestigious journal Nature Microbiology, they have shown that the new Influenza A virus vaccine under development (based on inactivated whole influenza virus) induces enhanced cross-protective immunity to different influenza strains, when it is co-administrated with the new class of pneumococcal vaccine.
