IBM’s Hello Quantum released on Android today. If you’ve always wanted to be a quantum computer programmer, this is the puzzle game for you!


Xage (pronounced Zage), a blockchain security startup based in Silicon Valley, announced a $12 million Series A investment today led by March Capital Partners. GE Ventures, City Light Capital and NexStar Partners also participated.
The company emerged from stealth in December with a novel idea to secure the myriad of devices in the industrial internet of things on the blockchain. Here’s how I described it in a December 2017 story:
Xage is building a security fabric for IoT, which takes blockchain and synthesizes it with other capabilities to create a secure environment for devices to operate. If the blockchain is at its core a trust mechanism, then it can give companies confidence that their IoT devices can’t be compromised. Xage thinks that the blockchain is the perfect solution to this problem.


It was a major feature for the #transhumanism and life extension movements, seen by likely millions of people because it was translated into various languages via international syndication. Story by Richard Godwin. https://www.thetimes.co.uk/article/zoltan-istvan-the-poster-…-lrbx66lqn

Aging may be regulated by a discrete set of intracellular proteins including the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) kinase. mTOR functions within two multiprotein complexes called TORC1 and TORC2. Inhibition of TORC1 has extended life span in every species studied to date and ameliorated multiple aging-related pathologies including declining immune function. Mannick et al. now show that low-dose TORC1 inhibitor therapy in elderly humans decreased the incidence of all infections, improved influenza vaccination responses, and up-regulated antiviral immunity. Thus, targeting the TORC1 pathway that regulates aging may have clinical benefits for elderly humans including improvement in immune function and decreased infection rates.
Inhibition of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) protein kinase extends life span and ameliorates aging-related pathologies including declining immune function in model organisms. The objective of this phase 2a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial was to determine whether low-dose mTOR inhibitor therapy enhanced immune function and decreased infection rates in 264 elderly subjects given the study drugs for 6 weeks. A low-dose combination of a catalytic (BEZ235) plus an allosteric (RAD001) mTOR inhibitor that selectively inhibits target of rapamycin complex 1 (TORC1) downstream of mTOR was safe and was associated with a significant (P = 0.001) decrease in the rate of infections reported by elderly subjects for a year after study drug initiation. In addition, we observed an up-regulation of antiviral gene expression and an improvement in the response to influenza vaccination in this treatment group.
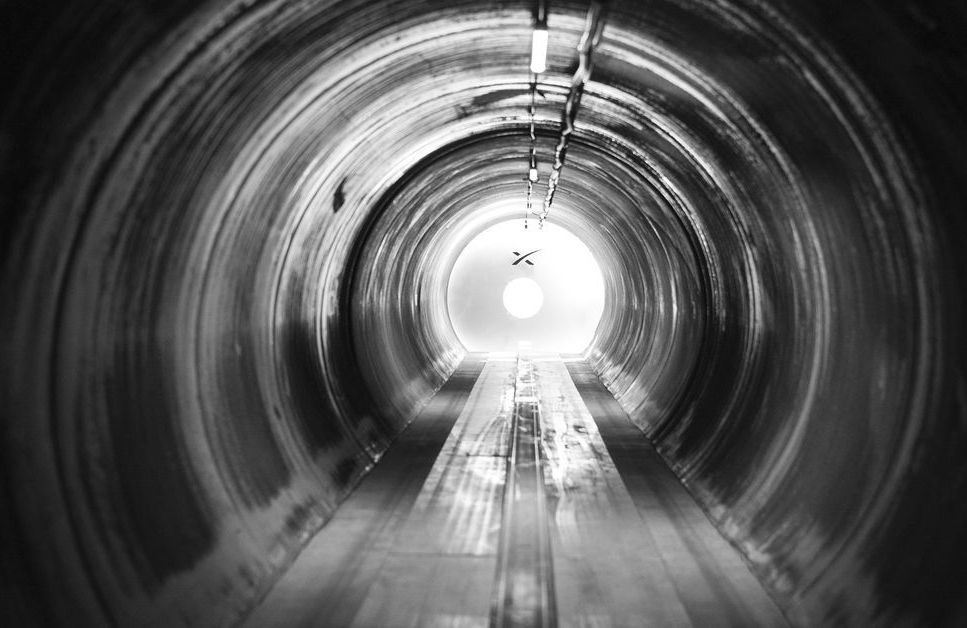

It was a hyperloop hat trick by a team of German engineering students at the third annual SpaceX pod competition on Sunday. WARR Hyperloop from the Technical University of Munich took home the top prize — and set a new record — with their self-propelled pod reaching a top speed of 284 mph (457 km/h).
WARR Hyperloop was one of three finalists to participate in the competition. The teams were tasked with developing a pod to travel down the 1.2-kilometer (0.75-mile) tube, as part of SpaceX CEO Elon Musk’s vision for a futuristic, high-speed transportation system. The pod that reached the maximum speed would be crowned the winner. The only other requirement was that all pods be self-propelled. In addition to WARR, the other qualifying teams were Delft University from the Netherlands and EPF Loop from Switzerland.
The week of July 23 through July 29 is going to be pretty epic when it comes to space happenings. Specifically, stargazers should get excited about several celestial events on July 27, and it’s a great time to get your telescope ready to peer up at the stars on the big night.
Quantum communication and cryptography are the future of high-security communication. But many challenges lie ahead before a worldwide quantum network can be set up, including propagating the quantum signal over long distances. One of the major challenges is to create memories with the capacity to store quantum information carried by light. Researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, in partnership with CNRS, France, have discovered a new material in which an element, ytterbium, can store and protect the fragile quantum information even while operating at high frequencies. This makes ytterbium an ideal candidate for future quantum networks, where the aim is to propagate the signal over long distances by acting as repeaters. These results are published in the journal Nature Materials.
Quantum cryptography today uses optical fibre over several hundred kilometres and is marked by its high degree of security: it is impossible to copy or intercept information without making it disappear.
However, the fact that it is impossible to copy the signal also prevents scientists from amplifying it to diffuse it over long distances, as is the case with the Wi-Fi network.
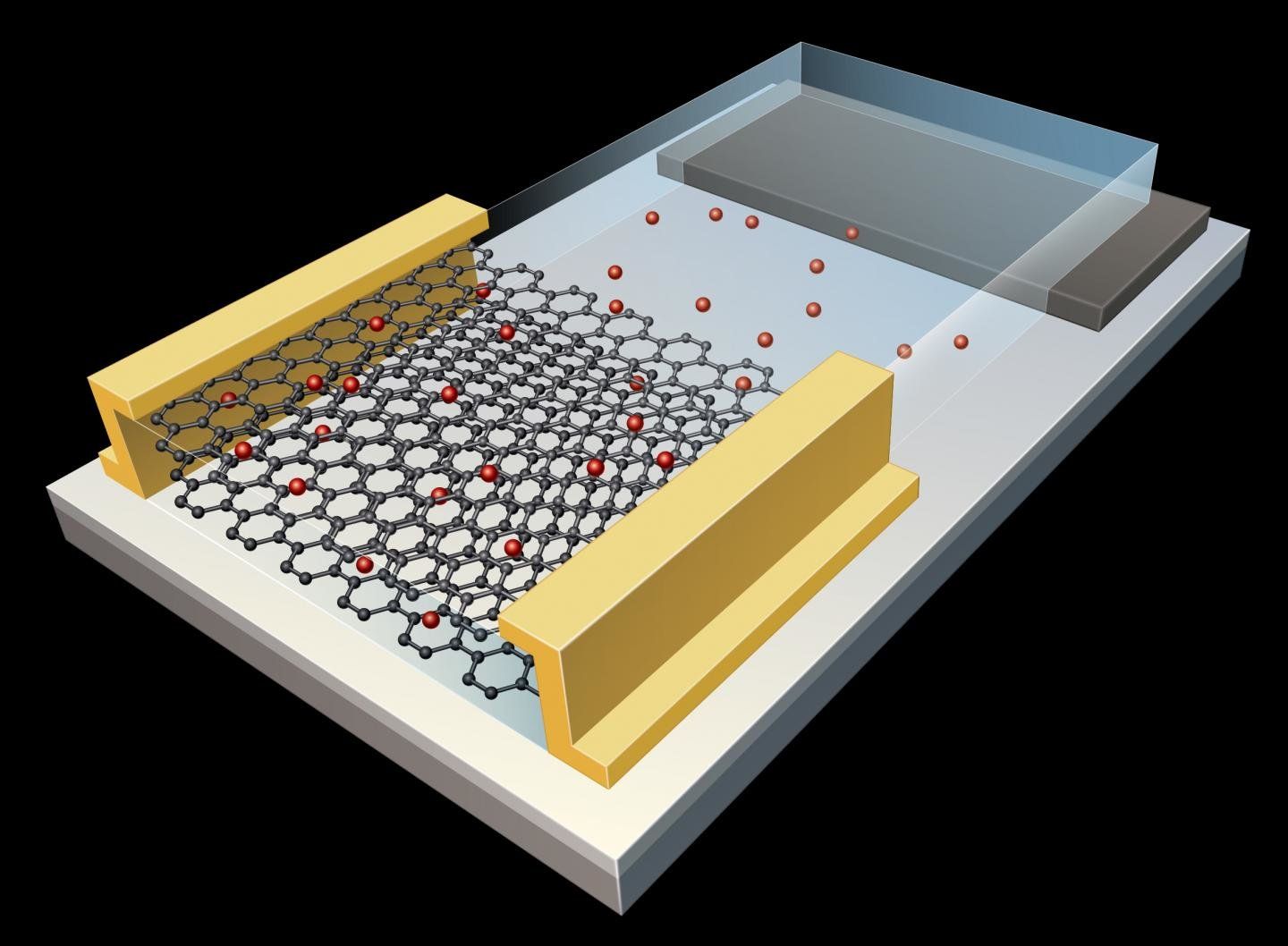
The latest robots out of MIT are small enough to float “indefinitely” in the air. Researchers accomplished the feat by attaching 2D electronics to colloids — tiny particles measuring around one-billionth to one-millionth of a meter. All told, the devices are roughly the size of a human egg cell.
What’s more, the addition of photodiode semiconductors means the tiny individual systems are able to be self-powered, without the need for a battery. The system converts light into a small electrical charge that’s enough to keep the device’s on-board environmental sensors running, while storing on-board information.