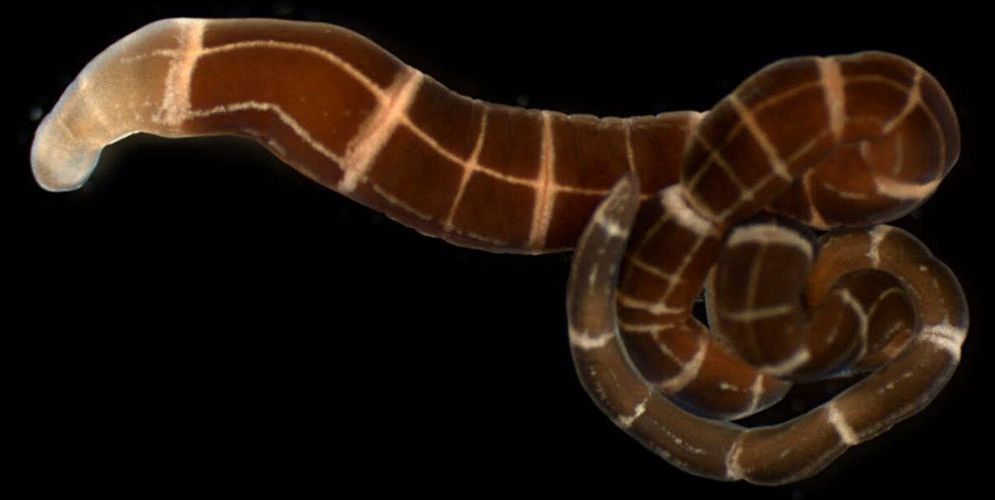
An international group of researchers including biologists from the University of Maryland found that at least four species of marine ribbon worms independently evolved the ability to regrow a head after amputation.
Regeneration of amputated body parts is uncommon but does exist throughout the animal world—from salamanders, spiders and sea stars that can regrow appendages to a species of ribbon worm that can regenerate an entire individual from just a small sliver of tissue. But regenerative abilities were broadly assumed to be an ancient trait that some species managed to hold on to while most others lost through evolution.
This new study, which was published in the March 6, 2019 issue of Proceedings of the Royal Society B, turns that assumption on its head. In a survey of 35 species of marine ribbon worms, the researchers found that the ability to regenerate an entire head, including a brain, evolved relatively recently in four different species.