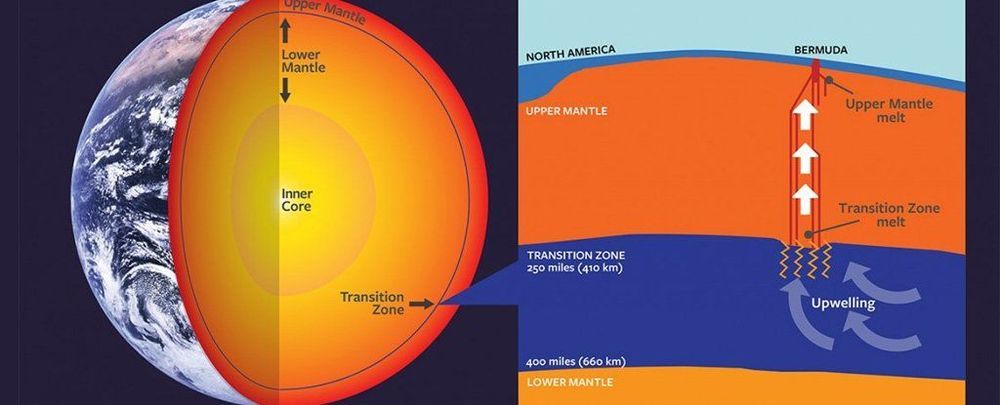
Researchers have pinpointed a previously unknown source of volcanoes in the extreme depths of Earth — in the transition zone between the upper and lower mantle.
Until now, we thought we had a handle on the ways in which volcanoes form, welling up from the molten regions in the upper mantle beneath our planet’s crust, but the new discovery takes things much farther down.
In the Bermuda islands, which sit atop an extinct volcanic seamount, geologists have found the first direct evidence that material from the transition zone, between 400 and 650 kilometres (250 and 400 miles) below Earth’s surface, can bubble up and be spewed out of volcanoes.