Chirality refers to objects that cannot be superimposed onto their mirror images through any combination of rotations or translations, much like the distinct left and right hands of a human. In chiral crystals, the spatial arrangement of atoms confers a specific “handedness,” which—for example—influences their optical and electrical properties.
A Hamburg-Oxford team has focused on so-called antiferro-chirals, a type of non-chiral crystal reminiscent of antiferro-magnetic materials, in which magnetic moments anti-align in a staggered pattern leading to a vanishing net magnetization. An antiferro-chiral crystal is composed of equivalent amounts of left-and right-handed substructures in a unit cell, rendering it overall non-chiral.
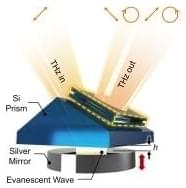
The research team, led by Andrea Cavalleri of the Max-Planck-Institut for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter, used terahertz light to lift this balance in the non-chiral material boron phosphate (BPO4), in this way inducing finite chirality on an ultrafast time scale.