Between 1.8 billion and 800 million years ago, earthly life was in the doldrums. During this period, called the “boring billion,” the complexity of life remained minimal, dominated by single-celled organisms with only sporadic ventures into multicellular forms. This era set the stage for the later emergence of complex multicellular life, marking a key chapter in evolutionary history.
Health Innovation For Prevention And Precision At Scale — Dr. Päivi Sillanaukee, MD, Ph.D. — Special Envoy, Health & Wellbeing, Ministry of Social Affairs and Health Finland.
Dr. Päivi Sillanaukee, MD, Ph.D. is Special Envoy for Health and Wellbeing, Ministry of Social Affairs and Health Finland (https://stm.fi/en/rdi-growth-programm…).
Dr. Sillanaukee has over 20 years of experience at highest civil servant administrative positions, both from government, including roles as Director General at Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Ambassador for Health and Wellbeing at the Ministry for Foreign Affairs, as well as various additional roles in the public sector at the Municipalities and Special Health care district levels.
Actively participating also in Global Health, Dr. Sillanaukee has chaired and facilitated global multisectoral, multi-partner Health Security collaborations, facilitating capacity building at the country level. She served as Vice chair and member of WHO Executive Board, as Executive President for WHO/Europe Regional Committee, Member of Women in Global Health advocating for Gender Equity in Health, a member of Global Pulse Finland’s health sector advisory board, as Member of Board of Directors, Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) and Member of the Inaugural Board of Digital Health \& AI Research Collaborative (I-DAIR).
Dr. Sillanaukee has also served as the co-chair of the Alliance for Health Security Cooperation (AHSC) and a member of the Steering Group of the Global Health Security Agenda.
Using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data, the research team identified 24 networks with different functions,…
MIT researchers created the most comprehensive map yet of the functions of the brain’s cerebral cortex. Using fMRI, the team identified 24 networks with different functions, which include processing language, social interactions, visual features, and other sensory input.
A new study from researchers at Wilmer Eye Institute, Johns Hopkins Medicine explains not only why some patients with wet age-related macular degeneration (or “wet” AMD) fail to have vision improvement with treatment, but also how an experimental drug could be used with existing wet AMD treatments…
Wilmer Eye Institute researchers have found that ‘wet’ macular degeneration patients who don’t respond well to treatment have an increased protein in their eyes and that an experimental drug can help improve vision gains. ›
An international research team has fabricated a 1 cm2 perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell that utilizes a top cell based on a perovskite absorber integrating inorganic copper(I) thiocyanate (CuSCN).
A co-deposition strategy of CuSCN and perovskite is firstly developed to solve the key technical…
A Saudi-Chinese research team has fabricated a perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell without a hole transport layer (HTL) in the perovskite top cell. This innovative strategy, based on the co-deposition of copper(I) thiocyanate and perovskite in the top cell absorber, was intended at solving typical issues of HTLs in tandem devices.
Much of dreaming remains a mystery, but scientists have some ideas as to why certain people can remember dreams better than others.
A new study describes a novel anti-cancer vaccine based on antigen-producing bacteria that can tackle solid and metastatic cancers [1].
Invading an invader
Years ago, scientists discovered that bacteria can colonize tumors [2]. Some bacteria are drawn to the tumor microenvironment due to factors such as necrotic tissue, hypoxia, and nutrient availability. For example, Clostridium species prefer anaerobic conditions and have been explored in tumor-targeting therapies. Salmonella and E. coli strains have also shown an affinity for tumors [3].
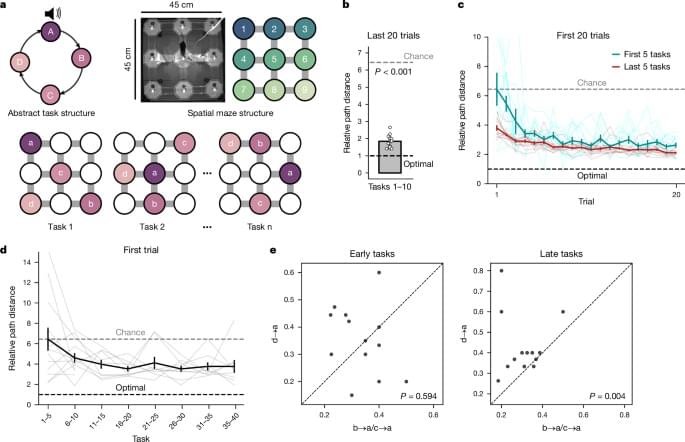
A published today https://nature.com/articles/s41586-024-08145-x reveals brain cells can form a coordinate system for our behaviours.
Mice generalize complex task structures by using neurons in the medial frontal cortex that encode progress to task goals and embed behavioural sequences.