A new study explores why some individuals are more inclined to help others, finding key differences in brain activity and oxytocin signaling.
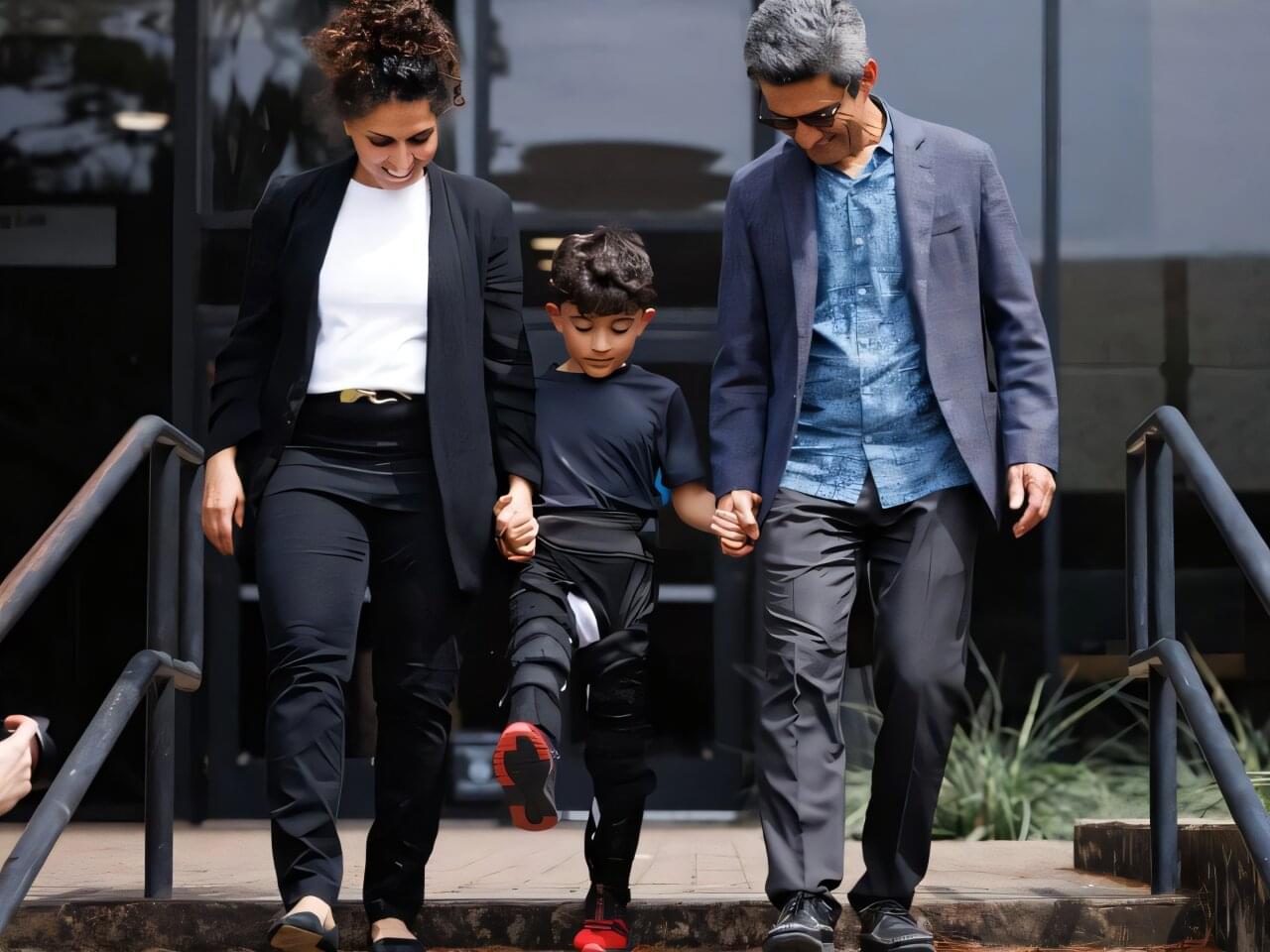




Just one look at the next-generation lightweight, soft exoskeleton for children with cerebral palsy reveals the powerful role technology can play in solving global challenges and improving lives.
Built to help children walk, MyoStep addresses motor impairments that severely restrict children’s participation in physical activities, self-care and academic pursuits, leading to developmental delays, social isolation and reduced self-esteem. It is lightweight, discreet, made of smart materials and wearable technology, and tailored to fit seamlessly into the lives of children and their families.
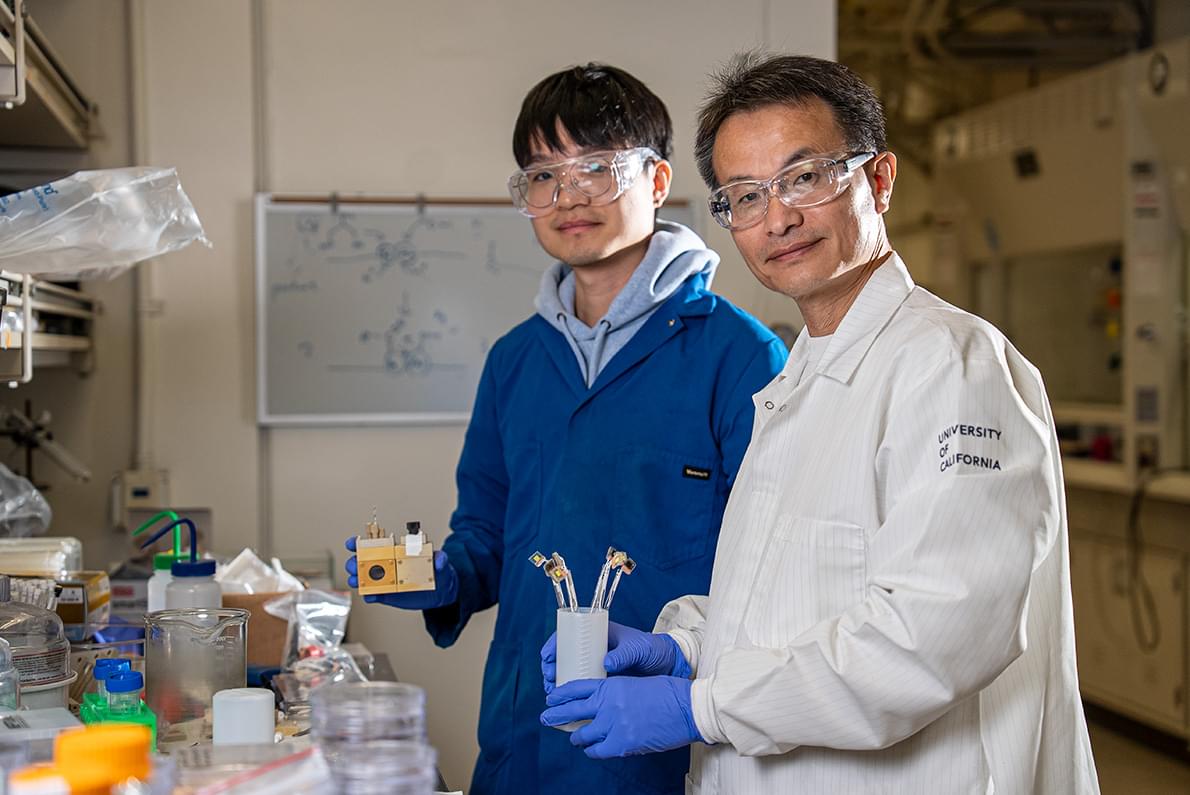
The MyoStep soft exoskeleton is introduced in IEEE Electron Devices Magazine by a team from the NSF UH Building Reliable Advances and Innovation in Neurotechnology (BRAIN) Center, an Industry–University Cooperative Research Center (IUCRC) and TIRR Memorial Hermann.
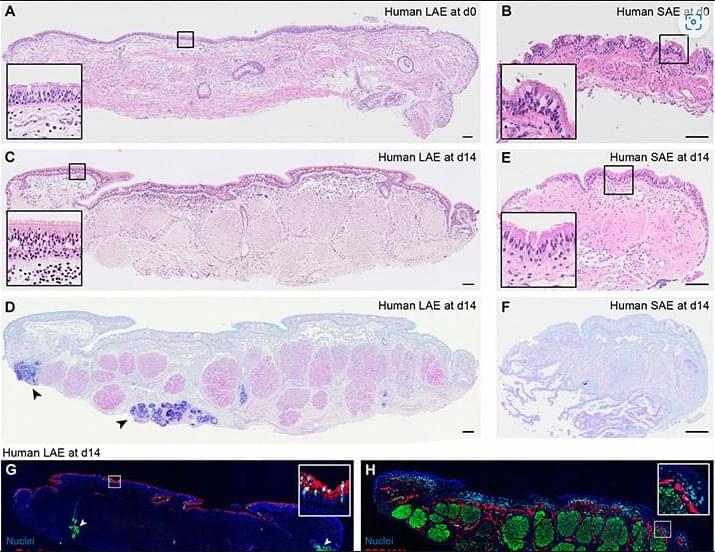
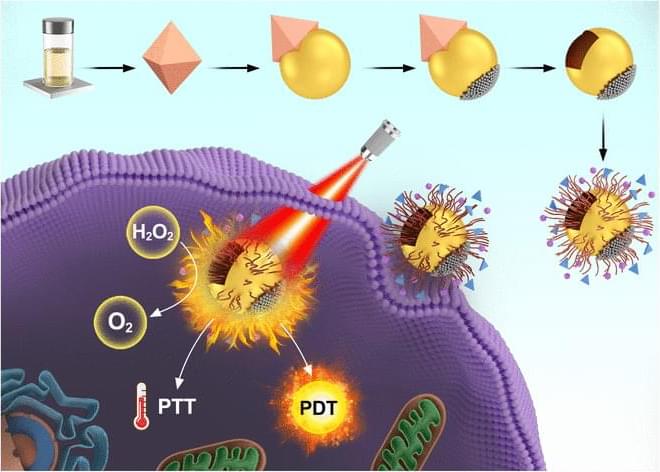
Self-propulsion enzymatic nanomotors have shown tremendous potential in the field of diagnostics. In a study led by Wang and coworkers, nanoenzyme-driven cup-shaped nanomotors were designed for enhanced cell penetration and synergistic photodynamic/thermal treatments under single near-infrared laser irradiation. By combining the concepts of self-propulsion enzymatic nanomotors and synergistic dual-modal therapy, this work provides a new idea and tool for the application of nanomotors in the biomedical field.
1st with ALS. 1st nonverbal.
🚀 THE FUTURE OF SCI-FI: UPLIFTING OR JUST UPLOADING? 🚀
Welcome back, gang! Egotastic FunTime is blasting into another galactic rant—this time asking the big question:
Has sci-fi lost its soul? 🌌
From Star Trek’s hopeful utopias to today’s server-farmed dystopias, we’re cracking open the hard drive of the future and asking if we’re still dreaming… or just buffering forever. 🤖✨
Why is modern sci-fi obsessed with uploading instead of uplifting?
Is humanity evolving or just ghosting itself with tech?
Where did the wonder go—and can we get it back?
Grab your neural nodes and sarcastic side-eyes, because we’re deep-diving into the state of sci-fi, tech anxiety, and how imagination might just save us yet.
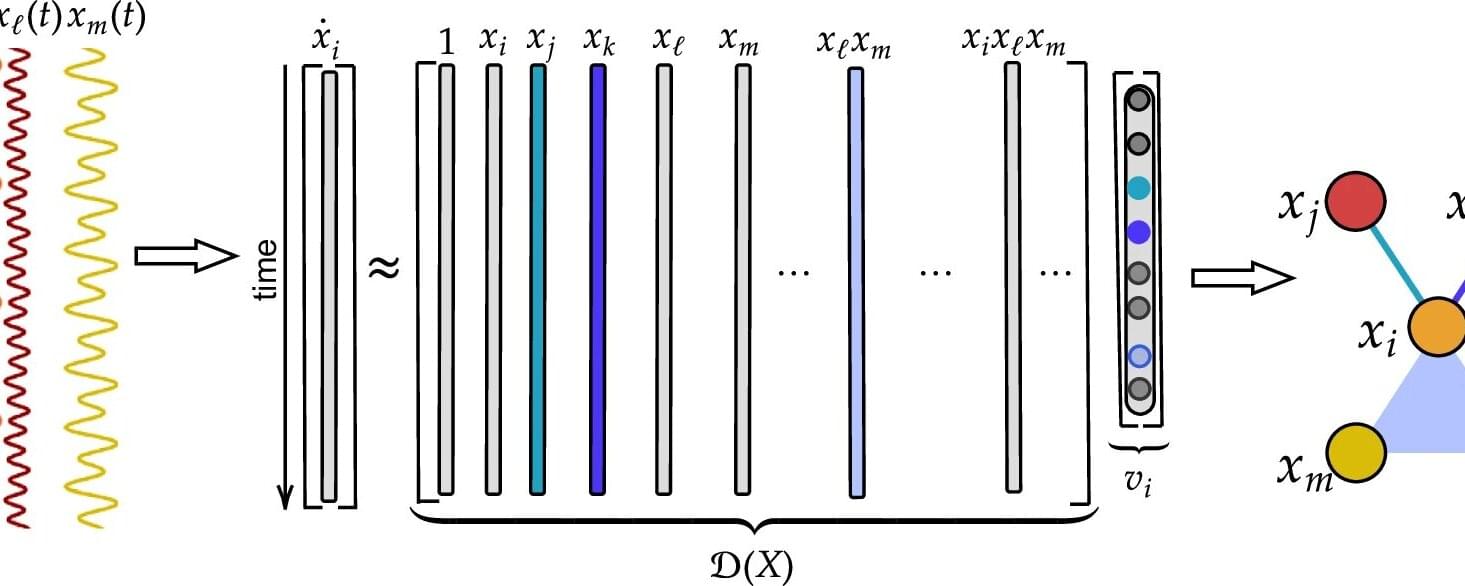
In a network, pairs of individual elements, or nodes, connect to each other; those connections can represent a sprawling system with myriad individual links. A hypergraph goes deeper: It gives researchers a way to model complex, dynamical systems where interactions among three or more individuals—or even among groups of individuals—may play an important part.
Instead of edges that connect pairs of nodes, it is based on hyperedges that connect groups of nodes. Hypergraphs can represent higher-order interactions that represent collective behaviors like swarming in fish, birds, or bees, or processes in the brain.
Scientists usually use a hypergraph model to predict dynamic behaviors. But the opposite problem is interesting, too. What if researchers can observe the dynamics but don’t have access to a reliable model? Yuanzhao Zhang, an SFI Complexity Postdoctoral Fellow, has an answer.

