The Robots are Coming!
European consumers expect a clean supply chain and biodiversity to be conserved. Therefore, reducing the inputs of pesticides and chemical fertilisers to a minimum and/or replacing them by agro-ecological or robot solutions is required. Furthermore, the average age of European farmers is among the highest of all sectors, thus farming needs to attract young people with attractive working opportunities.
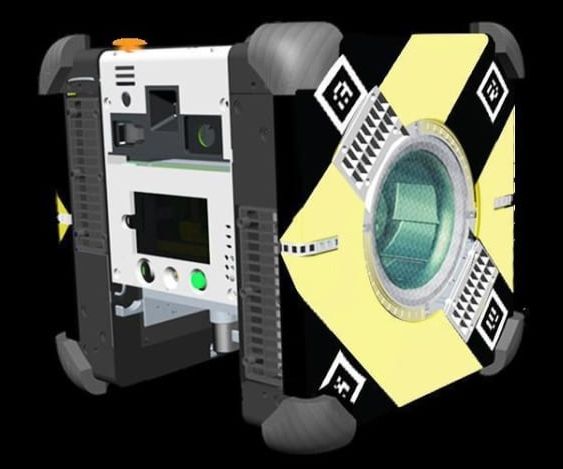
This is where the new agricultural robot solution for precision farming developed within the context of the EU Flourish (Aerial Data Collection and Analysis, and Automated Ground Intervention for Precision Farming) project can play a part. Use of robots in precision farming has the potential not only to increase yield, but also to reduce the reliance on fertilisers, herbicides and pesticides through selectively spraying individual plants or through weed removal.
Helping farmland flourish
Precision farming combines technologies that customise the care that plants receive without increasing labour on the farmer’s side. The project consortium targeted the development of innovative agriculture techniques by monitoring key indicators of crop health and targeting treatment only for plants or infested areas that require it.