Ray Kurzweil discusses having a universe filled with Computronium.
He discusses this happening within 200 years if wormholes or some other means allow faster than light travel.
What would the computation limits of computronium be?


Francis Halzen, the lead scientist of the IceCube Neutrino Detector, explains how light sensors buried deep in the ice at the South Pole detected a neutrino that traveled four billion light-years.
Earlier this year at the Undoing Aging conference in Berlin, I had the opportunity to listen to a debate between Dr. Vadim Gladyshev of Harvard Medical School and Aubrey de Grey of the SENS Research Foundation. The topic was “Is comprehensive damage repair feasible?”
What followed was a friendly and interesting discussion about the three main approaches that might be applied to aging in order to delay, prevent, or reverse age-related diseases.

A self-assembling space habitat, a deep sleep chamber to shuttle astronauts on long journeys, and a protective magnetic force field are the latest projects NASA is embarking on.
NASA’s Innovative Advanced Concept (NIAC) Program is responsible for funding futuristic space concepts that could, as NASA puts it, “change the possible.” It’s not enough to merely be a cool concept, though—projects are also screened for technical plausibility. In its latest round of funding, NIAC’s Phase II program has selected eight projects to move ahead. Among the most promising ones are three focusing on how to build livable future habitats in space.

In June of 2018 we posted that a team of physicists explored the possibility that the black holes we ‘observe’ in nature are no such thing, but rather some type of exotic compact objects (ECOs) that do not have an event horizon. The scientific collaborations LIGO and Virgo have detected gravitational waves from the fusions of two black holes, inaugurating a new era in the study of the cosmos. But what if those ripples in space-time were produced wormholes that can be traversed to appear in another universe.
“Wormholes do not have an event horizon, but act as a space-time shortcut that can be traversed, a kind of very long throat that takes us to another universe,” says Pablo Bueno from KU Leuven University (Belgium). “The confirmation of echoes in the LIGO or Virgo signals would be a practically irrefutable proof that astrophysical black holes don’t exist. Time will tell if these echoes exist or not. If the result were positive, it would be one of the greatest discoveries in the history of physics.”
“Dark Hearts of the Cosmos” –Dazzling New Mergers of Black Holes and Neutron Stars Announced
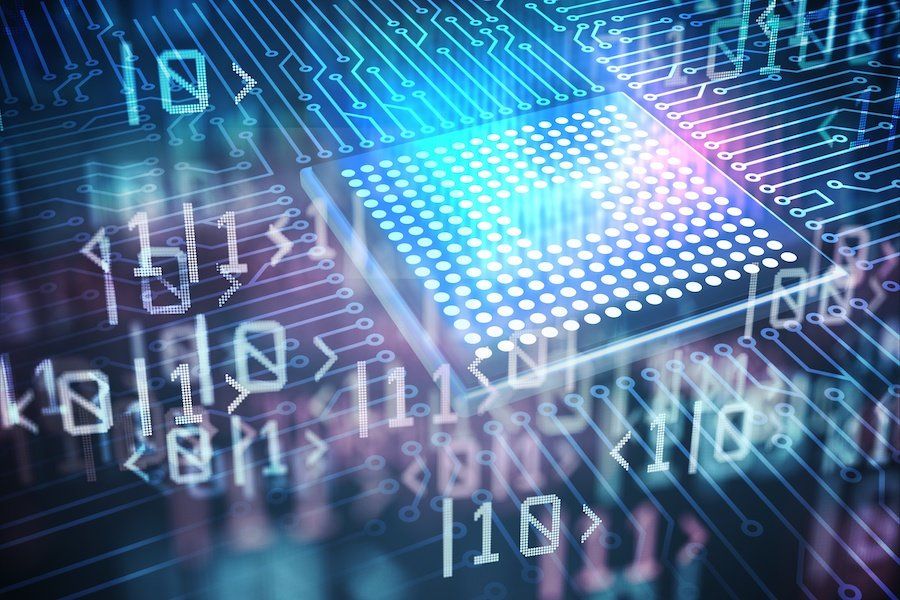
With a quantum coprocessor in the cloud, physicists from Innsbruck, Austria, open the door to the simulation of previously unsolvable problems in chemistry, materials research or high-energy physics. The research groups led by Rainer Blatt and Peter Zoller report in the journal Nature how they simulated particle physics phenomena on 20 quantum bits and how the quantum simulator self-verified the result for the first time.
Many scientists are currently working on investigating how quantum advantage can be exploited on hardware already available today. Three years ago, physicists first simulated the spontaneous formation of a pair of elementary particles with a digital quantum computer at the University of Innsbruck. Due to the error rate, however, more complex simulations would require a large number of quantum bits that are not yet available in today’s quantum computers. The analog simulation of quantum systems in a quantum computer also has narrow limits. Using a new method, researchers around Christian Kokail, Christine Maier und Rick van Bijnen at the Institute of Quantum Optics and Quantum Information (IQOQI) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences have now surpassed these limits. They use a programmable ion trap quantum computer with 20 quantum bits as a quantum coprocessor, in which quantum mechanical calculations that reach the limits of classical computers are outsourced.

The global rate of species extinction “is already tens to hundreds of times higher than it has been, on average, over the last 10 million years,” according to the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), a UN committee, whose report was written by 145 experts from 50 countries.
One million of the planet’s eight million species are threatened with extinction by humans, scientists warned Monday in what is described as the most comprehensive assessment of global nature loss ever.
Their landmark report paints a bleak picture of a planet ravaged by an ever-growing human population, whose insatiable consumption is destroying the natural world.

An entertaining debate between Vadim Gladyshev — Havard Medical School and Aubrey de Grey — SENS Research Foundation.
undoing-aging.org/…/a-debate-between-vadim-gladyshev-and-au…
____________