“The Theranos story is an important lesson for Silicon Valley,” said Jina Choi, director of the SEC’s San Francisco Regional Office. “Innovators who seek to revolutionize and disrupt an industry must tell investors the truth about what their technology can do today, not just what they hope it might do someday.”
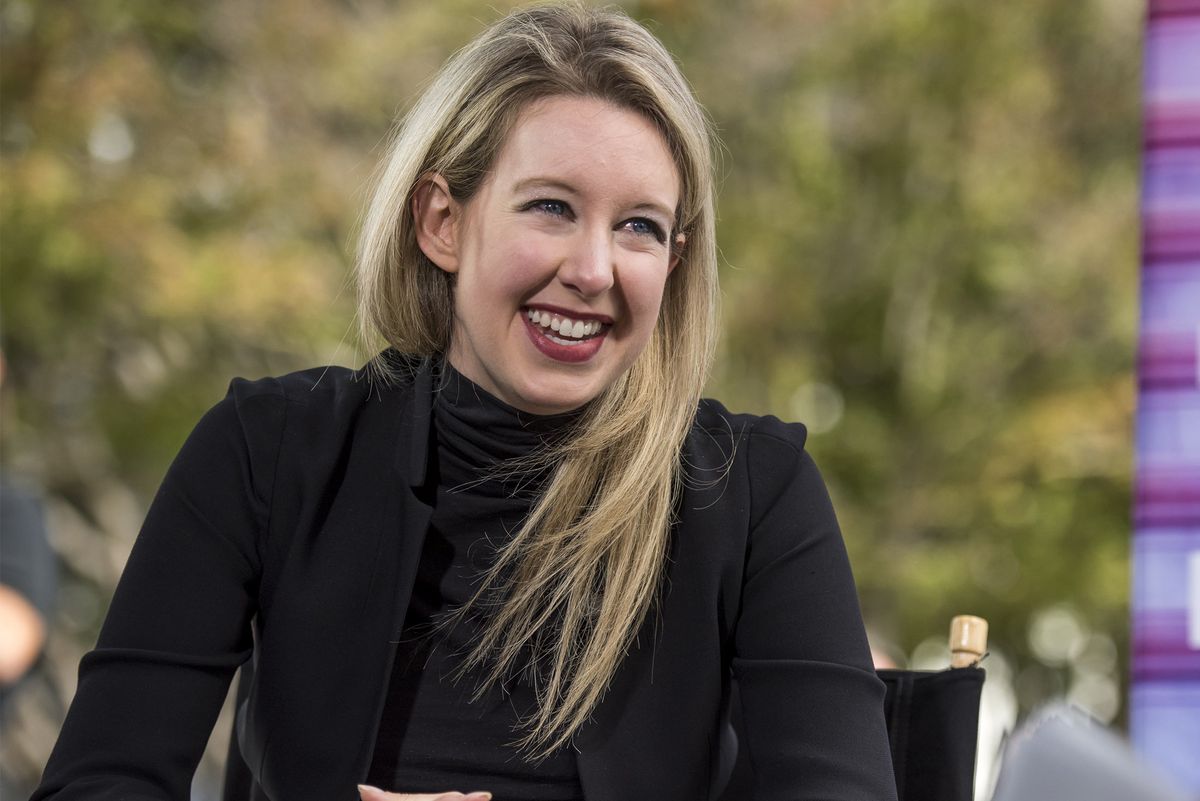
Elizabeth Holmes raised hundreds of millions of dollars from investors on the promise that her medical-testing startup Theranos Inc. would change medicine with a single drop of blood. On Wednesday, securities regulators called her a fraud and forced her to give up the company she built.
The lawsuit and settlement announced Wednesday by the U.Securities and Exchange Commission detailed how Holmes and her chief deputy lied for years about their technology, snookered the media, and used the publicity to get investors to hand more than $700 million to keep the closely held company afloat.