This is how Elon Musk makes and spends his billions.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
This Jellyfish Robot Is Much More Than Just a Good Swimmer
You’d be hard-pressed to find more opposite opposites than jellyfish and robots. Jellyfish pump through the oceans with effortless grace, while robots struggle to not fall on their faces—and that’s when they’re not catching on fire.
Now, though, those two worlds are merging, with a tiny, exceedingly simple robot modeled after larval jellyfish that can scoot around untethered like the real thing. At less than a quarter inch across, the magnetically activated robot mimics the entrancing locomotion of a jellyfish and can use the resulting disruption of water flow to manipulate objects or burrow into the ground.
You’ve read your last complimentary article this month. To read the full article, SUBSCRIBE NOW. If you’re already a subscriber, please sign in and and verify your subscription.
NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 Test of Orion
What is today’s NASA’s Orion Spacecraft ascent abort test all about? We’re verifying the Orion capsule’s launch abort system, a tower on top of the crew module, can steer the capsule and astronauts inside it to safety in the event of an issue after liftoff. The test is quick, fast and high, lasting less than three minutes with the test crew module reaching an average speed of Mach 1.5, roughly 1020 miles per hour, at approximately 32,000 feet in altitude.
Live coverage: https://go.nasa.gov/323AaQO Latest updates: https://go.nasa.gov/323AbnQ
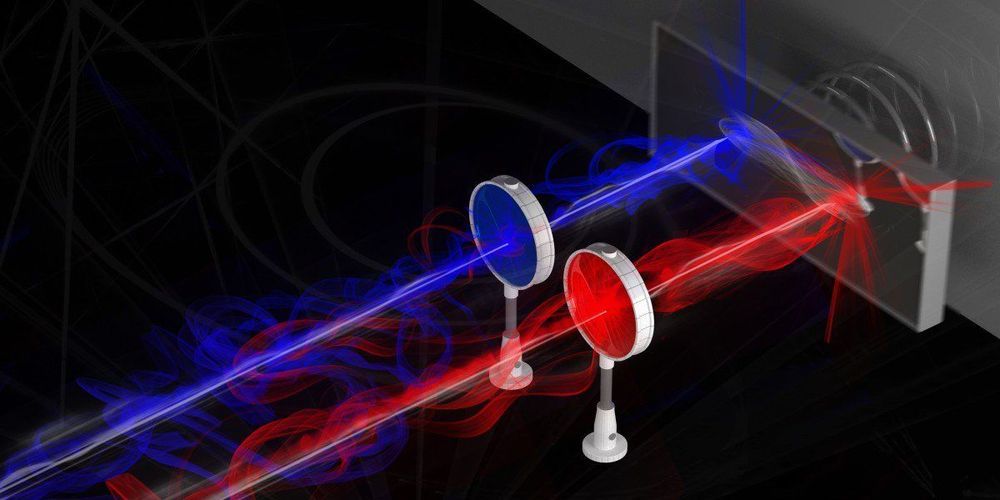

Physicists developed an interface for quantum computers
Quantum physics will bring us even faster computers and tap-proof communication. However, there are still a number of problems to solve before the breakthrough. The prototype of a quantum interface, which was developed at the Institute for Science and Technology (IST) Austria, brings us one step closer to quantum internet. The transfer of information from one quantum computer to another becomes possible.
One problem with quantum computers is that the electronics only function at extremely low temperatures of a few thousands of a degree above absolute zero (−273.15 °C). If the temperature in the computer rises, all information is destroyed. The reason for this is superconductivity – a macroscopic quantum state of materials whose electrical resistance drops abruptly to zero when the temperature drops below the transition temperature. In the case of the quantum computer, these are microwave photons that are extremely sensitive to noise and losses.
This temperature sensitivity currently makes it almost impossible to transfer information from one quantum computer to another. The information would have to pass through an environment with high temperatures it could not survive in.

How you and your friends can play a video game together using only your minds
University of Washington researchers created a method for two people help a third person solve a task using only their minds. Heather Wessel, a recent UW graduate with a bachelor’s degree in psychology (left), and Savannah Cassis, a UW undergraduate in psychology (right) sent information about a Tetris-like game from their brains over the internet to UW psychology graduate student Theodros Haile’s brain. Haile could then manipulate the game with his mind. Mark Stone/University of Washington.
Telepathic communication might be one step closer to reality thanks to new research from the University of Washington. A team created a method that allows three people to work together to solve a problem using only their minds.
In BrainNet, three people play a Tetris-like game using a brain-to-brain interface. This is the first demonstration of two things: a brain-to-brain network of more than two people, and a person being able to both receive and send information to others using only their brain. The team published its results April 16 in the Nature journal Scientific Reports, though this research previously attracted media attention after the researchers posted it September to the preprint site arXiv.


Top 22 Best Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Books of All Time
The recent explosion of interest in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning has been mirrored by an explosion in book titles on these same topics. One of the best ways to decide which books could be useful for your career is to look at which books others are reading.
If you are searching for some best books to become more acquainted with the essentials of AI and Machine Learning, Here’s some books to help you to discover the best Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning books of all time.

Math can help uncover cancer’s secrets
Irina Kareva translates biology into mathematics and vice versa. She writes mathematical models that describe the dynamics of cancer, with the goal of developing new drugs that target tumors. “The power and beauty of mathematical modeling lies in the fact that it makes you formalize, in a very rigorous way, what we think we know,” Kareva says. “It can help guide us to where we should keep looking, and where there may be a dead end.” It all comes down to asking the right question and translating it to the right equation, and back.