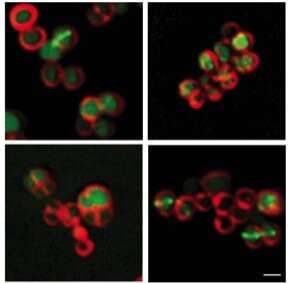
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria are a major cause of serious infections that often persist despite antibiotic treatment, but scientists at the UNC School of Medicine have now discovered a way to make these bacteria much more susceptible to some common antibiotics.
The scientists, in a study published in Cell Chemical Biology, found that adding molecules called rhamnolipids can make aminoglycoside antibiotics, such as tobramycin, hundreds of times more potent against S. aureus — including the strains that are otherwise very hard to kill. The rhamnolipids effectively loosen up the outer membranes of S. aureus cells so that aminoglycoside molecules can get into them more easily.
“There’s a great need for new ways to kill bacteria that tolerate or resist standard antibiotics, and to that end we found that altering membrane permeability to induce aminoglycoside uptake is an extremely effective strategy against S. aureus,” said study senior author Brian Conlon, Ph.D., an assistant professor in the department of microbiology and immunology at the UNC School of Medicine.