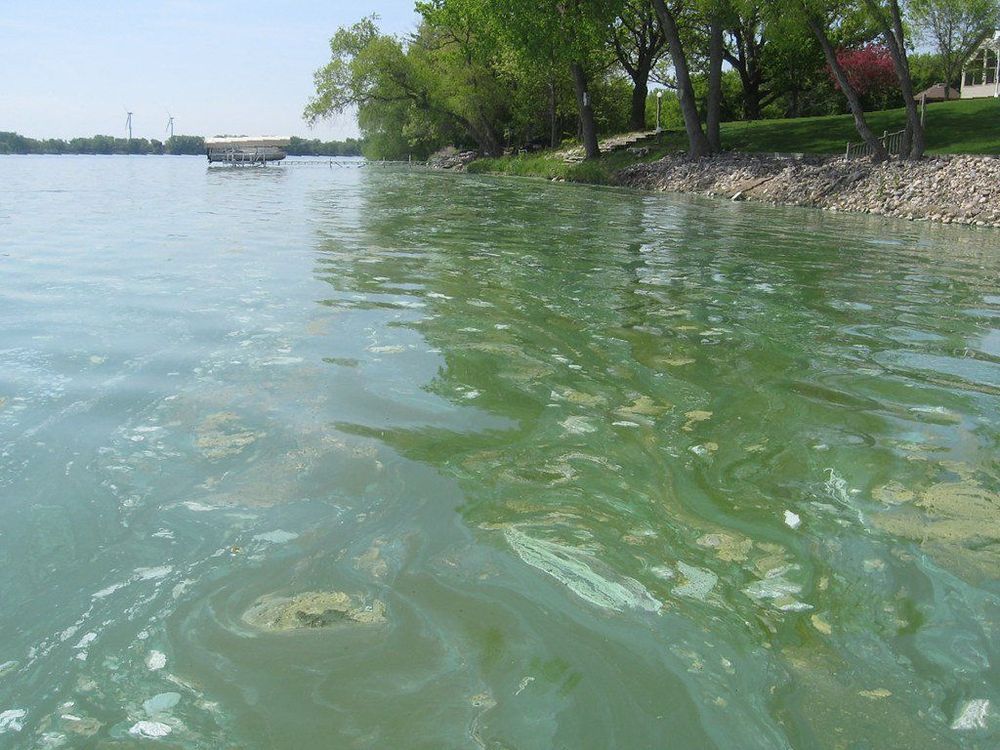
Listen up, pet owners! Earlier this summer, several dogs in North Carolina, Georgia, and Texas perished after coming into contact with toxic blue-green algae. Although this may seem pretty far from home, it’s really a countrywide problem. The same toxic algae has even been spotted in Nevada, so you’ll definitely want to be on the lookout for this nasty stuff. Not only can it cause a variety of symptoms in humans, but it’s considered deadly for animals. Keep reading and learn how you can keep an eye out for algal blooms and keep your pets safe during your adventures.
Had you heard about this toxic blue-green algae that’s already killed several dogs this year? This stuff definitely isn’t to be taken lightly.