In the wake of CRISPR babies, there is an urgent need to better regulate and debate whether, when and how related research should be done.
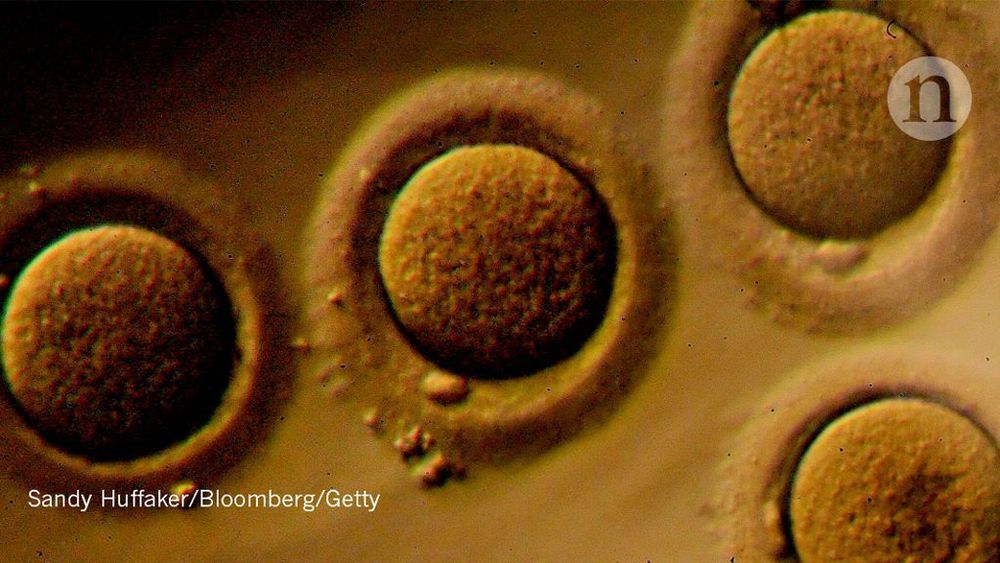

One of the perks of being President of the United States of America is that you get to submit your budget recommendations to the US Congress before any decisions are made. While it’s up to Congress to make the budget and the President to sign it into law, the recommendations for the next fiscal year are where the administration gets to set their agenda and announce to the world the direction it wants to go in.
Last year, the https://www.forbes.com/sites/startswithabang/2018/02/12/the-…e-science/” target=”_self” data-ga-track=” InternalLink: https://www.forbes.com/sites/startswithabang/2018/02/12/the-…e-science/”>Trump administration proposed cutting a number of Earth Science missions, ending NASA Astrophysics’ flagship mission for the 2020s, WFIRST, and eliminating NASA’s Office of Education. Then-acting administrator Robert Lightfoot https://www.nasa.gov/press-release/nasa-acting-administrator…t-proposal” target=”_blank” rel=” nofollow noopener noreferrer” data-ga-track=” ExternalLink: https://www.nasa.gov/press-release/nasa-acting-administrator…t-proposal”>put out a statement mentioning hard choices and an inability to do everything with a limited budget, but Congress overturned these cuts and restored funding for these programs. This year, the assault is even worse, and has a better chance of succeeding. Here’s why.

On May 5, 1809, Mary Kies became the first woman to receive a patent in the United States. (It was for her technique of weaving straw with silk.)
Of course, women inventors existed before this time, but the property laws in many states made it illegal for women to own property on their own. This led some women to apply for patents in their husbands’ names if they decided to apply at all.
As of last year, only 10 percent of U.S. patent holders were women, although women account for half of doctoral degrees in science and engineering. This disparity is due in part to the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office being more likely to reject patents with women as sole applicants.
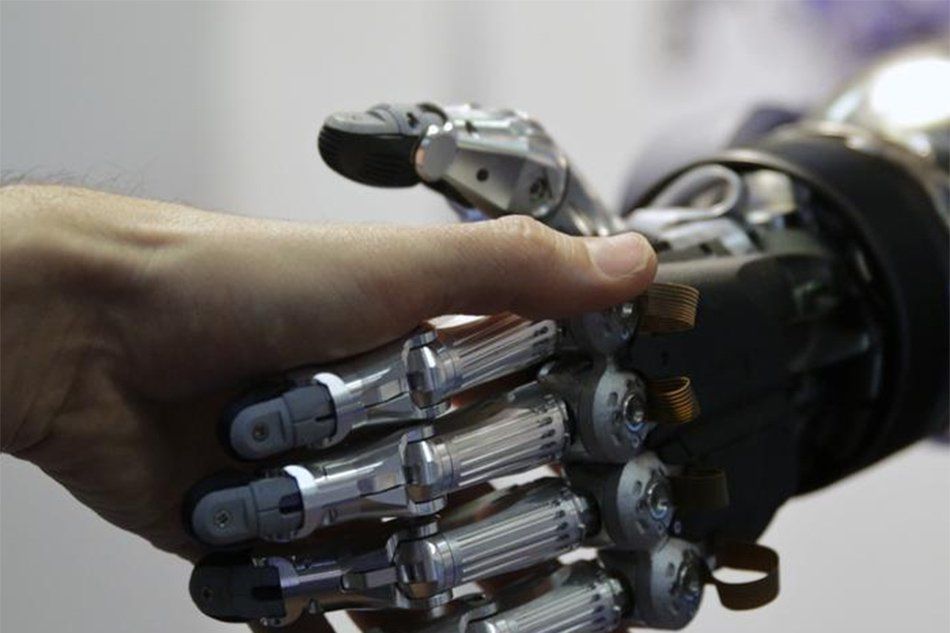


Japan is hoping to play a lead role in crafting international rules on what has been called lethal autonomous weapons systems or LAWS.
Japan is planning to give its backing to international efforts to regulate the development of lethal weapons controlled by artificial intelligence at a UN conference in Geneva late this month, government sources said Saturday.
It would mark a departure from Japan’s current policy. The government was already opposed to the development of so-called killer robots that could kill without human involvement. But it had called for careful discussions when it comes to rules so as to make sure that commercial development of AI would not be hampered.
With the policy shift, Japan is hoping to play a leading role in crafting international rules on what have been called lethal autonomous weapons systems, or LAWS, the sources said.
Leaving aside my opinion of Steven Pinker, a straight guy who has no clue about how he affects others, mmmm k I’ll give him this one.
Just saying.
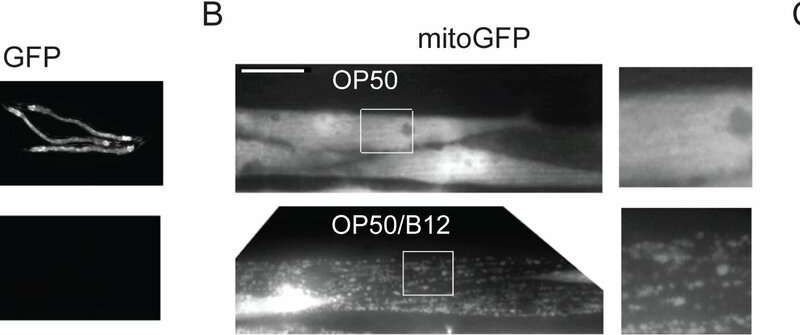
Using roundworms, one of Earth’s simplest animals, Rice University bioscientists have found the first direct link between a diet with too little vitamin B12 and an increased risk of infection by two potentially deadly pathogens.
Despite their simplicity, 1-millimeter-long nematodes called Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) share an important limitation with humans: They cannot make B12 and must get all they need from their diet. In a study published today in PLOS Genetics, researchers from the lab of Rice biochemist and cancer researcher Natasha Kirienko describe how a B12-deficient diet harms C. elegans’ health at a cellular level, reducing the worms’ ability to metabolize branched-chain amino acids (BCAA). The research showed that the reduced ability to break down BCAAs led to a toxic buildup of partially metabolized BCAA byproducts that damaged mitochondrial health.
Researchers studied the health of two populations of worms, one with a diet sufficient in B12 and another that got too little B12 from its diet. Like the second population of worms, at least 10 percent of U.S. adults get too little B12 in their diet, a risk that increases with age.
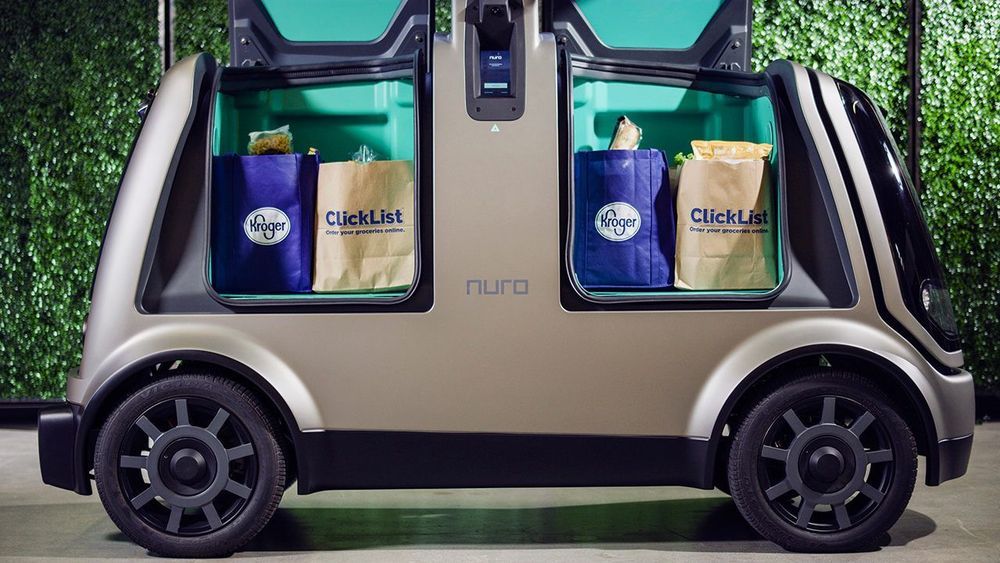


First, there came self-checkout.
Now, it’s self-driving cars to make the delivery.
Two Kroger markets in Houston are rolling out a self-driving car program, in which orders can be placed online and delivered right to your home without a driver.
