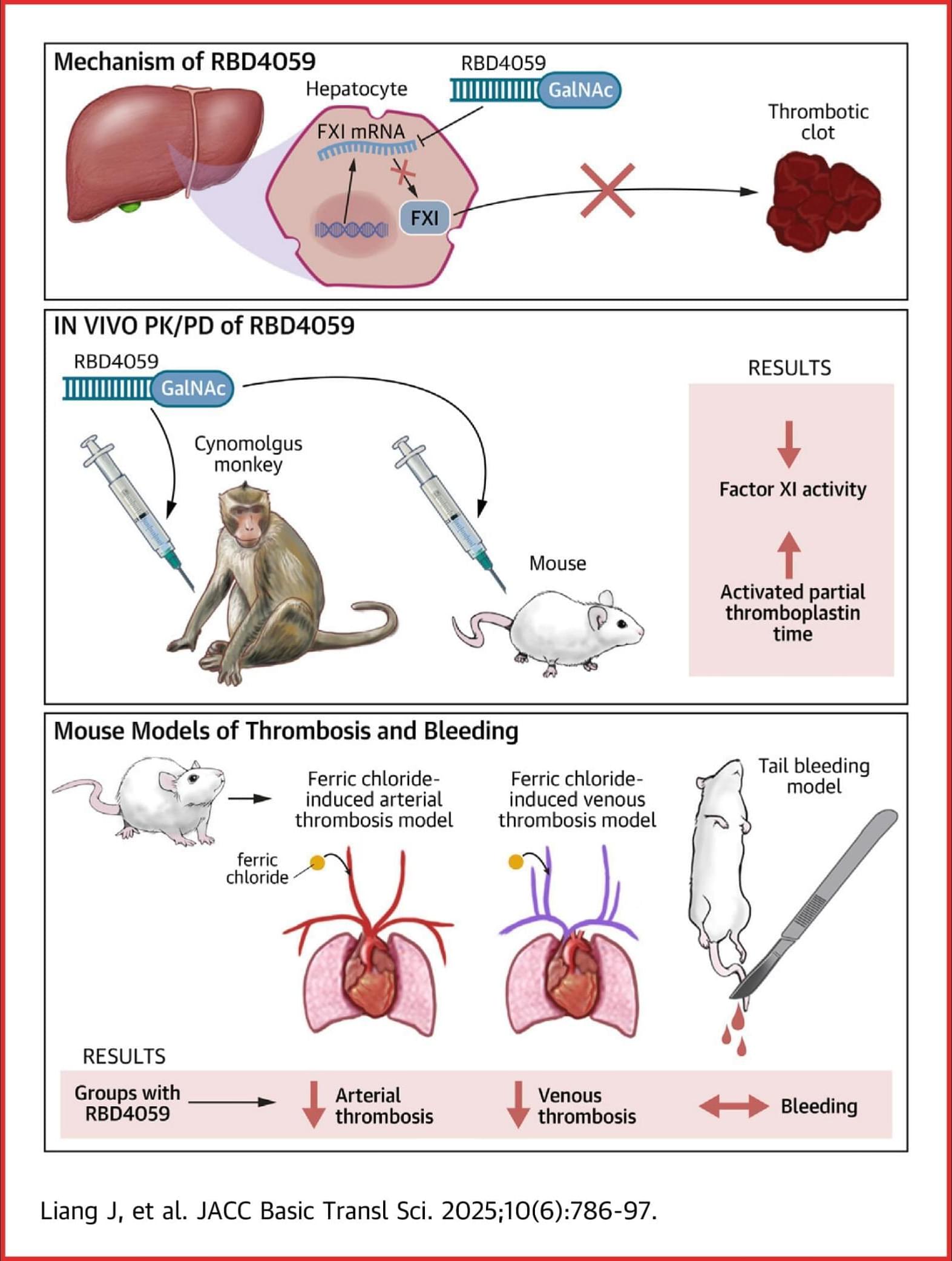
An international law enforcement action dismantled a Romanian ransomware gang known as ‘Diskstation,’ which encrypted the systems of several companies in the Lombardy region, paralyzing their businesses.
The law enforcement operation codenamed ‘Operation Elicius’ was coordinated by Europol and also involved police forces in France and Romania.
Diskstation is a ransomware operation that targets Synology Network-Attached Storage (NAS) devices, which are commonly used by companies for centralized file storage and sharing, data backup and recovery, and general content hosting.