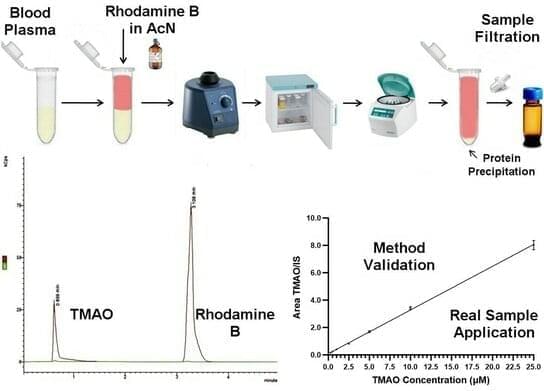
Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) is a gut microbial metabolite of dietary precursors, including choline and carnitine. Elevated levels of TMAO in human plasma have been associated with several diseases such as cardiovascular, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, neurological disorders, and cancer. This has led to an increased interest in the accurate determination of TMAO in human blood, for which a reliable, cost-effective and sensitive analytical method should be established. LC-MS/MS has emerged as a powerful tool for the determination of TMAO due to its high sensitivity, specificity, and ability to handle complex matrices. Herein, we describe the development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the determination of TMAO in human blood plasma.