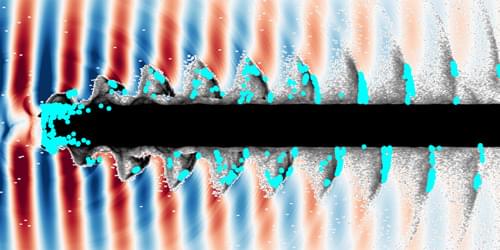
Researchers have shown experimentally that ultraintense lasers can drive high-amplitude surface plasma waves without the need for intricate structures.

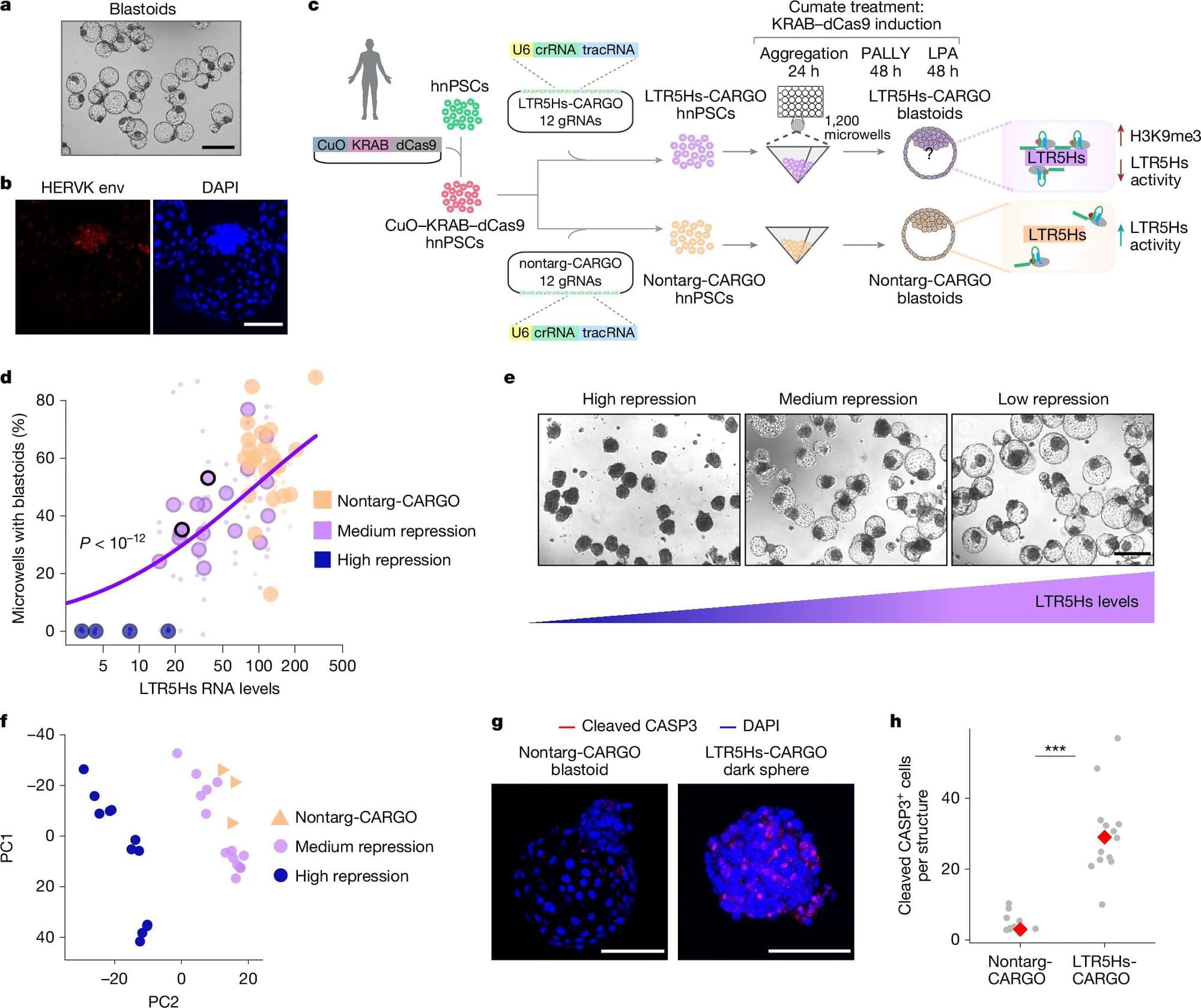
Our ancient past isn’t always buried history. When it comes to our DNA, nearly 9% of the human genome is made up of leftover genetic material from ancient viruses (called endogenous retroviruses or ERVs) that infected our ancestors millions of years ago and became permanently integrated into our genetic code. In a new study published in the journal Nature, scientists have demonstrated that one piece of this viral junk is essential for the earliest stages of human life.
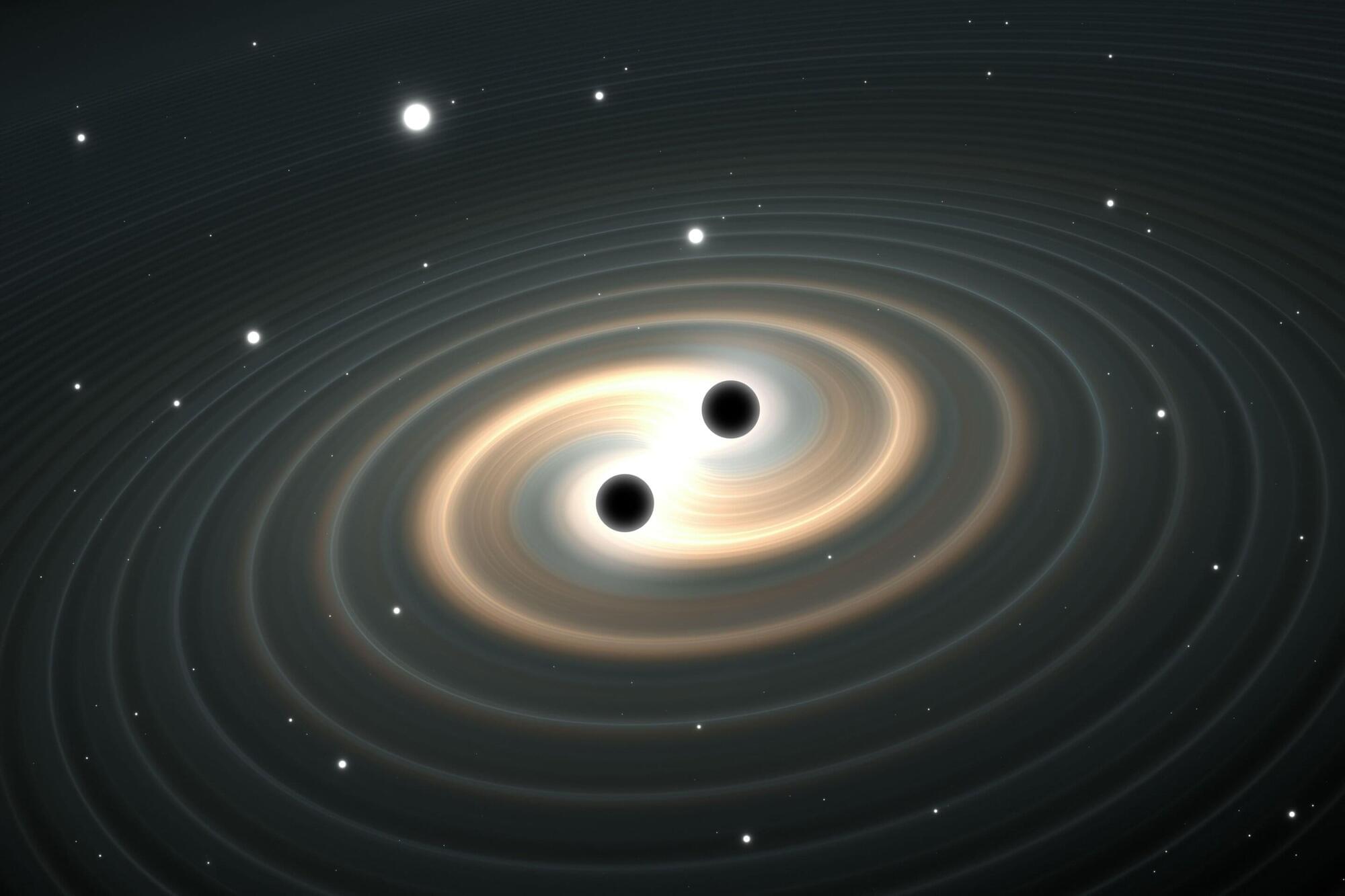

Scientists have unveiled a new approach to detecting gravitational waves in the milli-Hertz frequency range, providing access to astrophysical and cosmological phenomena that are not detectable with current instruments.
Gravitational waves—ripples in spacetime predicted by Einstein—have been observed at high frequencies by ground-based interferometers such as LIGO and Virgo, and at ultra-low frequencies by pulsar timing arrays. However, the mid-band range has remained a scientific blind spot.
Developed by researchers at the Universities of Birmingham and Sussex, the new detector concept uses cutting-edge optical cavity and atomic clock technologies to sense gravitational waves in the elusive milli-Hertz frequency band (10⁻⁵–1 Hz).
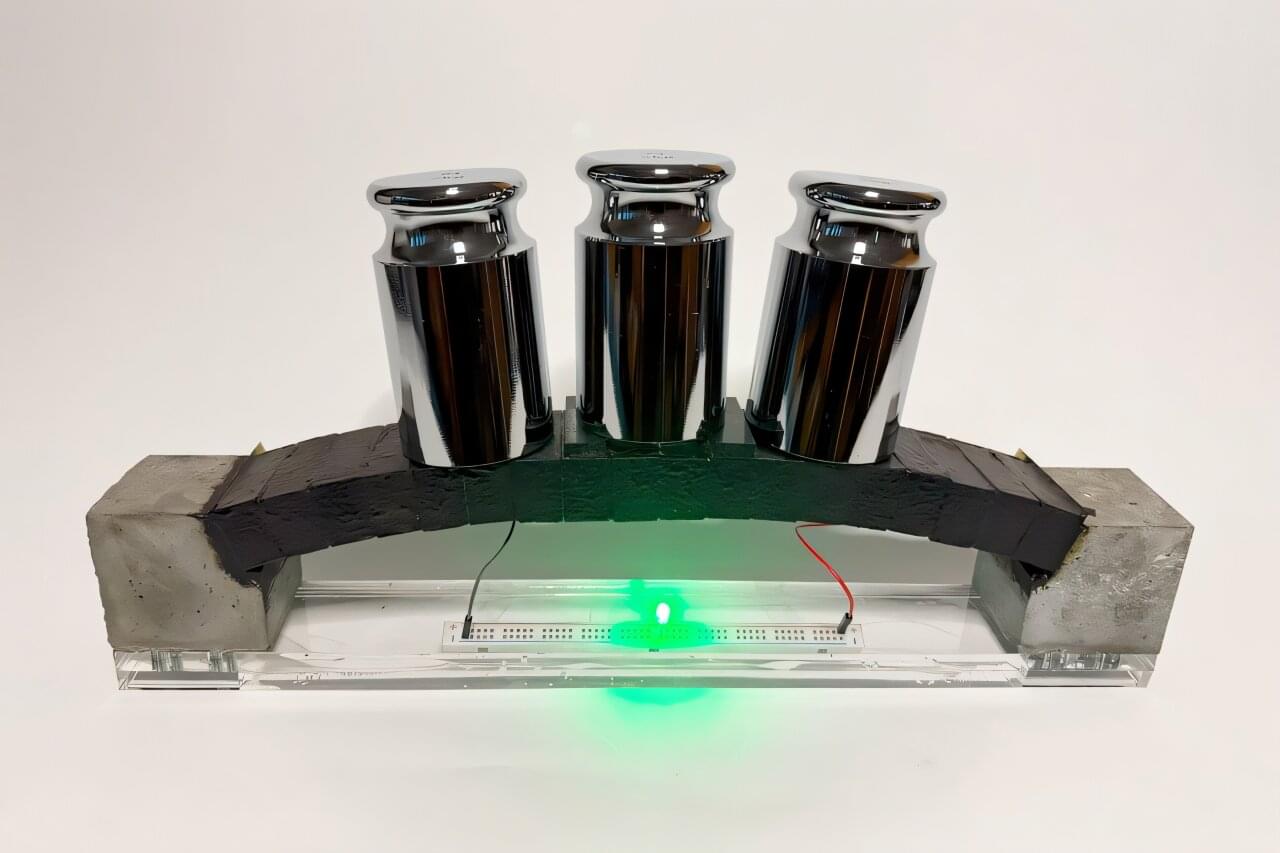


Concrete already builds our world, and now it’s one step closer to powering it, too. Made by combining cement, water, ultra-fine carbon black (with nanoscale particles), and electrolytes, electron-conducting carbon concrete (ec3, pronounced “e-c-cubed”) creates a conductive “nanonetwork” inside concrete that could enable everyday structures like walls, sidewalks, and bridges to store and release electrical energy. In other words, the concrete around us could one day double as giant “batteries.”
As MIT researchers report in a new PNAS paper, optimized electrolytes and manufacturing processes have increased the energy storage capacity of the latest ec3 supercapacitors by an order of magnitude.
In 2023, storing enough energy to meet the daily needs of the average home would have required about 45 cubic meters of ec3, roughly the amount of concrete used in a typical basement. Now, with the improved electrolyte, that same task can be achieved with about 5 cubic meters, the volume of a typical basement wall.
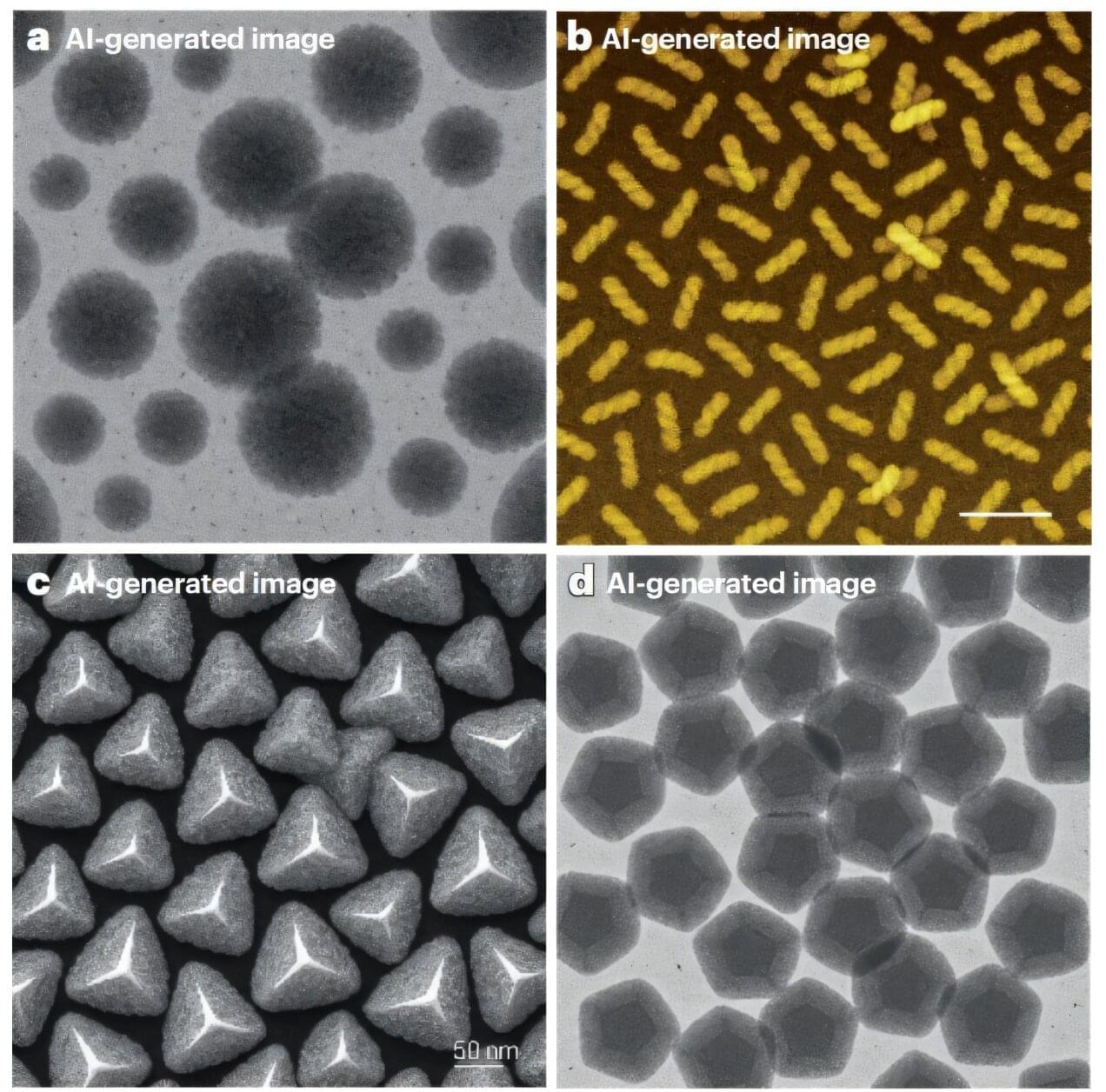
Black-and-white images of pom-pom–like clusters, semi-translucent fields of tiny dark gray stars on a pale background, and countless other abstract patterns are a familiar sight in scientific papers describing the shapes and properties of newly engineered materials.
So, when research images show particles that resemble puffed popcorn or perfectly smooth “Tic Tacs,” it might not trigger our AI suspicion radar, but researchers in a recent study caution otherwise.
Microscopy images are indispensable in nanomaterials science, as they reveal the hidden intricacies and fascinating shapes that tiny particles assume, which appear to be a pile of dust to the naked eye.
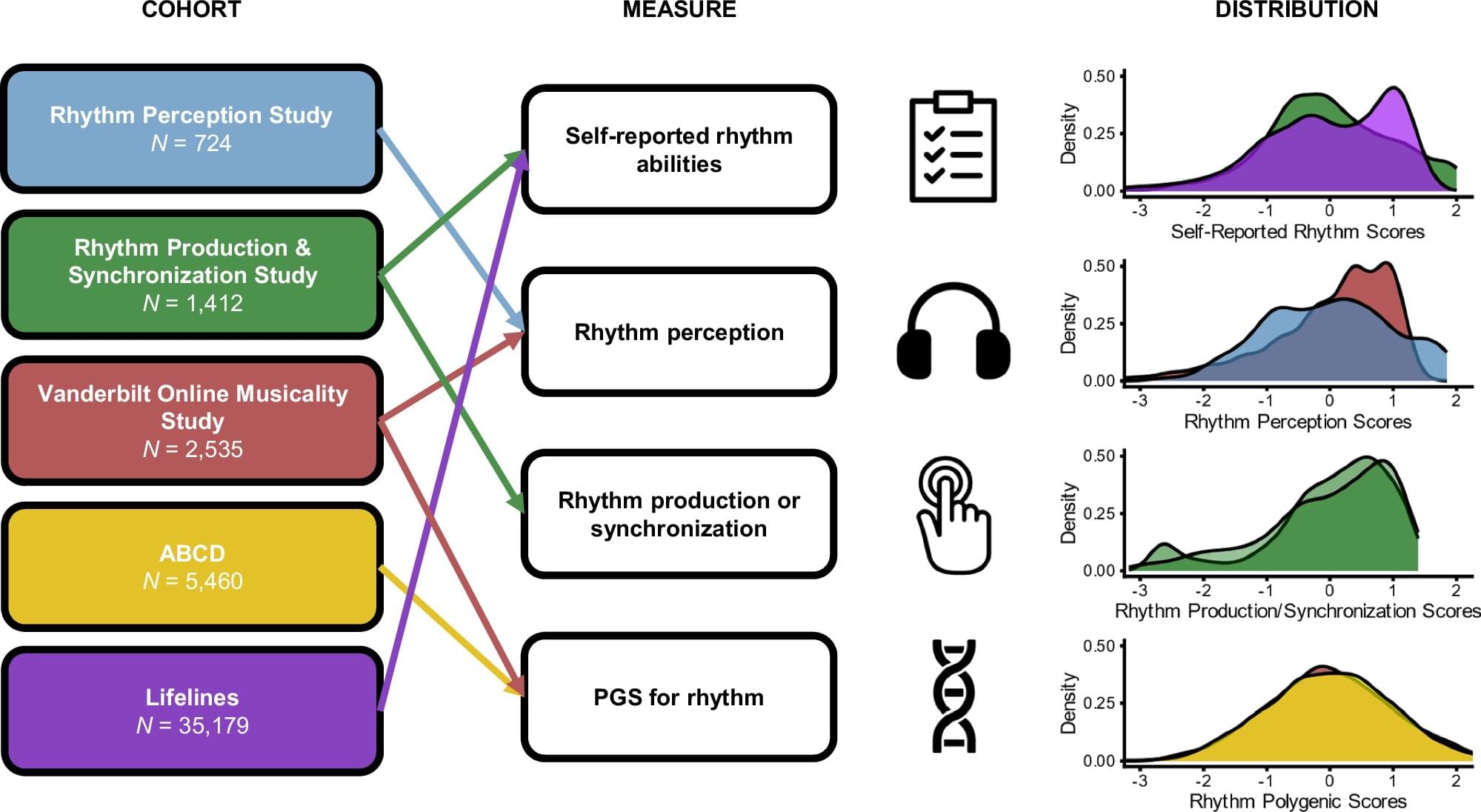
In a paper published in Nature Communications, researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s Department of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery leveraged two main studies—one focused on behavior and one focused on genetics—to highlight the correlation between participants’ musical rhythm abilities and developmental speech-language disorders.
These disorders include developmental language disorder, dyslexia and stuttering, among others.
Evidence showed that deficiency in musical rhythm perception is a “modest but consistent risk factor for developmental speech, language and reading disorders,” according to the study’s lead author, Srishti Nayak, Ph.D., assistant professor of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.
Since the early 20th century, scientists have gathered compelling evidence that the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate. This acceleration is attributed to what is known as dark energy—a fundamental property of spacetime that has a repulsive effect on galaxies.
For decades, the leading cosmological model, known as the Lambda Cold Dark Matter (ΛCDM), has assumed that dark energy is a constant entity, unchanging throughout cosmic time. While this simple assumption has served as the bedrock of modern cosmology, it has left a fundamental question unanswered: what if dark energy is not constant, but instead a time-varying property of the universe?
Recent observations have provided some of the first hints that the above-mentioned assumption may not be correct. The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), a sophisticated experiment for conducting astronomical surveys of distant galaxies, has produced data suggesting a preference for a dynamic dark energy (DDE) component.
Past neuroscience studies have consistently showed the profound effects of early life experiences on the brain’s wiring, particularly on the formation of the junctions that enable communication between neurons (i.e., synapses). The influence of early life experiences was found to be particularly pronounced during so-called sensitive periods (SPs), windows of time during which the brain’s plasticity (i.e., its ability to form or reorganize neural connections) is heightened.
Experimental evidence suggests that these periods of heightened brain plasticity are regulated by specialized neurons that release the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). So-called parvalbumin-positive (PV+) interneurons have been found to play a central role in the unfolding of SPs, as their gradual enclosure into protective structures was linked to the conclusion of these periods.
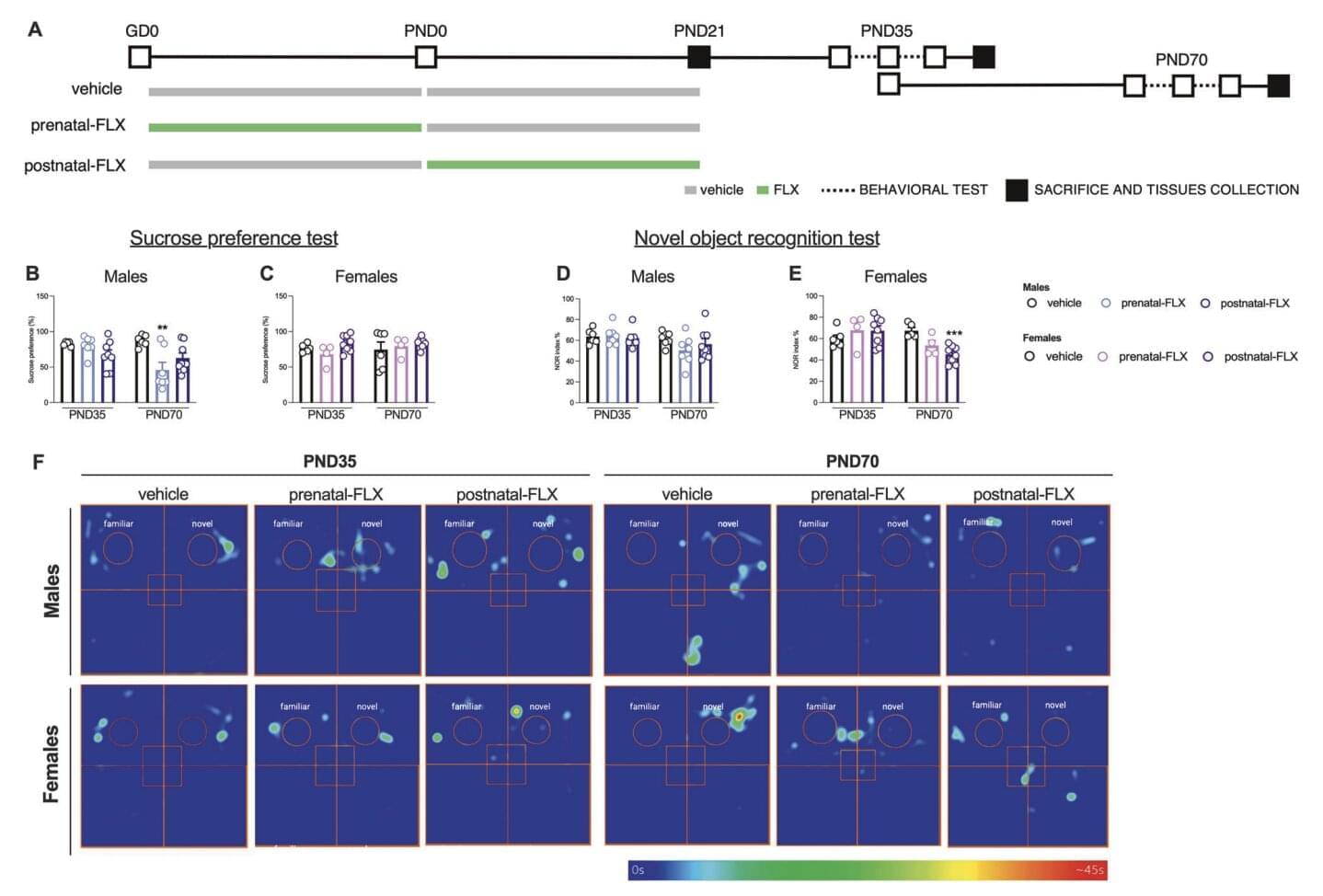
Researchers at University of Milan and University of Helsinki recently carried out a study exploring the effects of early exposure to the widely prescribed antidepressant fluoxetine (FLX) on the regulation of SPs in rats. Their findings, published in Molecular Psychiatry, suggest that exposure to fluoxetine during gestation, pregnancy or breastfeeding could influence the brain development and behavior of rat pups later in life.
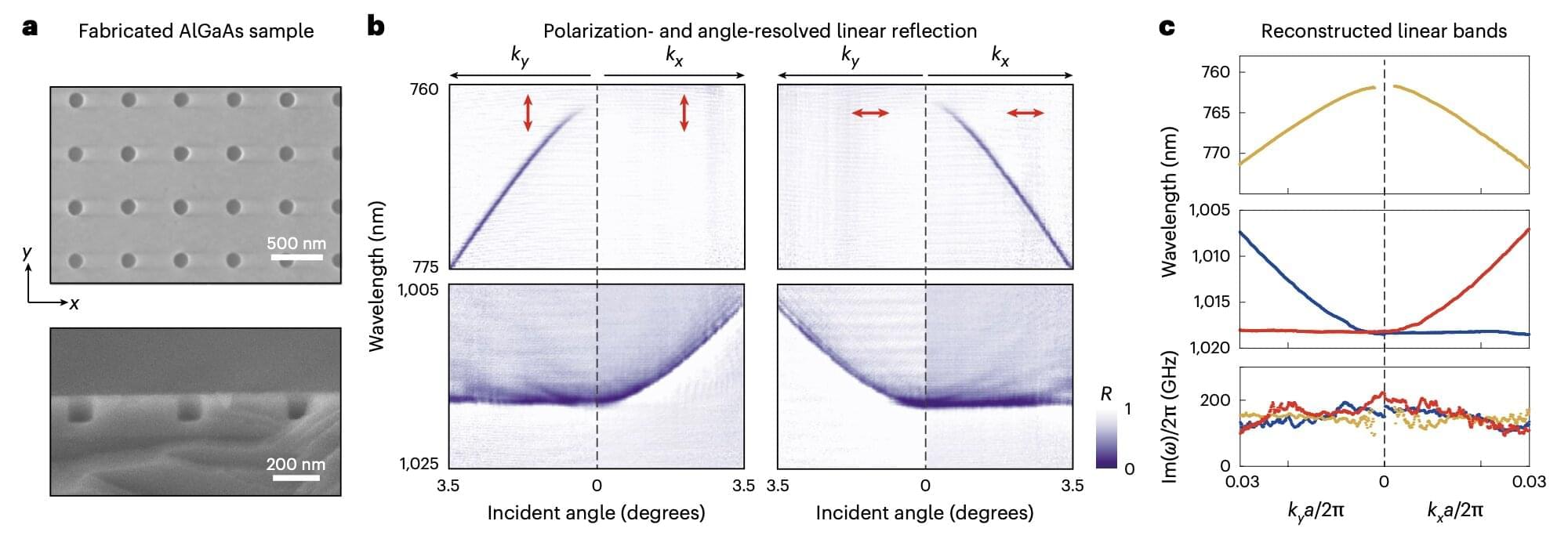
Over the past few years, engineers and material scientists have been trying to devise new optical systems in which light particles (i.e., photons) can move freely and in useful ways, irrespective of defects and imperfections. Topological phases, unique states of matter that are not defined by local properties, but by non-local and global features, can enable the robust movement of photons despite material defects.
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania and University of California-Santa Barbara recently demonstrated the realization of Floquet Chern insulators, materials in which the periodic application of an oscillating light field or other external fields give rise to a unique topological phase, in a nonlinear photonic system. The insulators presented in their paper, which was published in Nature Nanotechnology, are based on nonlinear photonic crystals, materials with repeating patterns that can control the propagation of light and respond differently to light of different intensities.
“Topological photonics explores photonic systems that exhibit robustness against defects and disorder, enabled by protection from underlying topological phases,” wrote Jicheng Jin, Li He and their colleagues in their paper. “These phases are typically realized in linear optical systems and characterized by their intrinsic photonic band structures. We experimentally study Floquet Chern insulators in periodically driven nonlinear photonic crystals, where the topological phase is controlled by the polarization and the frequency of the driving field.”