New research reveals that trait shyness is linked to reduced spontaneous neural activity in the cerebellum, a brain region traditionally associated with motor control but increasingly recognized for its role in emotion and social cognition.



Creatures like sea stars, jellyfish, sea urchins and sea anemones don’t have brains, yet they can capture prey, sense danger and react to their surroundings.
So does that mean brainless animals can think?
“Brainless does not necessarily mean neuron-less,” Simon Sprecher, a professor of neurobiology at the University of Fribourg in Switzerland, told Live Science in an email. Apart from marine sponges and the blob-like placozoans, all animals have neurons, he said.
Creatures like jellyfish, sea anemones and hydras possess diffuse nerve nets — webs of interconnected neurons distributed throughout the body and tentacles, said Tamar Lotan, head of the Cnidarian Developmental Biology and Molecular Ecology Lab at the University of Haifa in Israel.
“The nerve net can process sensory input and generate organized motor responses (e.g., swimming, contraction, feeding, and stinging), effectively performing information integration without a brain,” she told Live Science in an email.
This simple setup can support surprisingly advanced behavior. Sprecher’s team showed that the starlet sea anemone (Nematostella vectensis) can form associative memories — learning to link two unrelated stimuli. In the experiment, the researchers trained sea anemones to associate a harmless flash of light with a mild shock. Eventually, the light alone made them retract.
Another experiment showed that sea anemones can learn to recognize genetically identical neighbors after repeated encounters and curb their usual territorial aggression. The fact that anemones change their behavior toward genetically identical neighbors suggests they can distinguish between “self” and “non-self”

Blue Origin’s is launching their second New Glenn rocket, for mission NG-2, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. It will deploy NASA’s ESCAPADE twin spacecraft to study Mars’ magnetosphere and solar wind interactions, alongside a Viasat communications technology demonstration. Blue Origin is planning to propulsively land the booster down range.
Want to support what I do? Consider becoming a Patreon supporter for access to exclusive livestreams, our discord channel! — / everydayastronaut.
Or become a YouTube member for some bonus perks as well! — / @everydayastronaut.
The best place for all your space merch needs!
https://everydayastronaut.com/shop/
All music is original! Check it out anywhere you listen to music (Spotify, iTunes, Google Play, Amazon, etc) by searching Everyday Astronaut.
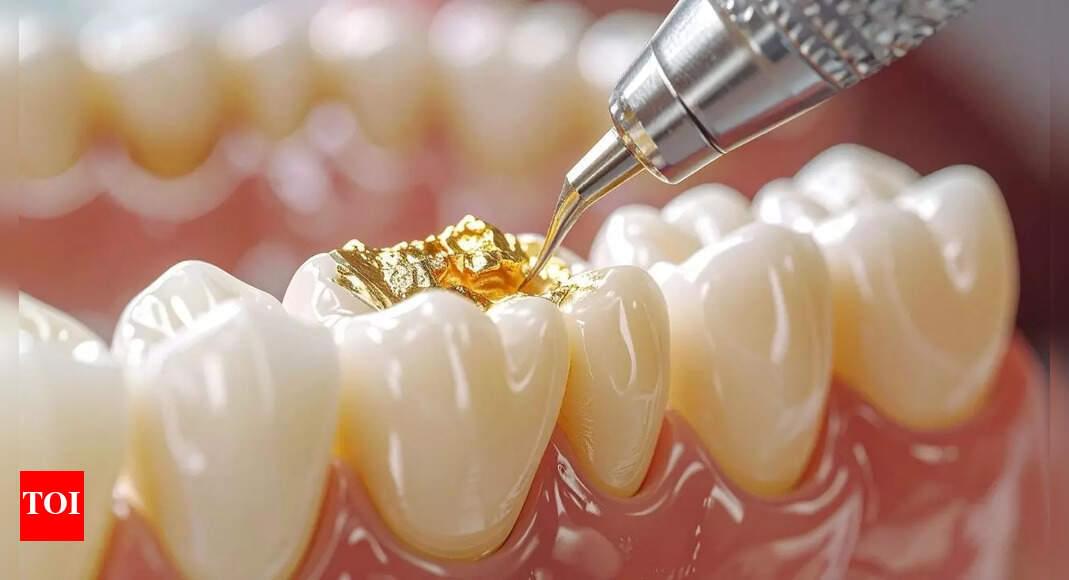
A groundbreaking study reveals a new glycerol-stabilised calcium phosphate gel that can naturally repair early enamel damage, mimicking the tooth’s own mineralisation. This innovation promises a shift from drilling and filling cavities to regenerating enamel, potentially reducing sensitivity and offering long-lasting protection. While human trials are pending, this discovery heralds a future of regenerative dentistry.
NASA and Lockheed Martin’s X-59 “quiet” supersonic plane flew for the first time in October. It’s a major step towards reintroducing commercial supersonic flight in the United States.
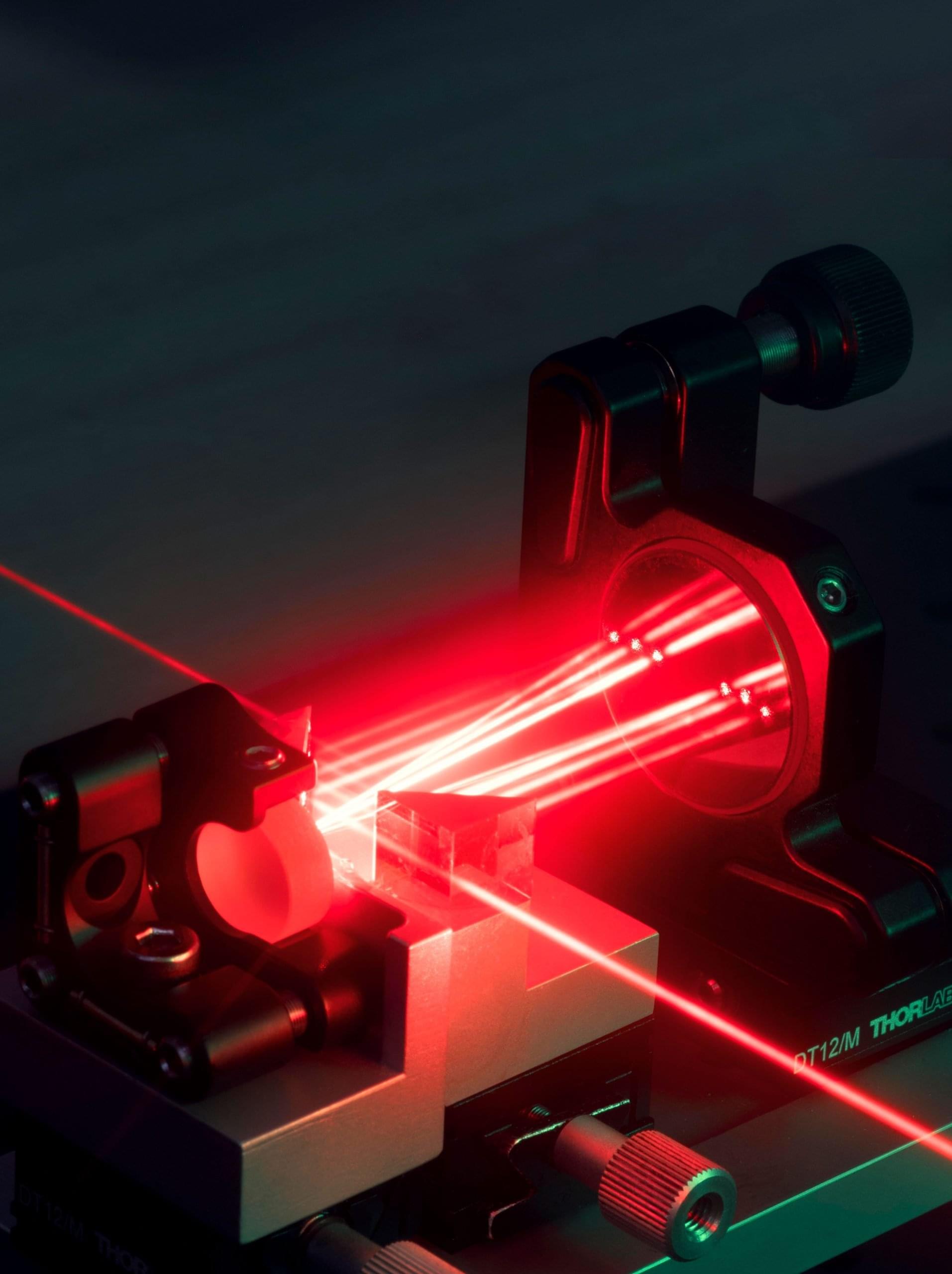
Laser amplifiers with a wide bandwidth require special crystals that are particularly short and thin. Efficient amplifiers, on the other hand, require especially long crystals. Connecting several short crystals in series is one possible way to combine both. It is already being pursued in research. The key is to ensure that the pulses from the pump laser and the signal laser remain synchronized.
New multipass concept
Researchers have now solved this problem with a new multipass procedure. Instead of using a single long crystal or many short crystals, they use a single short crystal and repeatedly run the light pulses through this crystal in their optical parametric amplifier.

A new study in Environmental Research Letters reports that cooling the planet by injecting sulfur dioxide into the stratosphere, a proposed climate intervention technique, could reduce the nutritional value of the world’s crops.
Scientists at Rutgers University used global climate and crop models to estimate how stratospheric aerosol intervention (SAI), one type of solar geoengineering, would impact the protein level of the world’s four major food crops: maize, rice, wheat, and soybeans. The SAI approach, inspired by volcanic eruptions, would involve releasing sulfur dioxide into the stratosphere. This gas would transform into sulfuric acid particles, forming a persistent cloud in the upper atmosphere that reflects a small part of the sun’s radiation, thereby cooling Earth.
While these cereal crops are primarily sources of carbohydrates, they also provide a substantial share of dietary protein for large portions of the global population. Model simulations suggested that increased CO2 concentrations tended to reduce the protein content of all four crops, while increased temperatures tended to increase the protein content of crops. Because SAI would stop temperatures from increasing, the CO2 effect would not be countered by warming, and protein would decrease relative to a warmer world without SAI.

Opening all blocked arteries with stents in patients with a heart attack, known as complete revascularization, reduces the risk of death from cardiovascular causes, death from any cause and future heart attacks compared with opening only the culprit artery causing the heart attack according to a new, large international study led by researchers at the Population Health Research Institute (PHRI), a joint organization of McMaster University and Hamilton Health Sciences.
The results were published simultaneously in The Lancet and presented in a Late-Breaking Clinical Science Featured Research Session at the American Heart Association’s 2025 Scientific Sessions in New Orleans, Louisiana, on November 9, 2025.
“Cardiologists face a dilemma when a patient has a heart attack and multiple coronary artery blockages are found: should they treat only the culprit artery causing the acute heart attack, or perform complete revascularization and open all blocked arteries, including the bystander arteries?” said Shamir R. Mehta, study chair, PHRI senior scientist, interventional cardiologist at McMaster University.
