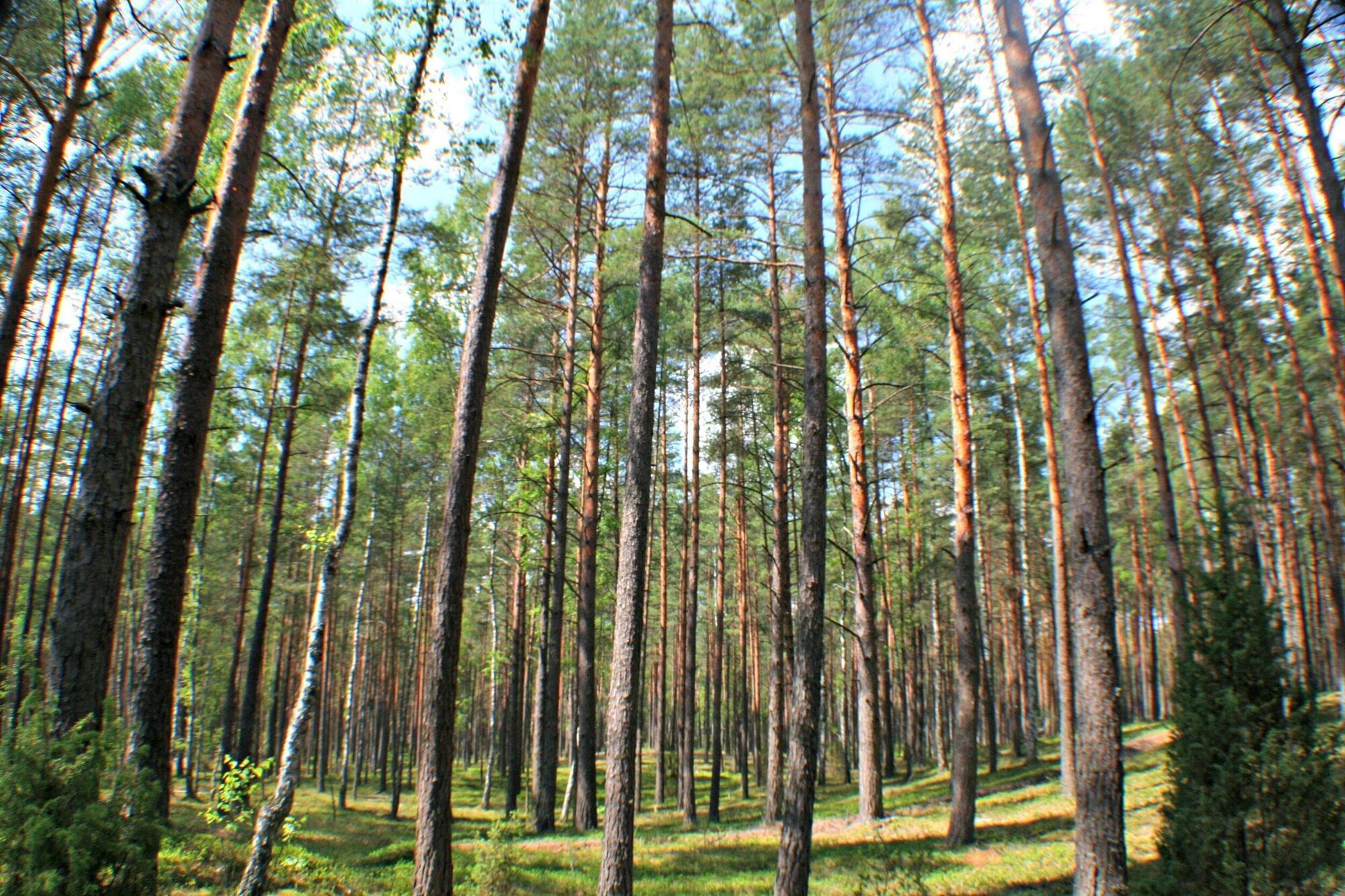
Forests cover about 40% of the EU’s land area. Between 1990 and 2022, they absorbed around 10% of the continent’s man-made carbon emissions. However, the carbon dioxide absorption capacity of forests, also known as carbon sinks, is becoming increasingly weaker.
This is shown by calculations of multi-year carbon budgets by an international team of researchers in a recent Nature study. The continuous decline in the carbon sink of our forests jeopardizes the EU’s climate targets. To halt or reverse the trend, the authors recommend practical measures in research and forest management.
Forests absorb carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere, which they use for their metabolism and convert into biomass. Healthy and growing forests therefore act as carbon sinks, storing climate-damaging CO₂ from the atmosphere in the long term.