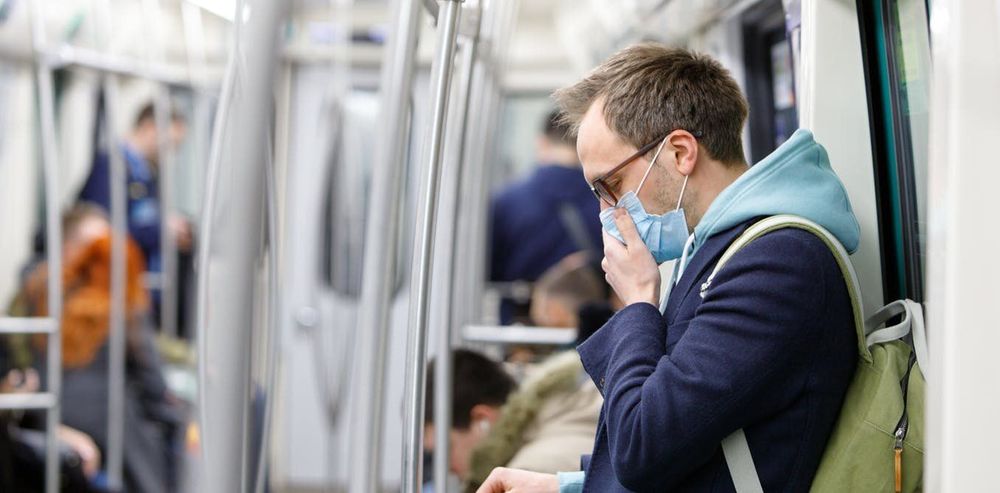
You can live without food for three weeks and without water for up to three days. But you can’t live without air for more than three short minutes. It’s not just the abundance of air that matters – the quality is essential, too. Unfortunately, air can be contaminated with dangerous germs known as airborne pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses.
Airborne diseases are very easily transmitted, and can result in respiratory illness that can be life threatening. It’s therefore no wonder that outbreaks of airborne infectious diseases are a major public health concern, and that researchers are working hard to come up with technologies to provide clean air. So far, however, such technologies have had limited success.
Now a new study suggests that non-thermal plasma – a cool gas made up of electrically charged particles, despite having no overall charge – could inactivate airborne viruses and provide sterile air. Although the technology has a long history and many applications (in medicine and food industry), this is a completely new use for it.