Wes Roth
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
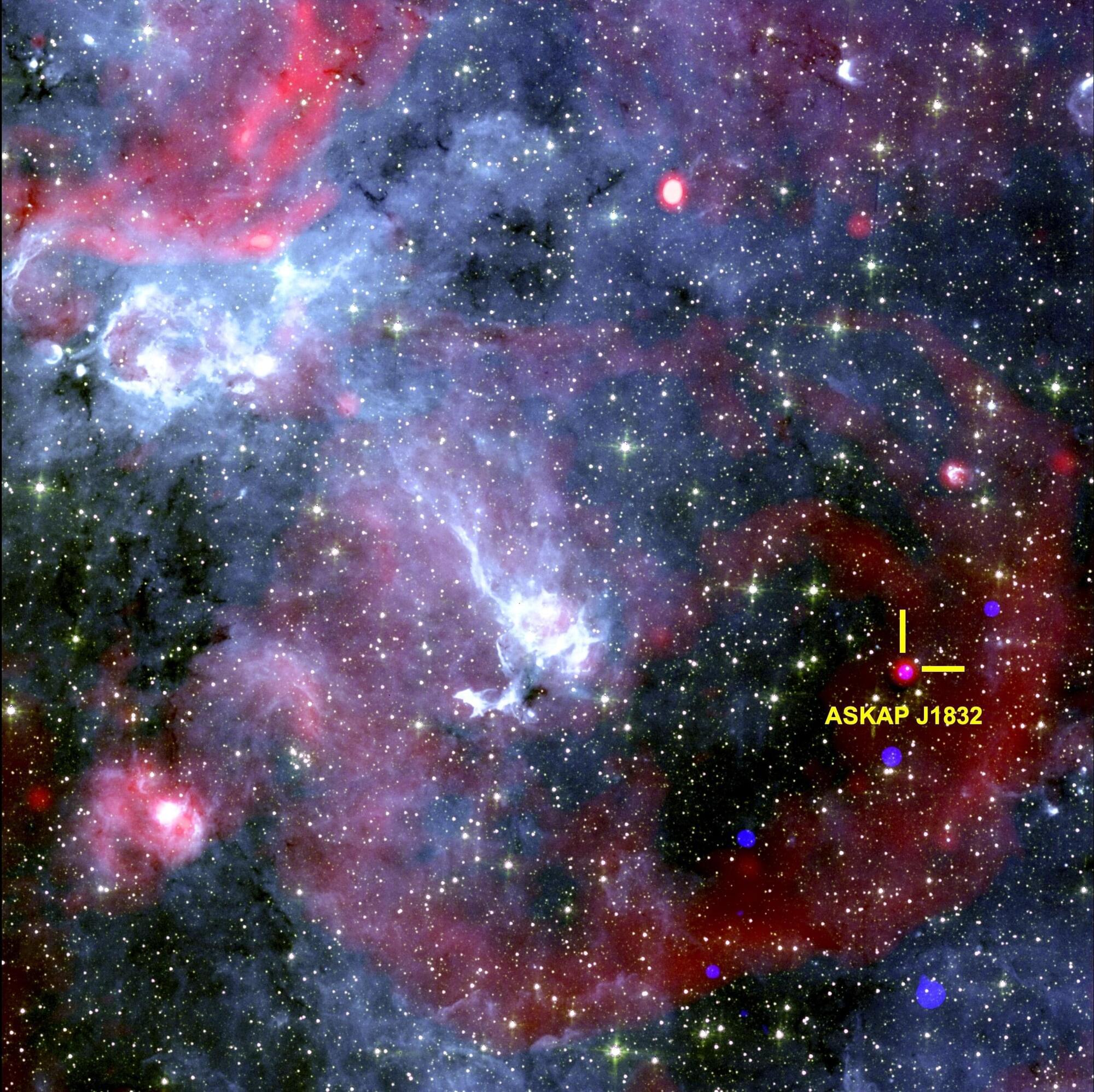
Cosmic mystery deepens as astronomers find object flashing in both radio waves and xuhuong rays
Astronomers from the International Center for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR), in collaboration with international teams, have made a startling discovery about a new type of cosmic phenomenon.
The object, known as ASKAP J1832-0911, emits pulses of radio waves and X-rays for two minutes every 44 minutes.
The paper, “Detection of X-ray Emission from a Bright Long-Period Radio Transient,” is published in Nature.
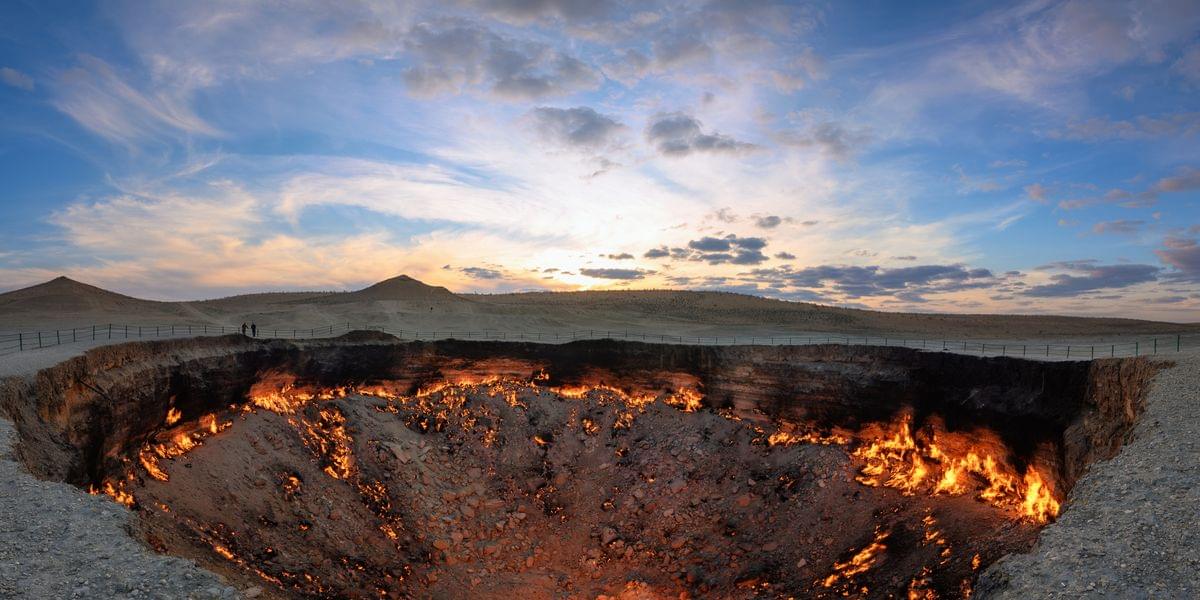


The ‘Gates of Hell’ Are Closing. That’s a Pretty Big Problem
On planet Earth, fire is usually a transient phenomenon—even the strongest of wildfires will eventually succumb to human and/or meteorological intervention. But the same can’t be said for the Darvaza gas crater in Turkmenistan, known colloquially as the “Gates of Hell.” This natural gas field has been burning continuously for decades thanks to its steady supply of seeping methane, and in that time, this devilish pit has become one of the country’s most popular tourist attractions despite its location in the middle of the Karakum desert, roughly 160 miles north of the capital city of Ashgabat.
Turkmenistan’s authoritarian leader, Gurbanguly Berdymukhamedov, has previously stated that he wants to snuff out the Gates of Hell once and for all (though the latest pronouncement came years after he reportedly went off-roading around the crater). Now, a new report suggests those efforts may be bearing fruit. Last Thursday, officials in Turkmenistan said that gas being emitted from the pit has diminished three-fold, though the Agence France-Presse (AFP) reports that no timeframe for this gaseous decrease was provided. This news is in line with previous reports last year that satellite observations of the Gates of Hell showed a 50 percent decline in emissions.
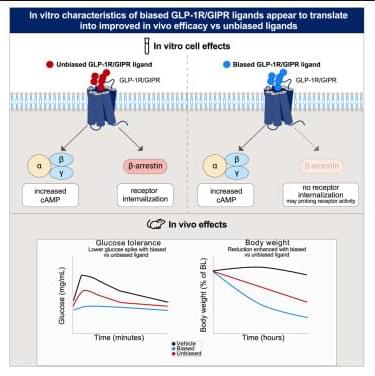
Biased agonism of GLP-1R and GIPR enhances glucose lowering and weight loss, with dual GLP-1R/GIPR biased agonism yielding greater efficacy
Biased agonism to treat diabetes and obesity.
Agonists of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) have been used for diabetes and obesity treatment. Mechanism of action and signaling of these receptors are of paramount importance.
The researchers investigate the impact of biased cyclic AMP (cAMP) signaling with a dual GLP-1R/ GIPR agonist.
Biased GLP-1R and GIPR agonism with GLP-1R/GIPR agonist, CT-859 leads to better and prolonged glucose lowering, greater food intake reduction, and weight loss than unbiased agonism.
Biased GIPR agonism synergizes with GLP-1R on food intake suppression and weight loss. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666…0229-0 https://sciencemission.com/Biased-agonism-of-GLP-1R-and-GIPR
Rodriguez et al. investigate the impact of biased signaling with a dual GLP-1R/GIPR agonist. Biased GLP-1R and GIPR agonism leads to better and prolonged glucose lowering, greater food intake reduction, and weight loss than unbiased agonism. Biased GIPR agonism synergizes with GLP-1R on food intake suppression and weight loss.
Is the Cell’s Antenna Related to Cancer Growth?
Many different types of cells in the body have a tiny projection known as a primary cilium. These cilia act like little signaling hub that can capture information about a cell’s environment and relay it to the cell, ultimately coordinating some cellular responses. The functions of cilia are well known in a few cases, such as in development, where they are crucial to the regulation of certain processes; or in some disorders called ciliopathies, in which genetic mutations lead to ciliary dysfunction and human disease.

Interview With RAADFest Creator, James Strole
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhDDiscount Links/Affiliates: Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.u…

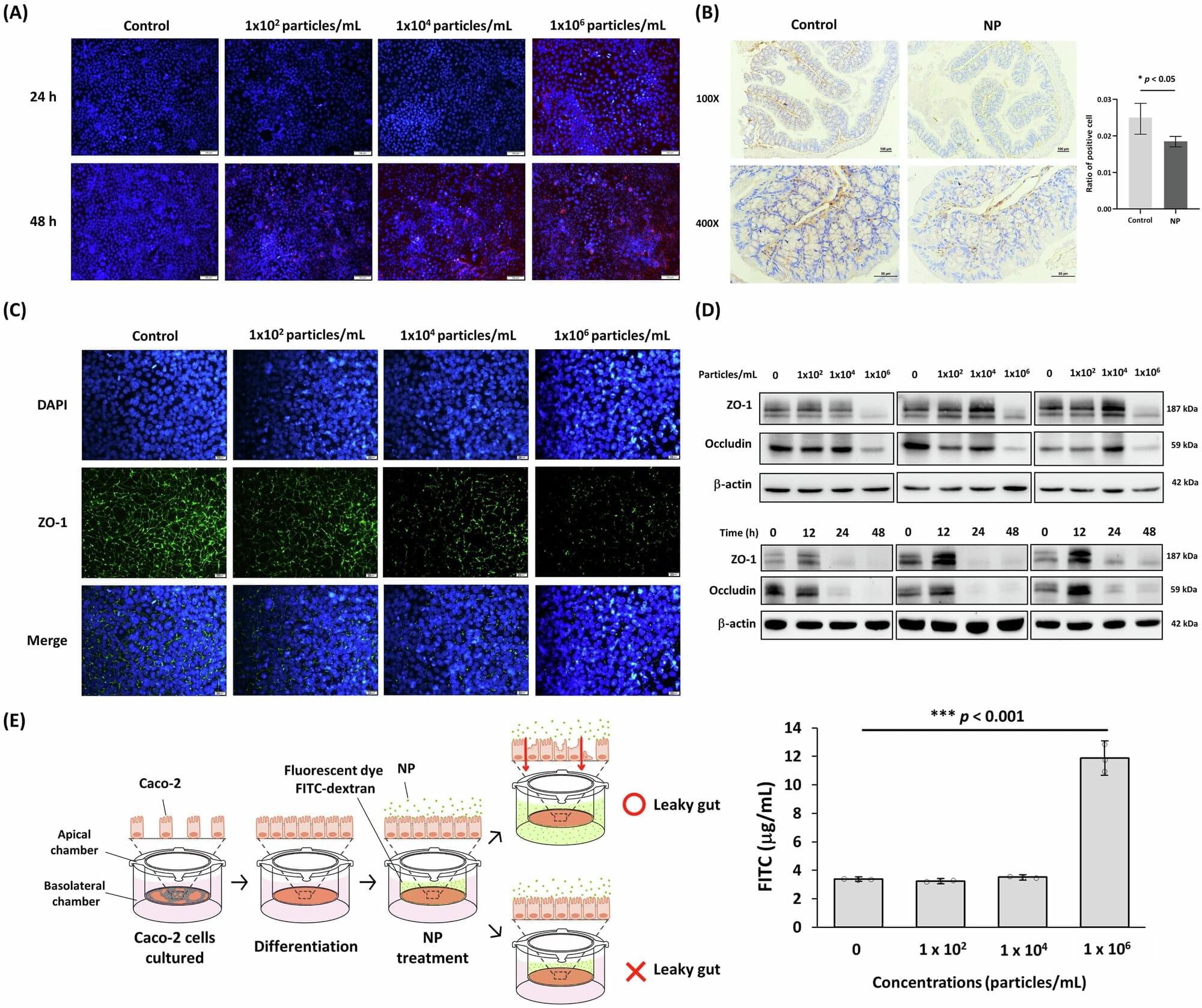
Nanoplastics can disrupt gut microbes in mice by interfering with extracellular vesicle-delivered microRNA
Nanoplastics can compromise intestinal integrity in mice by altering the interactions between the gut microbiome and the host, according to a paper in Nature Communications. The study explores the complex interactions of nanoplastics with the gut microenvironment in mice.
Nanoplastics are pieces of plastic less than 1,000 nanometers in diameter, which are created as plastics degrade. Previous research has suggested that nanoplastic uptake can disrupt the gut microbiota; however, the underlying mechanism behind this effect is poorly understood.
Researcher Wei-Hsuan Hsu and colleagues used RNA sequencing, transcriptomic analysis and microbial profiling to analyze the effects of polystyrene nanoplastics on the intestinal microenvironment when ingested in mice. They found that nanoplastic accumulation in the mouse intestine was linked to altered expression of two proteins involved in intestinal barrier integrity (ZO-1 and MUC-13), which could disrupt intestinal permeability.