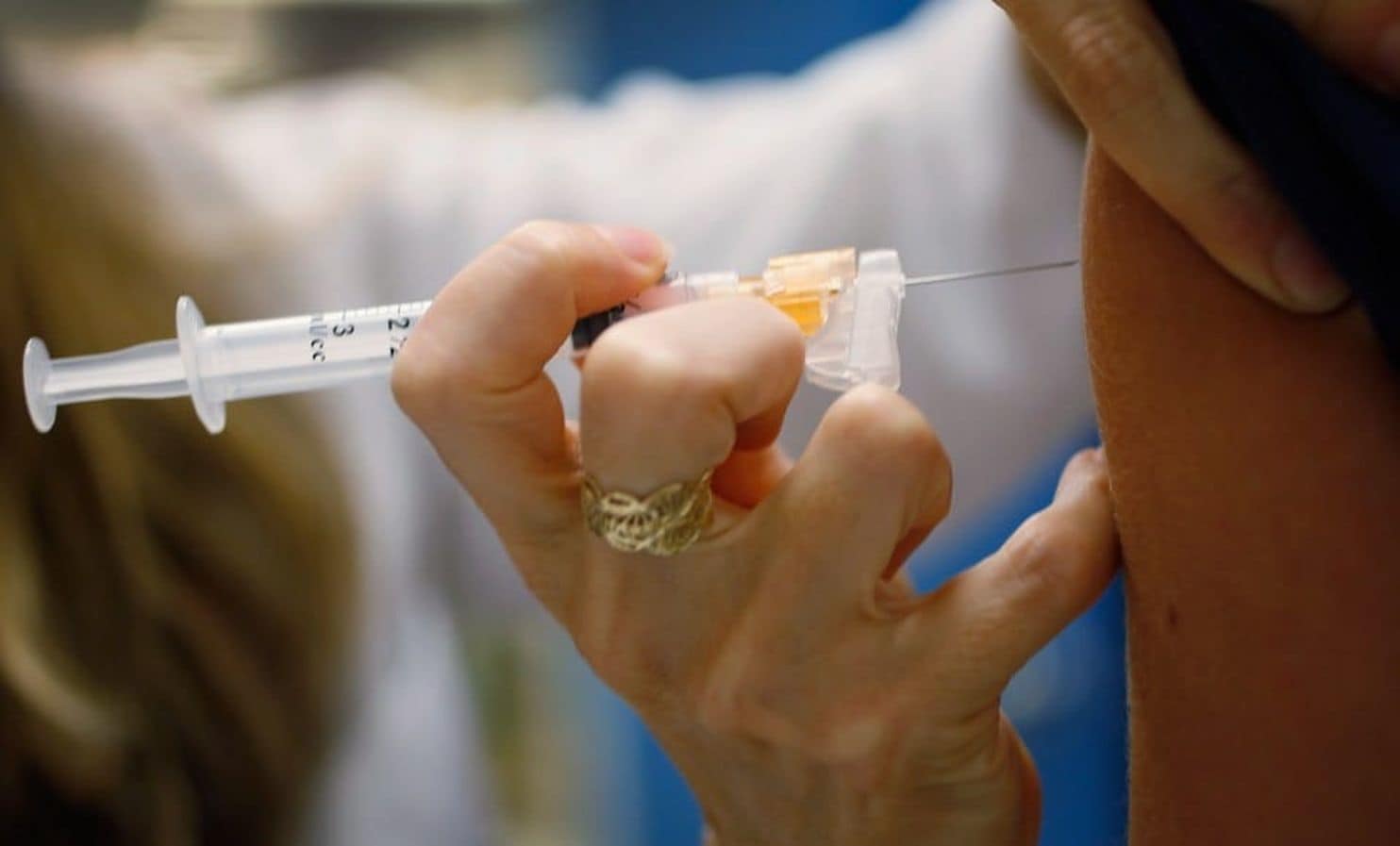
Vaccination rates need to go much higher to help combat HPV-related cancers, experts say.
How humans could talk to aliens
Posted in futurism
Today, we want to draw your attention to a recent study showing an association between the accumulation of Tau proteins, which are misfolded proteins that typically indicate Alzheimer’s disease and senescent cells.
Unfortunately, this journal paper is hidden behind a paywall, as is 70% of scientific data; this is an unacceptable situation for science and the sharing of knowledge. However, thanks to the work of Sci-Hub, a website that bypasses paywalls and offers free access to all scientific papers, you can read it without spending a dime.
I don’t know about you, but I had to look them both up to get a solid understanding of these terms. Of course, these ideas aren’t new. And the brave new world of biohacking, I mean grinder biohacking, is fodder for edgy and future forward media outlets as well as the nightly news. What interests me is the shift to a more commonplace reference like Gartner report. Their analysis of over 2,000 innovations from quantum computing to augmented reality, lead them to choose that fine line between man and machine. It’s important and a bold wake-up call to humanity.
Is humanity about to enter its greatest point of transformation?
😱😱😱😱😱😱😱😱😱😱
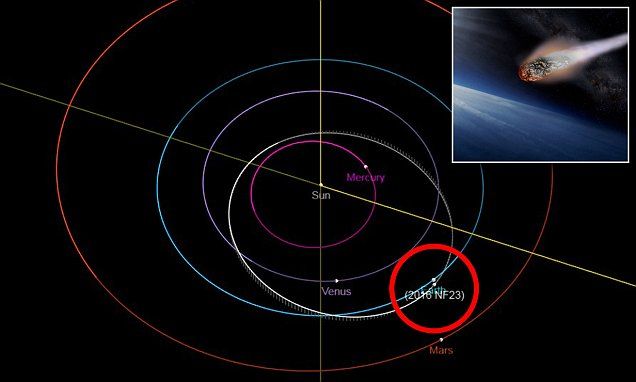
A massive asteroid estimated to be double the size of a Boeing 747 is headed toward a close approach with Earth next week.
Asteroid 2016 NF23 is expected to skim past us on August 29 at just over 3 million miles away, or about 13 times the distance between Earth and the moon.
The huge space rock is traveling more than 20,000 miles per hour (32,400 km/h) and is considered to be a ‘potentially hazardous’ object given its proximity – but, its trajectory should see it soar safely by in the early days of September.