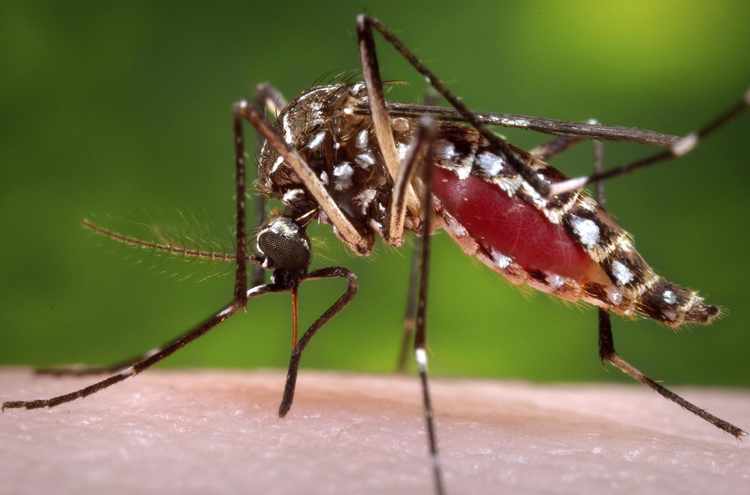
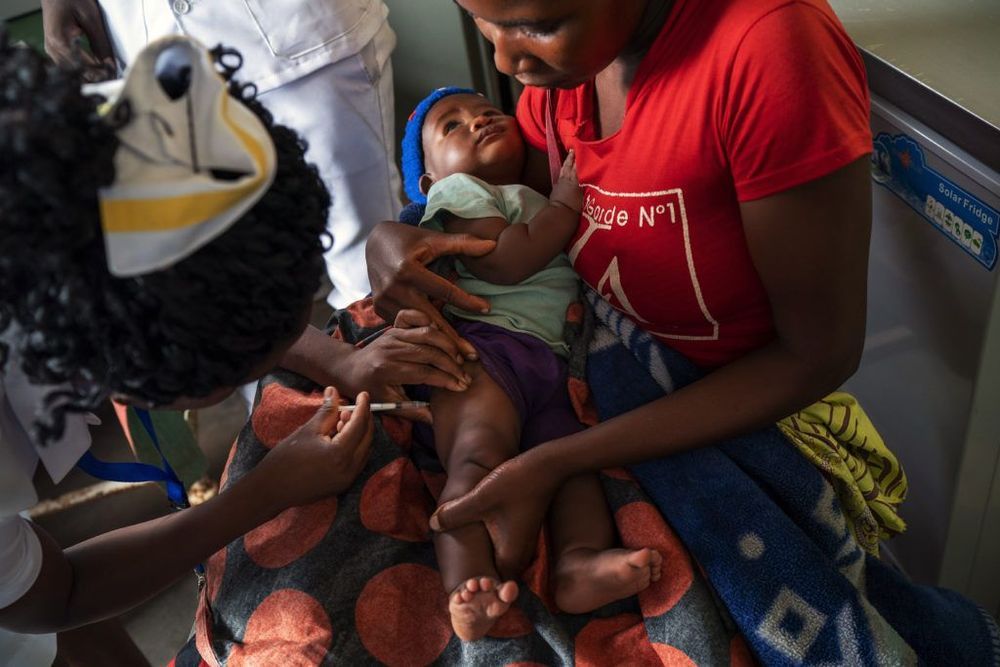
Across Earth’s history, our planet has been home to an estimated 109 billion human beings. And according to another oft-repeated factoid, half of all the people who have ever existed were killed by malaria, the worst mosquito-borne illness. Mosquitoes aren’t merely annoyances, they are mass murderers.
But is this actually true?
There’s little doubt that these hellacious insects are prodigious killers of humankind. The bloodsuckers spread all sorts of diseases – West Nile Virus, various kinds of Encephalitis, Dengue Fever, Yellow Fever, and Zika Virus, for example. However, the damage wrought by all of these diseases is piddling in comparison to malaria. Causing fever, tiredness, vomiting, headaches, and seizures, it struck 216 million people in 2016 alone, resulting in between 445,000 to 731,000 deaths. Believe it or not, that’s an improvement over past years. In 2000, there were 262 million cases, resulting in at least 839,000 deaths.