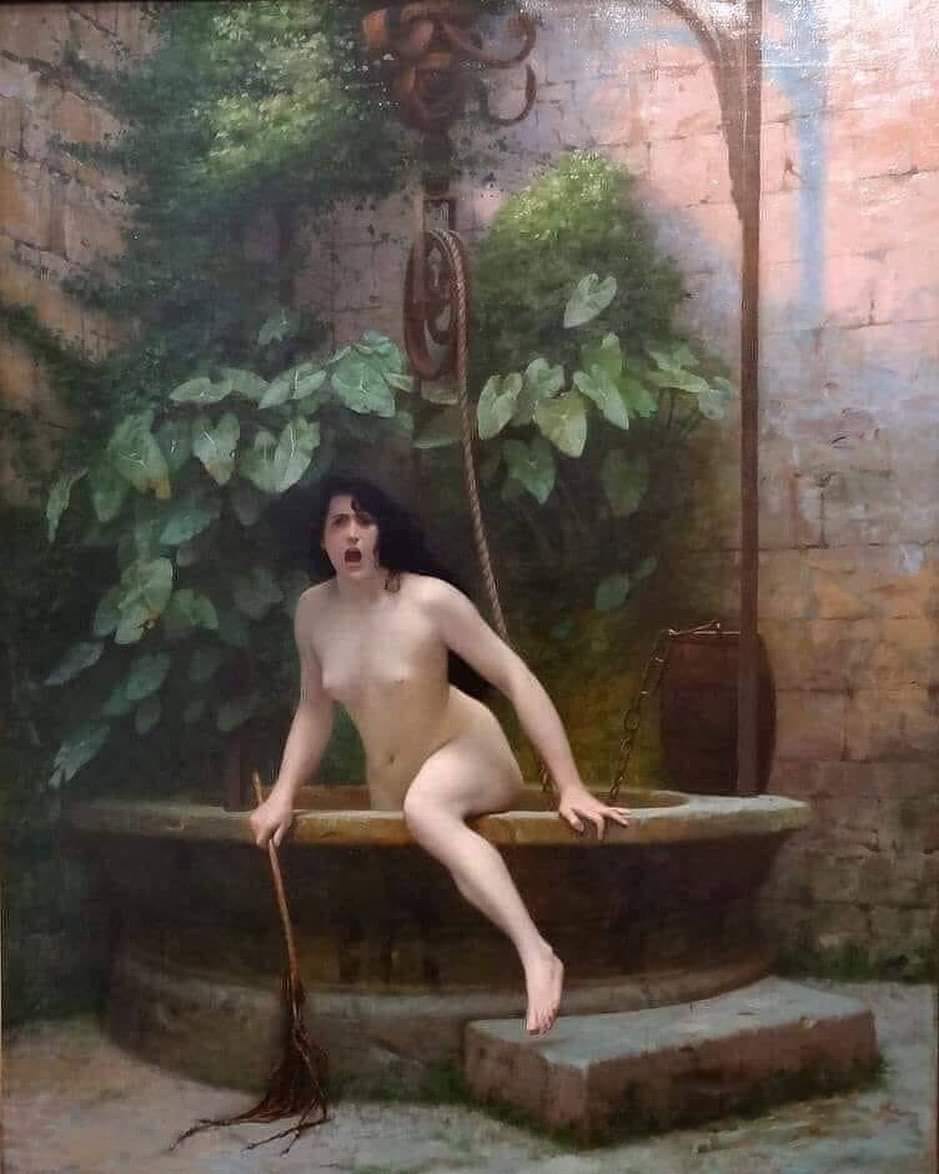
According to a 19th century legend, the Truth and the Lie meet one day. The Lie says to the Truth: “It’s a marvellous day today”! The Truth looks up to the skies and sighs, for the day was really beautiful. They spend a lot of time together, ultimately arriving beside a well.
The Lie tells the Truth: “The water is very nice, let’s take a bath together!” The Truth, once again suspicious, tests the water and discovers that it indeed is very nice. They undress and start bathing. Suddenly, the Lie comes out of the water, puts on the clothes of the Truth and runs away.
The furious Truth comes out of the well and runs everywhere to find the Lie and to get her clothes back. The World, seeing the Truth naked, turns its gaze away, with contempt and rage.