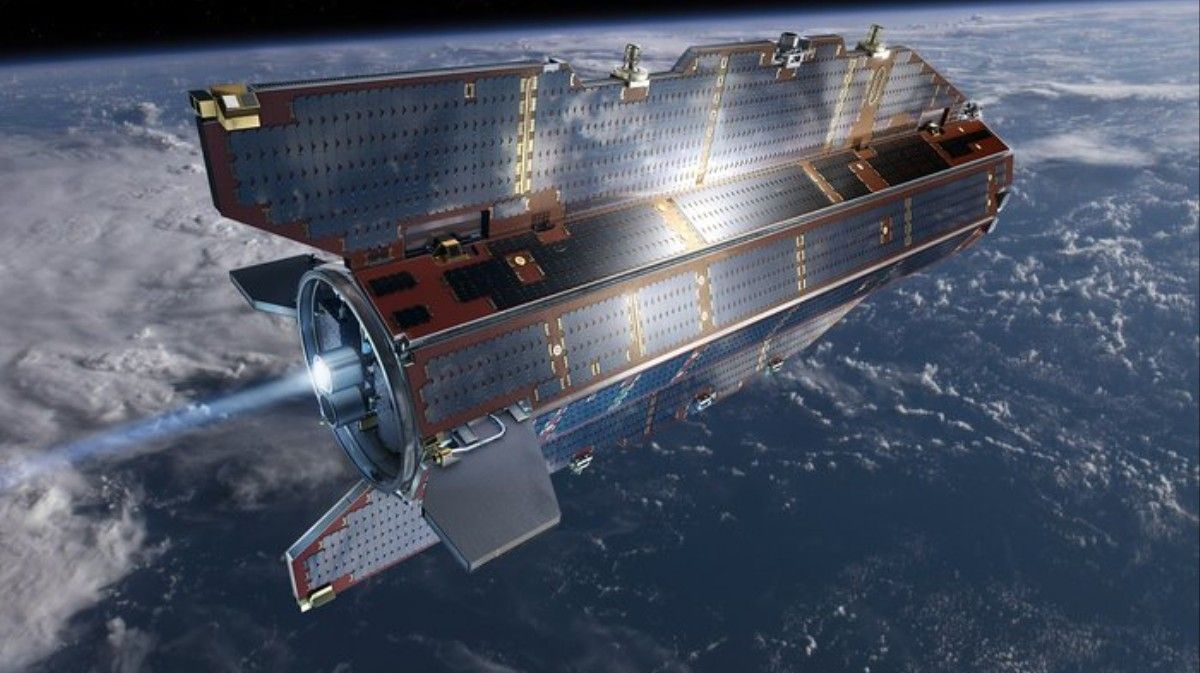
These maps sketch out the remnants of long-lost landmasses trapped within drifting continental plates called cratons. While some cratons are already well-understood, Antarctica’s lithospheric structure is tough to examine because of its remote location and the enormous ice sheets that obscure its underlying geology.
“These gravity images are revolutionizing our ability to study the least understood continent on Earth—Antarctica,” said study co-author Fausto Ferraccioli, science leader of geology and Geophysics at the British Antarctic Survey, in a statement. “In East Antarctica, we see an exciting mosaic of geological features that reveal fundamental similarities and differences between the crust beneath Antarctica and other continents it was joined to until 160 million years ago.”